Metrohm 840 PC Control 5.0 / Touch Control User Manual
Page 245
4
Parameters
PC Control / Touch Control
233
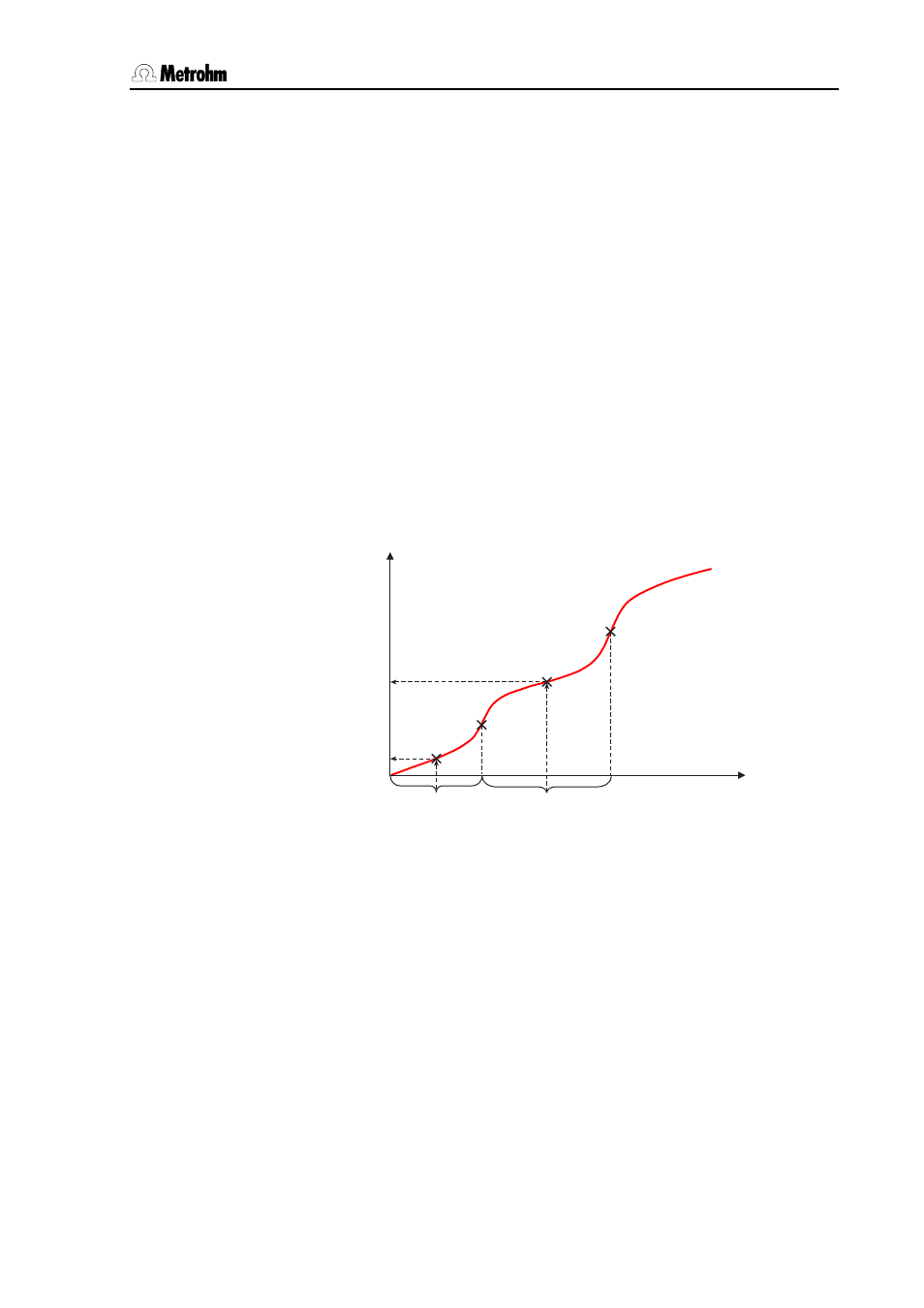
4.4.2 Evaluation of pK value and half neutralization potential
(EVAL pK/HNP)
The pK value can be determined for pH titrations (DET and MET) and
the half neutralization potential can be determined for U titrations.
The activities of conjugated acid-base pairs are linked by the following
equation (Henderson-Hasselbalch equation):
pH = pK
a
+ log (a
B
/a
A
)
If the activities of the acid and the conjugated base are equal (a
A
= a
B
),
then pH=pK
a
. This is the value at the half neutralization point and can
be extrapolated from the titration curve. A careful pH calibration is nec-
essary for pK evaluations and even then the determined pK value is
only an approximation, as the ionic strengths are not taken into ac-
count. In order to obtain a more accurate value, titrations must be car-
ried out with decreasing ionic strengths and the results extrapolated to
the ionic strength zero. pK evaluation in aqueous solution is limited to
the range 3.5 < pK < 10.5 because of the leveling effect of strong ac-
ids and the lack of jumps with very weak acids. pK values of mixtures of
acids and polyvalent acids can also be determined.
1/2
Volume
1/2
1/2
1/2
EP2
pK2
EP1
pK1
Measured value
Fig. 4.15: Determining the pK value from the titration curve
In non-aqueous solutions the half neutralization potential (HNP) is fre-
quently used instead of the pK value. The HNP is evaluated in the same
way as the pK value.
No parameters can be edited for the command EVAL pK/HNP. If a start
volume is to be added then it must be smaller than 1/2 V
EP1
.
