EXFO CableSHARK P3 VF/DSL Cable Qualifier User Manual
Page 19
CableSHARK P3 User Guide
7
DMT standards suggest that equipment can use up to 15 bits/bin to encode data per sub-channel. However,
using the maximum 15 bits/bin may result in the ADSL modems having to transmit at a higher power than
would be practical or allowed in a cable bundle. For the most part, ADSL makers have limited their designs
to use 13 or 14 bits/bin. This lowers the power transmitted between modems and maximizes the reach of
transmission without compromising potential data rates.
Rate adaptive Digital Subscriber Line
- R-ADSL. This was an early name for a specific type of ADSL. These
days most ADSL modems are rate adaptive. They adjust the transmission speed dynamically to the length
and quality of the local loop. Most DSLAM network management systems allow the transmission speed to be
set or limited to a maximum bit rate.
G.Lite
– A ‘lighter’ version of ADSL where downstream rates are limited to approx. 1.5 Mbps. G.Lite uses
128 bins rather than 256 (still using 4.3125 kHz sub-channel bandwidth) and only up to 8 bits/bin can be
encoded per sub-channel.
ADSL2
– ADSL2 offers data rates of up to 12 – 15 Mbps.
ADSL2+
– ADSL2+ offers data rates of up to 24 Mbps by increasing the frequency range to 2.2 MHz.
Symmetrical High-Speed Digital Subscriber Line
– SHDSL is a technology that is similar to HDSL and
HDSL2. SHDSL operates over a single pair or 2 pairs of wire depending upon the application. For single pair
operation, SHDSL offers data rates from 192 kbps to 2.3 Mbps while two pair operation offers data rates
ranging from 384 kbps to 4.72 Mbps.
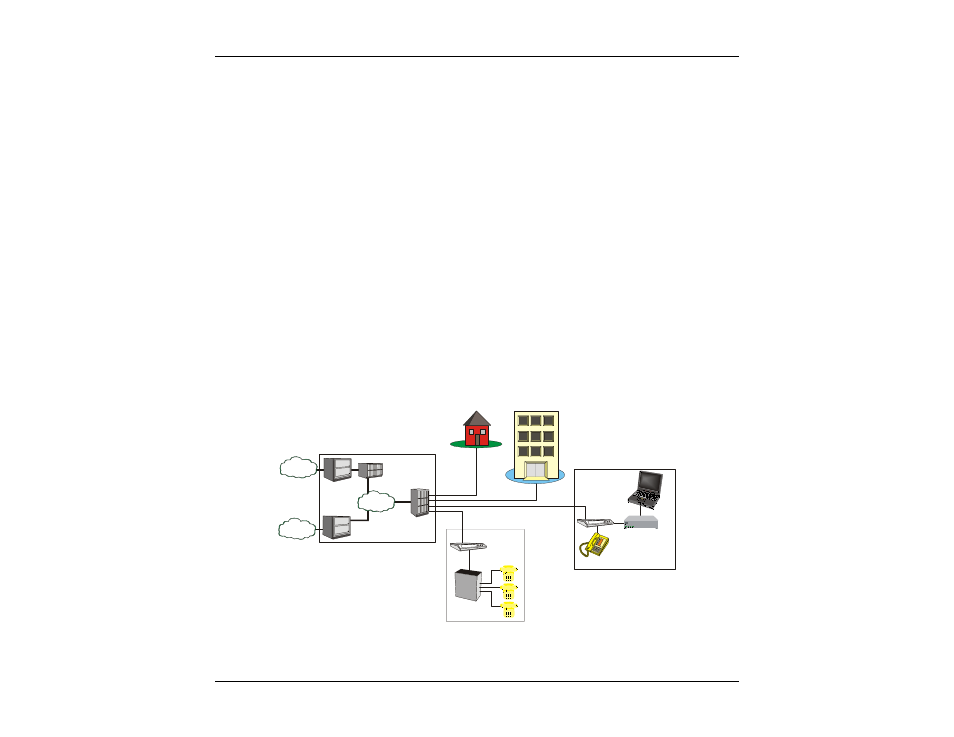
Internet
PSTN
Analog Phone
Router
PBX
Voice
Switch
Voice
Gateway
ATM
Backbone
ISP
DSLAM
PC
G.SHDSL
IAD
SME
G.SHDSL
IAD
Figure 2F – SHDSL Architecture
