2 motorola spi, Figure 16-13. motorola spi with sscr[tte]=1, Note: sscr1[ttelp] must be 0 for motorola spi – Intel PXA26X User Manual
Page 562: 3 national semiconductor microwire, Figure 16-12
16-14
Intel® PXA26x Processor Family Developer’s Manual
Network/Audio Synchronous Serial Protocol Serial Ports
Note:
If SSPSCLK is an input, the device driving SSPSCLK must provide another clock edge to cause
the TXD line to go to Hi-Z.
16.4.4.2
Motorola SPI
When SSCR1[TTE] is 0, the SSP behaves as described in
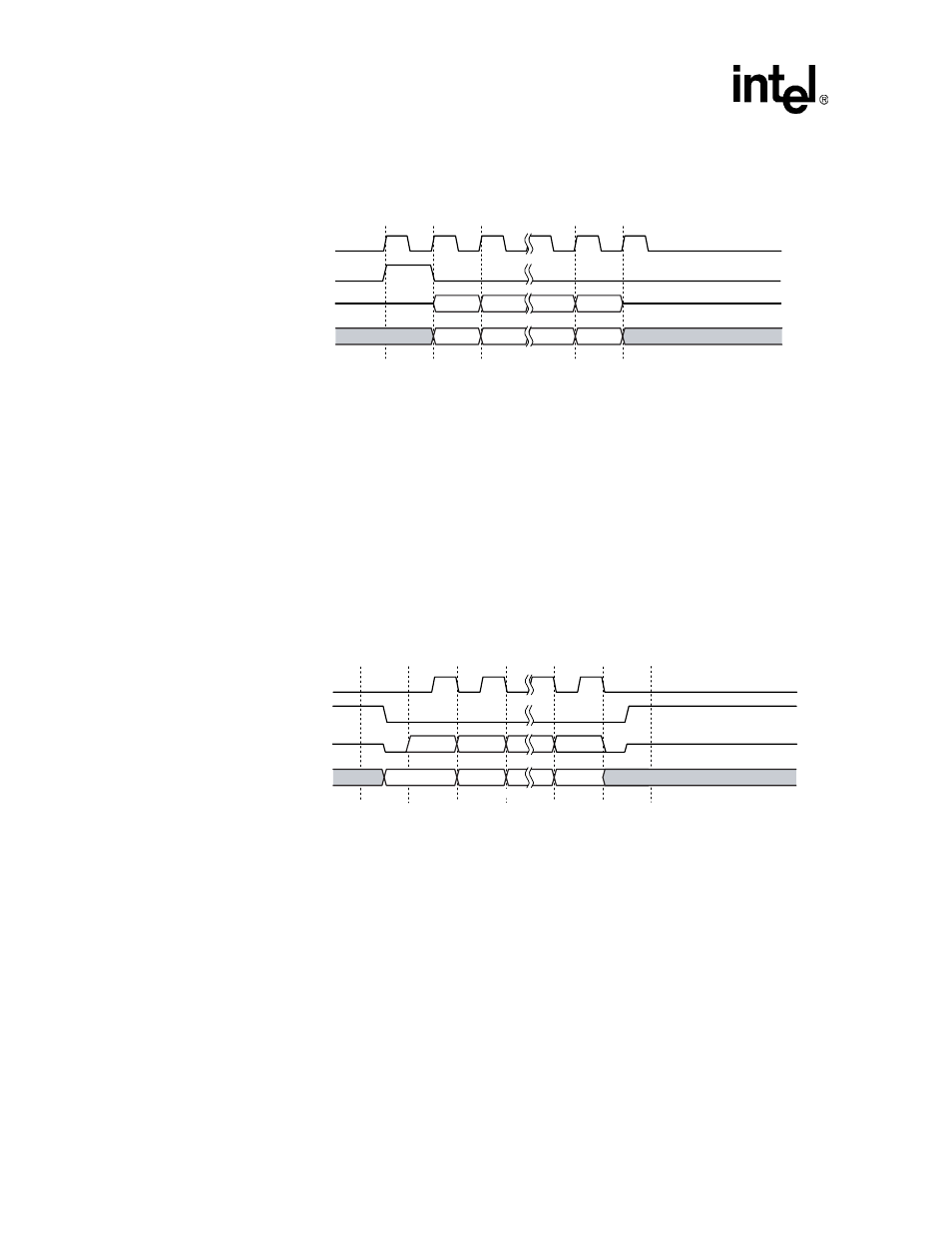
If SSCR1[TTE] is 1, SSPTXD is driven only when SSPSFRM is 0. When SSPSFRM is 1, SSPTXD
is Hi-Z. During the time between the last falling edge and SSPSFRM rising, SSPSP[EDTS]
controls the value driven on SSPTXD.
shows the pin timing for this mode.
Note:
SSCR1[TTELP] must be 0 for Motorola SPI.
16.4.4.3
National Semiconductor Microwire
When SSCR1[TTE] is 0, the SSP behaves as described in
If SSCR1[TTE] is 1, SSPTXD is driven at the same clock edge that the MSB is driven. SSPTXD is
Hi-Z after the next rising edge of SSPSCLK for the LSB (1 clock edge after the clock edge that
starts the LSB).
shows the pin timing for this mode.
Figure 16-12. TI SSP with SSCR[TTE]=1 and SSCR[TTELP]=1
A9975-01
SSPRXD
SSPSFRM
SSPSCLK
SSPTXD
MSB
4 to 32 Bits
LSB
Bit[N]
Bit[N-1]
Bit[1]
Bit[0]
Bit[N]
Bit[N-1]
Bit[1]
Bit[0]
Undefined
Undefined
Figure 16-13. Motorola SPI with SSCR[TTE]=1
A9976-01
SSPRXD
SSPSFRM
SSPSCLK
SSPTXD
MSB
LSB
Bit[N]
Undefined
Undefined
Bit[N-1]
Bit[1]
Bit[0]
Bit[N]
Bit[N-1]
Bit[1]
Bit[0]
4 to 32 Bits
