Altera Arria V Hard IP for PCI Express User Manual
Page 151
Chapter 7: IP Core Interfaces
7–53
Physical Layer Interface Signals
December 2013
Altera Corporation
Arria V Hard IP for PCI Express
User Guide
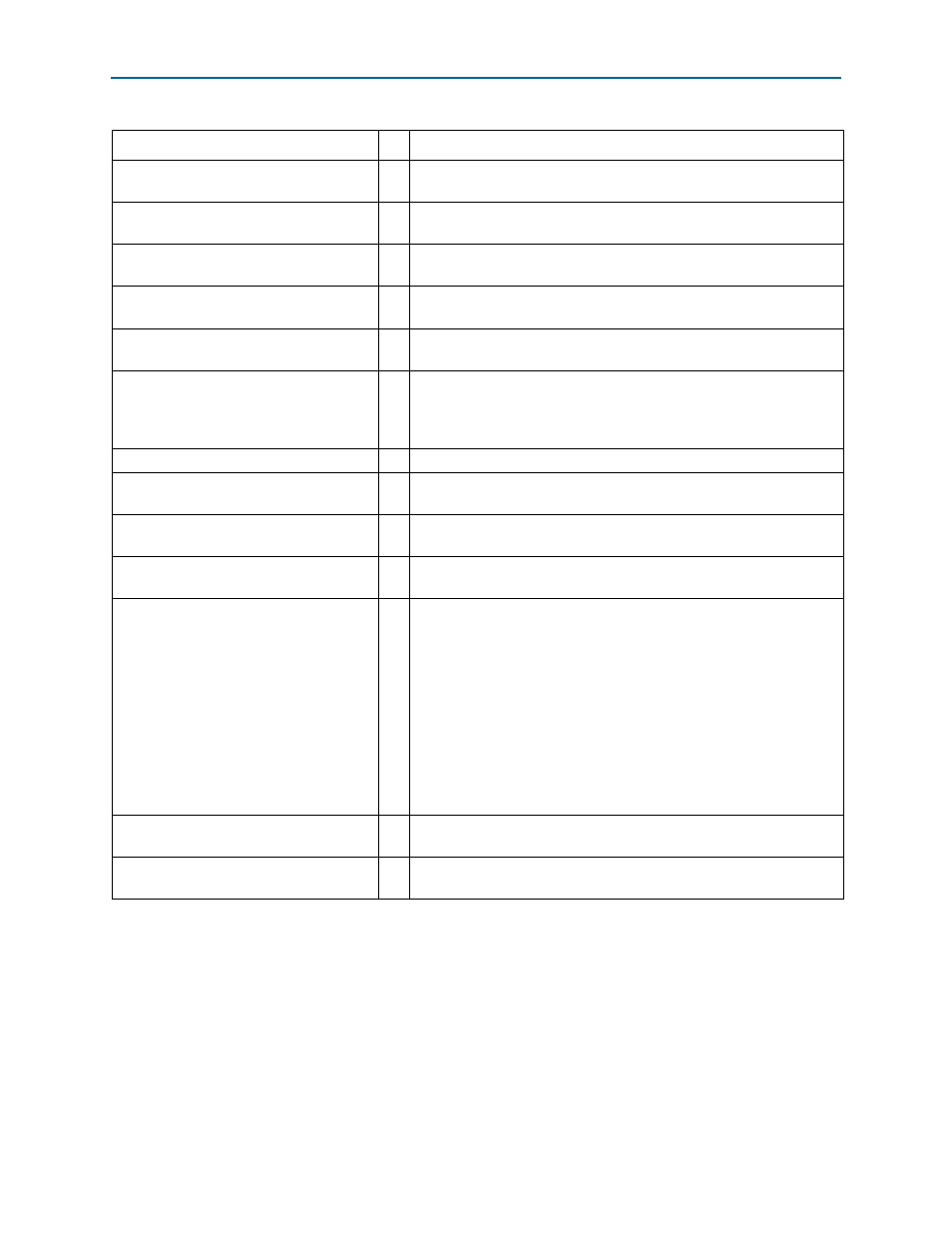
txcompl0
(1)
O
Transmit compliance
. This signal forces the running disparity to
negative in compliance mode (negative COM character).
rxpolarity0
(1)
O
Receive polarity
. This signal instructs the PHY layer to invert the
polarity of the 8B/10B receiver decoding block.
powerdown0[1:0]
(1)
O
Power down
. This signal requests the PHY to change its power state
to the specified state (P0, P0s, P1, or P2).
tx_deemph0
O
Transmit de-emphasis selection. The Arria V Hard IP for PCI Express
sets the value for this signal based on the indication received from the
other end of the link during the Training Sequences (TS). You do not
need to change this value.
rxdata0[7:0]
(1) (2)
I
Receive data
. This bus receives data on lane
.
rxdatak0[1:0]
(1) (2)
I
Receive data control
. This signal separates control and data
symbols.
rxvalid0
(1) (2)
I
Receive valid
. This symbol indicates symbol lock and valid data on
rxdata
and
rxdatak
.
phystatus0
(1) (2)
I
PHY status
. This signal communicates completion of several PHY
requests.
eidleinfersel0[2:0]
O
Electrical idle entry inference mechanism selection. The following
encodings are defined:
■
3'b0xx: Electrical Idle Inference not required in current LTSSM state
■
3'b100: Absence of COM/SKP Ordered Set the in 128 us window for
Gen1 or Gen2
■
3'b101: Absence of TS1/TS2 Ordered Set in a 1280 UI interval for
Gen1 or Gen2
■
3'b110: Absence of Electrical Idle Exit in 2000 UI interval for Gen1 and
16000 UI interval for Gen2
■
3'b111: Absence of Electrical idle exit in 128 us window for Gen1
rxelecidle0
(1) (2)
I
Receive electrical idle
. This signal forces the receive output to
electrical idle.
rxstatus0[2:0]
(1) (2)
I
Receive status
. This signal encodes receive status and error codes
for the receive data stream and receiver detection.
Table 7–26. PIPE Interface Signals (Part 2 of 4)
Signal I/O
Description
