SkyTrak 8042 Service Manual User Manual
Page 185
Boom
3.124
Model 8042, 10042, 10054 Legacy
Rev. 03/04
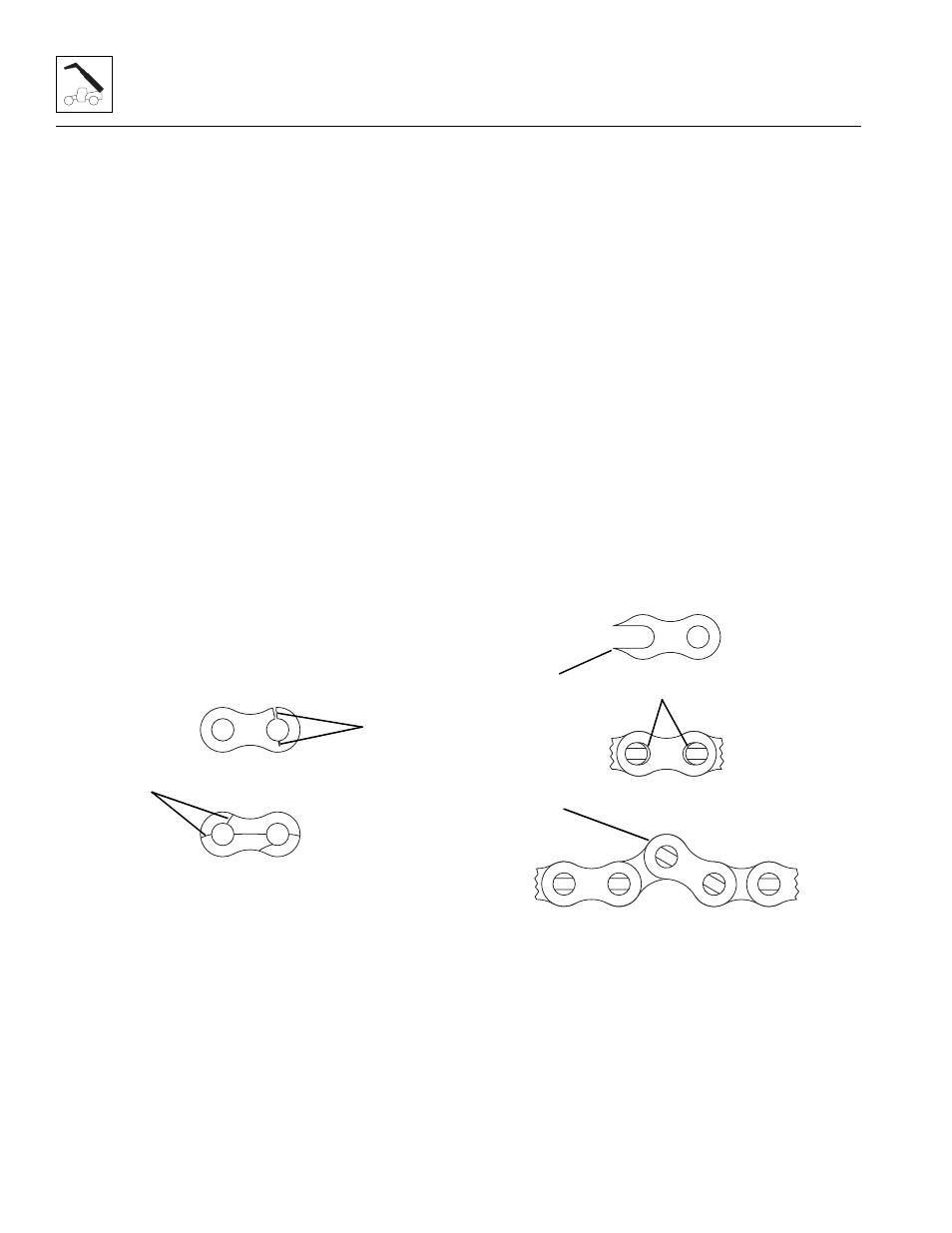
• Fatigue Cracking - Fatigue cracks (1) are a result of
repeated cyclic loading beyond the chain’s
endurance limit. The size of the load and the
frequency of its occurrence are factors which
determine when fatigue failure will occur. The
loading can be continuous or intermittent
(impulse load).
• Stress Corrosion Cracking - The outside link
plates are particularly susceptible to stress corrosion
cracking (2). Like fatigue cracks, these initiate at the
point of highest stress but tend to extend in an
arc-like path between holes in the pin plate. More
than one crack can often appear on a link plate. In
addition to rusting, this condition can be caused by
exposure to an acidic or caustic medium or
atmosphere.
Stress corrosion is an environmentally assisted failure.
Two conditions must be present: corrosive agent and
static stress. In the chain, static stress is present at the
aperture due to the press fit pin. No cyclic motion is
required, and the plates can crack during idle periods.
• Corrosion Fatigue Cracking - Corrosion fatigue
cracks are very similar to fatigue cracks (1) in
appearance. They generally begin at the aperture
and grow perpendicular to the chain pitch line.
Corrosion fatigue is not the same as stress
corrosion. Corrosion fatigue is the combined action
of an aggressive environment and cyclic stress, not
a static stress alone, as in stress corrosion.
Other Modes of Failure
• Ultimate Strength Failure - These types of failures
are caused by overloads far in excess of the design
load. Either fractured plates (3) or enlarged holes (4)
can occur. If either of these failures occurs, the chain
must be replaced immediately. (Refer to Section
3.7.6, “Boom Extend and Retract Chains Removal
and Replacement.”)
Note: The tight joints inspection must be done with the
chain disconnected from the boom. (Refer to Section
3.7.6, “Boom Extend and Retract Chains Removal and
Replacement.”)
• Tight Joints - All joints in the chain must flex freely.
Tight joints (5) resist flexing and increase internal
friction, thus increasing chain tension required to lift
a given load. Increased tension accelerates wear
and fatigue problems.
If the problem is caused by dirt or foreign substance
packed in the joints, clean and lubricate thoroughly
before re-installing the chain.
If the problem is caused by corrosion and rust or bent
pins, replace the chain. (Refer to Section 3.7.6, “Boom
Extend and Retract Chains Removal and Replacement.”)
MM2080
MM2070
1
2
MM2100
MM2110
MM2090
3
4
5
