Asynchronous serial communication interface (asci), Figure 51. nmi and dma operation timing diagram – Zilog Z80180 User Manual
Page 130
Z8018x
Family MPU User Manual
UM005003-0703
115
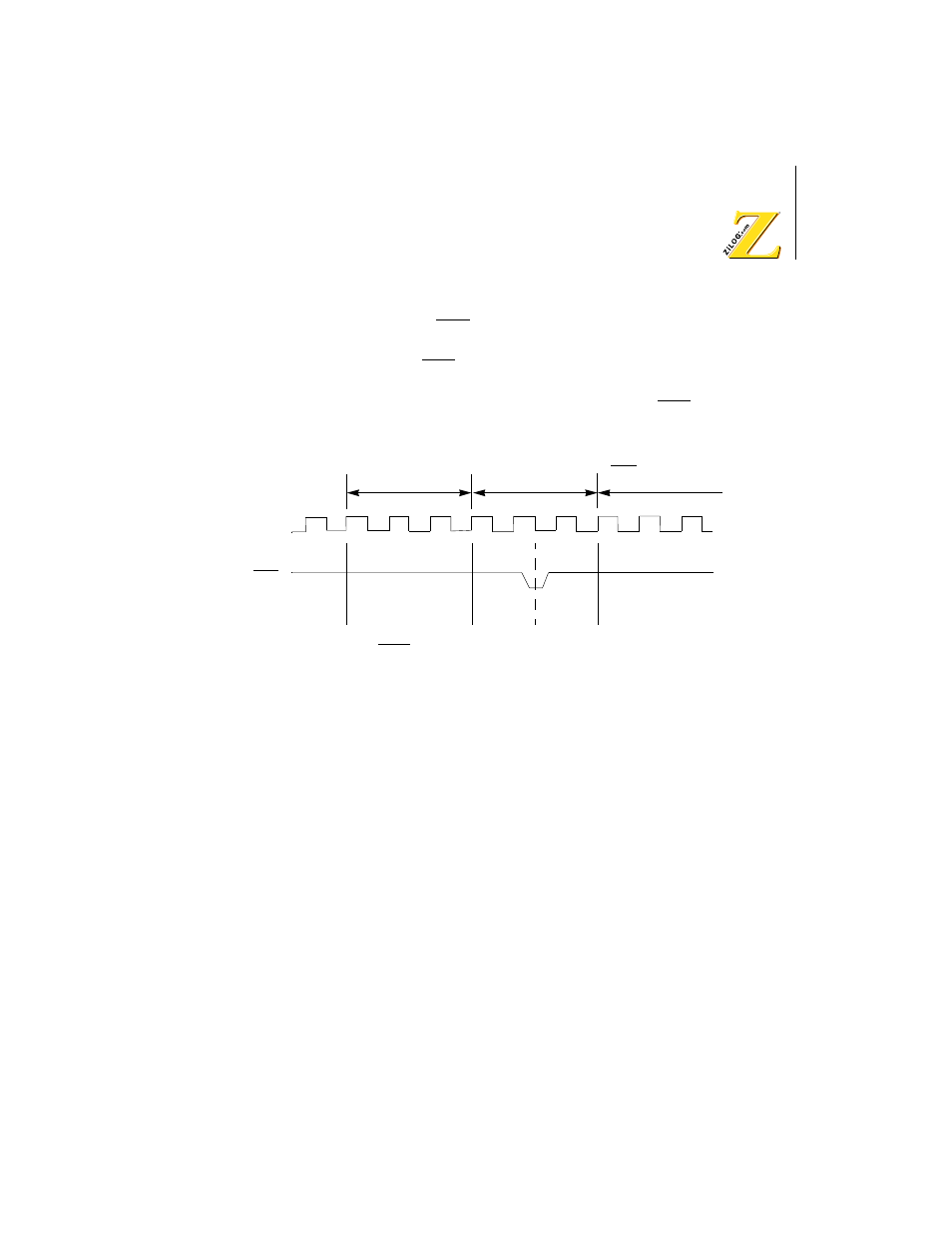
If the falling edge of NMI occurs before the falling clock of the state prior
to T3 (T2 or Tw) of the DMA write cycle, the DMAC is suspended and
the CPU starts the NMI response at the end of the current cycle. By
setting a channel's DE bit to
1
, the channel's operation is restarted and
DMA correctly resumes from its suspended point by NMI. (Reference
Figure 51.)
Figure 51. NMI and DMA Operation Timing Diagram
DMAC and RESET
During RESET the bits in DSTAT, DMODE, and DCNTL are initialized
as stated in their individual register descriptions. Any DMA operation in
progress is stopped, allowing the CPU to use the bus to perform the
RESET sequence. However, the address register (SAR0, DAR0 MAR1,
IAR1) and byte count register (BCR0 BCR1) contents are not changed
during RESET.
Asynchronous Serial Communication Interface (ASCI)
The Z8X180 on-chip ASCI has two independent full-duplex channels.
Based on full programmability of the following functions, the ASCI
directly communicates with a wide variety of standard UARTs (Universal
Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter) including the Z8440 SIO and the
Z85C30 SCC.
NMI
Phi
DMA write cycle
T1
T2
T3
T3
T2
T1
DMA read cycle
NMI acknowledge cycle
DME = “0” (DMA Stop)
T1
