Micromod Micro-DCI: 53MC5000 Multi-Loop Process Controller Instruction Manual User Manual
Page 346
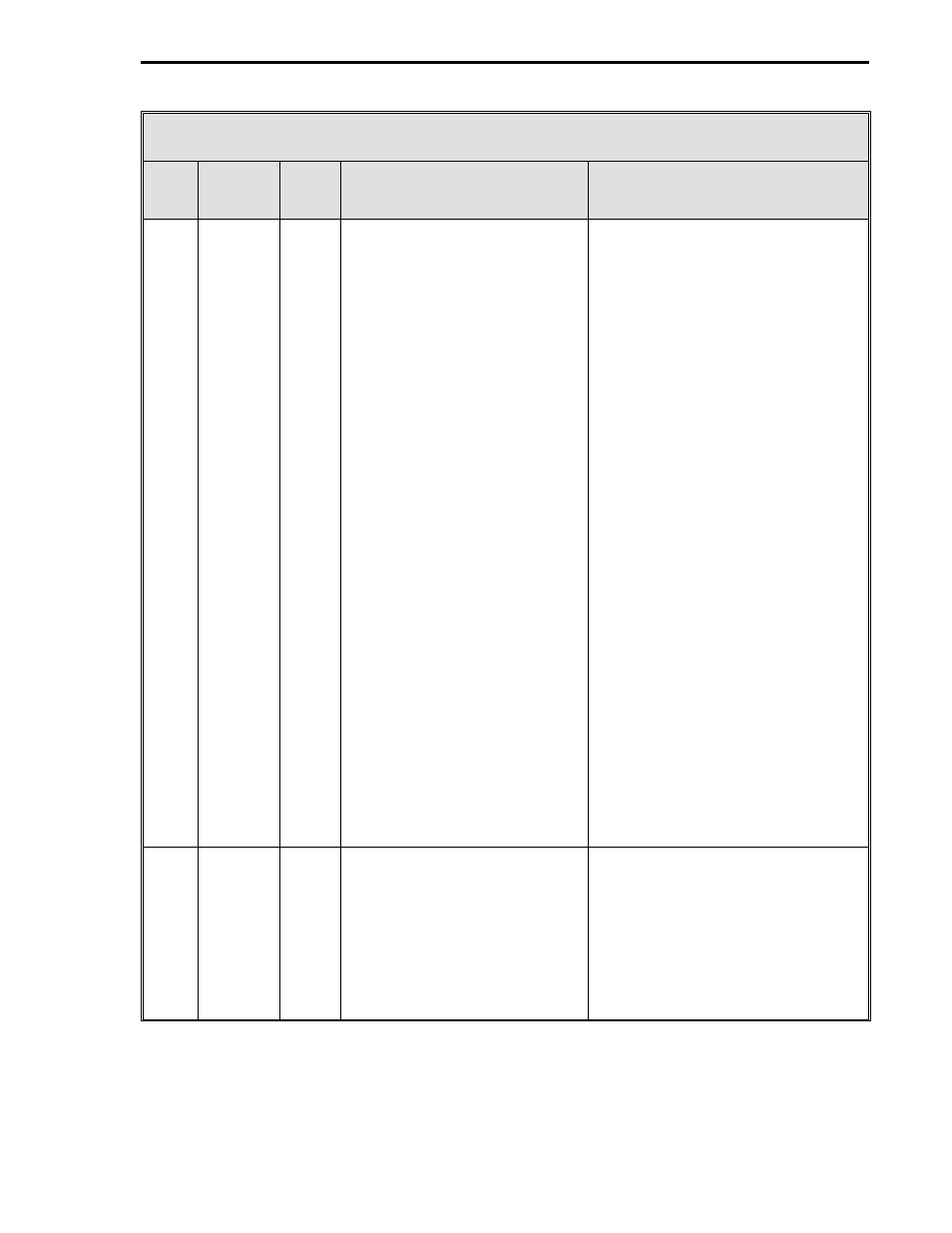
Table B-3. Controller Memory Address Scheme
Data
Type
Base
Memory
Address
Byte
Size
Data Format
Address Calculation Algorithm
H
F00
H
5
Represents high precision
floating point values that have a
resolution of one part in 2 billion
(31 bits) and a dynamic range of
±
10
38
. The first four bytes
represent a 2’s complement
notation in fractional form (2
-n
)
whose absolute value is
between 0.5 and 0.9999. The
fifth byte is the power of 2 in 2’s
complement notation. Floating
point example: 9C
H
00
H
00
H
00
H
07
H
= -100. The 2’s
complement notation bit in the 9
= 1 (1001) indicating a negative
number; therefore, 9C must be
re-complemented . 9C = 1001
1100, change 1’s to 0’s and 0’s
to 1’s = 0110 0011 and add 1=
0110 0100 (64
H
). Fractional
binary weights left to right for
0110 0100 are 0 = 2’s
complement positive, 1 = 2
-1
=
1/2 = 0.5, 1 = 2
-2
= 1/4 = 0.25,
0=0, 0=0, 1= 2
-5
= 1/32 =
0.03125, 0=0, 0=0. 64
H
= 0.5 +
0.25 + 0.03125 = 0.78125.
07
H
=128
D
, 128
D
X 0.78125
D
=
100. A negative sign is
assigned (-100) because the
original 2’s complement binary
bit in the 9 (1001) of 9C was set
indicating a negative number.
Address =
H
Base + (5 X
H
Number)
= F00
H
+ (5 X
H
Number)
Address example: H001 location
F00
H
+ (5 X 1) = F00
H
+ 5
D
= F00
H
+ 5
H
= F05
H
.
A (F)*
1400
H
10 (A)
5 (F)*
The
A data format represents
text strings that are 10
characters long.
The
F data format represents
text strings that are 5 characters
long.
Address = A Base + (10 X Number)
= 1400
H
+ (10 X Number)
Address example: A015 location
1400
H
+ (10 X 15) =
1400
H
+ 150
D
= 1400
H
+ 96
H
1496
H
. (For A data type.)
Address = F Base + (5 X Number)
= 1400
H
+ (5 X Number)
(For F data type within A database.)
*
F data types are 5 bytes long and are mapped onto A data types.
2 of 2
Appendix B. Communications
B-7
