Metrohm viva 1.0 Manual User Manual
Page 604
5.6 Evaluation subwindow
■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■
592
■■■■■■■■
viva 1.0
Name
Symbol
Unit
Electrical potential
U
V = WA
-1
5.6.7.2
Result calculation from calibration curves and error calculation
For all three possible calibration methods, the concentration (e.g. a mass
concentration, a volume concentration or a molar concentration) must be
determined in the measuring vessel with the help of a calibration curve.
This calibration curve itself must be determined by the measurement of
solutions for which the concentrations are known. The parameters for a
specified linear or non-linear curve function are then calculated from the
value pairs Evaluation quantity / concentration. Because of the fact
that, as a general principle, the calculations of the calibration curves and
of the results based upon them, in addition to the associated error calcula-
tion, remain the same for all calibration methods, the calculation proce-
dure that is applied shall be described in general terms in the following.
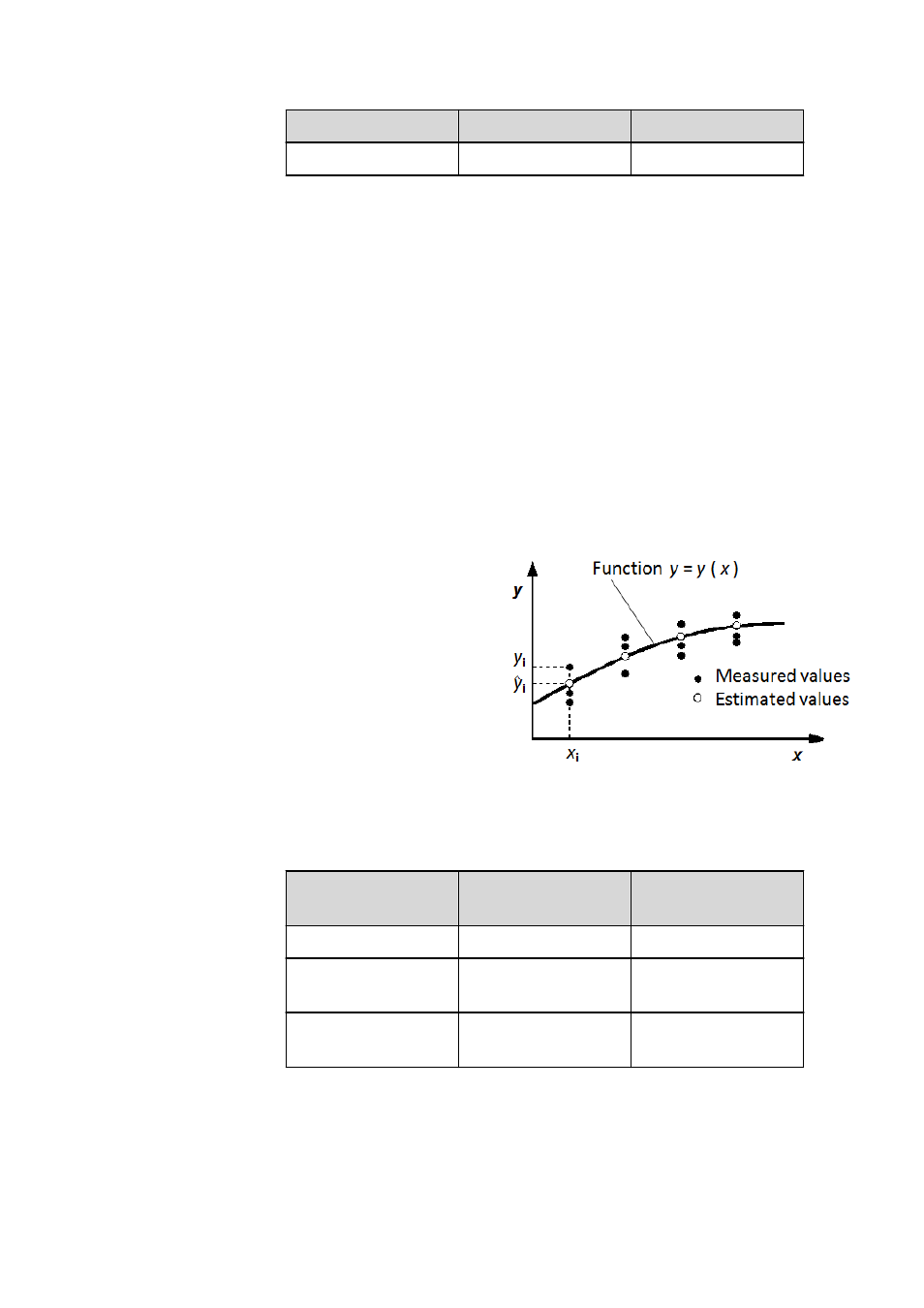
The connection between the variables x and y are sought on the basis of
the measured values x
i
, y
i
, for which it is assumed that the following pre-
requisites apply:
■
The variable x is error-
free.
■
The variable y is
dependent on x and
can be described by the
function y = y(x).
■
The error with the mea-
surement of y is distrib-
uted normally and is
sufficiently small to be
able to apply linear
error calculation.
Depending on the calibration method selected, the following model func-
tions are available for the calculation of the calibration curve y = y(x):
Selected curve type
Calibration func-
tion
Description
Linear regression
y = a + bx
Line
Quadratic regres-
sion
y = a + bx + cx
2
Non-linear curve of
the 2nd degree
Nonlinear regres-
sion
y = a + bx + dx
4
Non-linear curve of
the 4th degree
