Table 6-21. 16-bit bus write access – Intel PXA26X User Manual
Page 232
6-42
Intel® PXA26x Processor Family Developer’s Manual
Memory Controller
The RT fields in the MSCx registers specify the type of memory:
•
Non-burst ROM or flash
•
SRAM
•
Variable latency I/O
•
Burst-of-four ROM or flash
•
Burst-of-eight ROM or flash
The RBW fields specify the bus width for the memory space selected by nCS[5:0]. For a 16-bit bus
width transactions occur on MD[15:0]. The BOOT_SEL pins or SXCNFG register must be used to
configure nCS[3:0] for SMROM or some other type of Synchronous Static Memory.
6.8.1.1
Static Memory SA-1111 Compatibility Configuration Register
(SA1111CR)
The SA1111CR register was added to the PXA26x processor family to facilitate interfaces that
behave differently based upon the size of the transfer requested, such as a PCI bridge. Normally,
when an 8 or 16 bit read is requested, the PXA26x processor family asserts all DQM signals and
sets the lowest address pins (MA[1:0] for 32 bit external bus and MA[0] for 16 bit external bus) to
zero and discards the unwanted portion of data. When the SA-1111 compatibility bit is set for a
static memory partition, then two things will happen.
•
First, on reads for asynchronous memory, the lower address bits will correctly reflect the
starting byte address. This is MA[0] for 16-bit external memory and MA[1:0] for 32-bit
external memory. This is based on the byte enables that may be associated with the read
request from the internal bus. See
Table 6-22, “32-Bit Byte Address Bits MA[1:0] for Reads
Table 6-23, “16-Bit Byte Address Bit MA[0] for Reads Based on
for specifics on the external address for this mode.
•
Second, on reads, the DQM pins will correctly reflect the byte enables received for the reads.
16 bit
00
1100
16 bit
10
0011
32 bit
00
0000
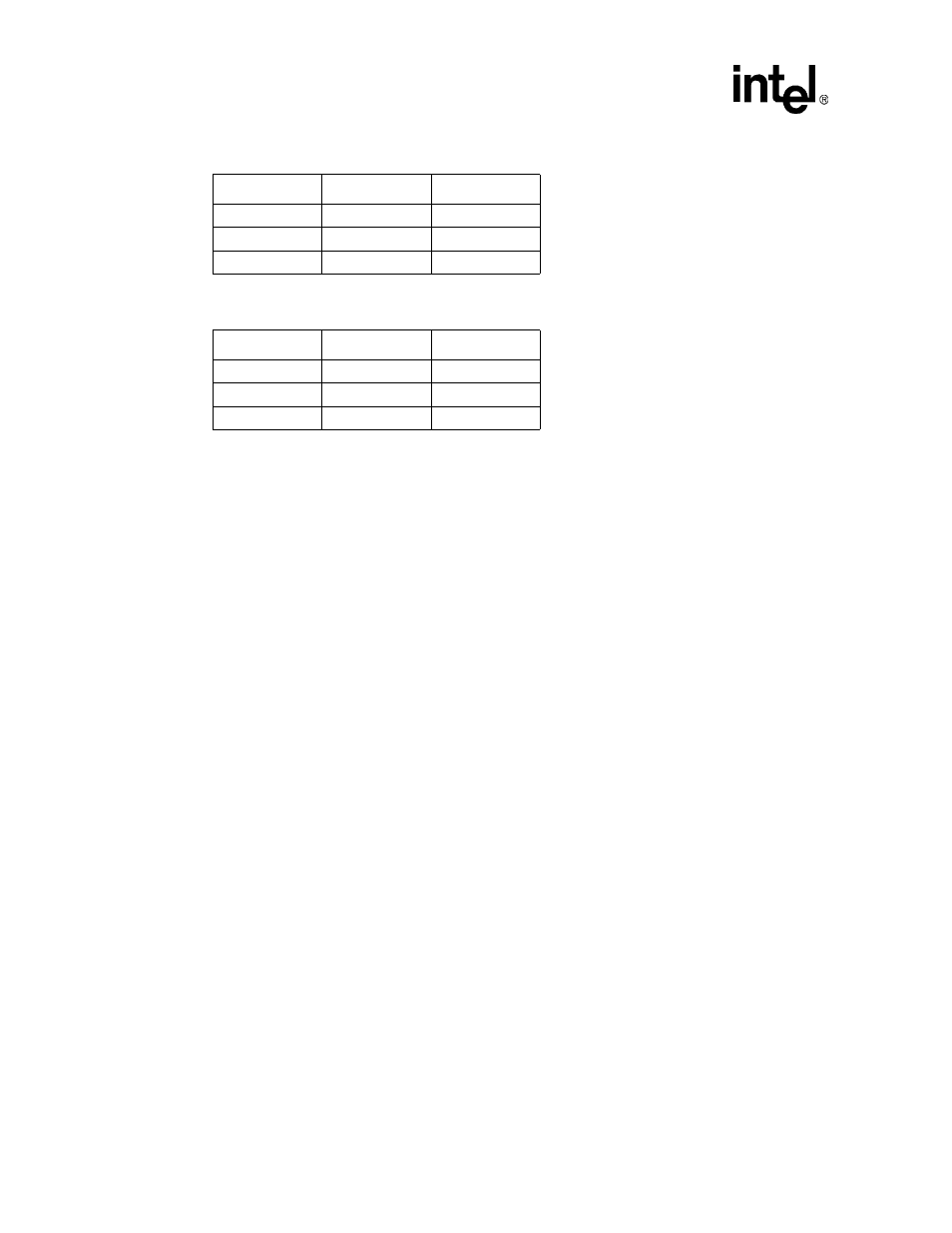
Table 6-21. 16-Bit Bus Write Access
Data Size
MA[0]
DQM[1:0]
8 bits
0
10
8 bits
1
01
16 bits
0
00
Table 6-20. 32-Bit Bus Write Access (Sheet 2 of 2)
Data Size
MA[1:0]
DQM[3:0]
