Brocade FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing Configuration Guide User Manual
Page 258
NSSAs are especially useful when you want to summarize Type-5 External LSAs (external routes)
before forwarding them into an OSPF area. The OSPF specification (RFC 2328) prohibits
summarization of Type-5 LSAs and requires OSPF to flood Type-5 LSAs throughout a routing domain.
When you configure an NSSA, you can specify an address range for aggregating the external routes
that the NSSA's ABR exports into other areas.
The implementation of NSSA is based on RFC 1587.
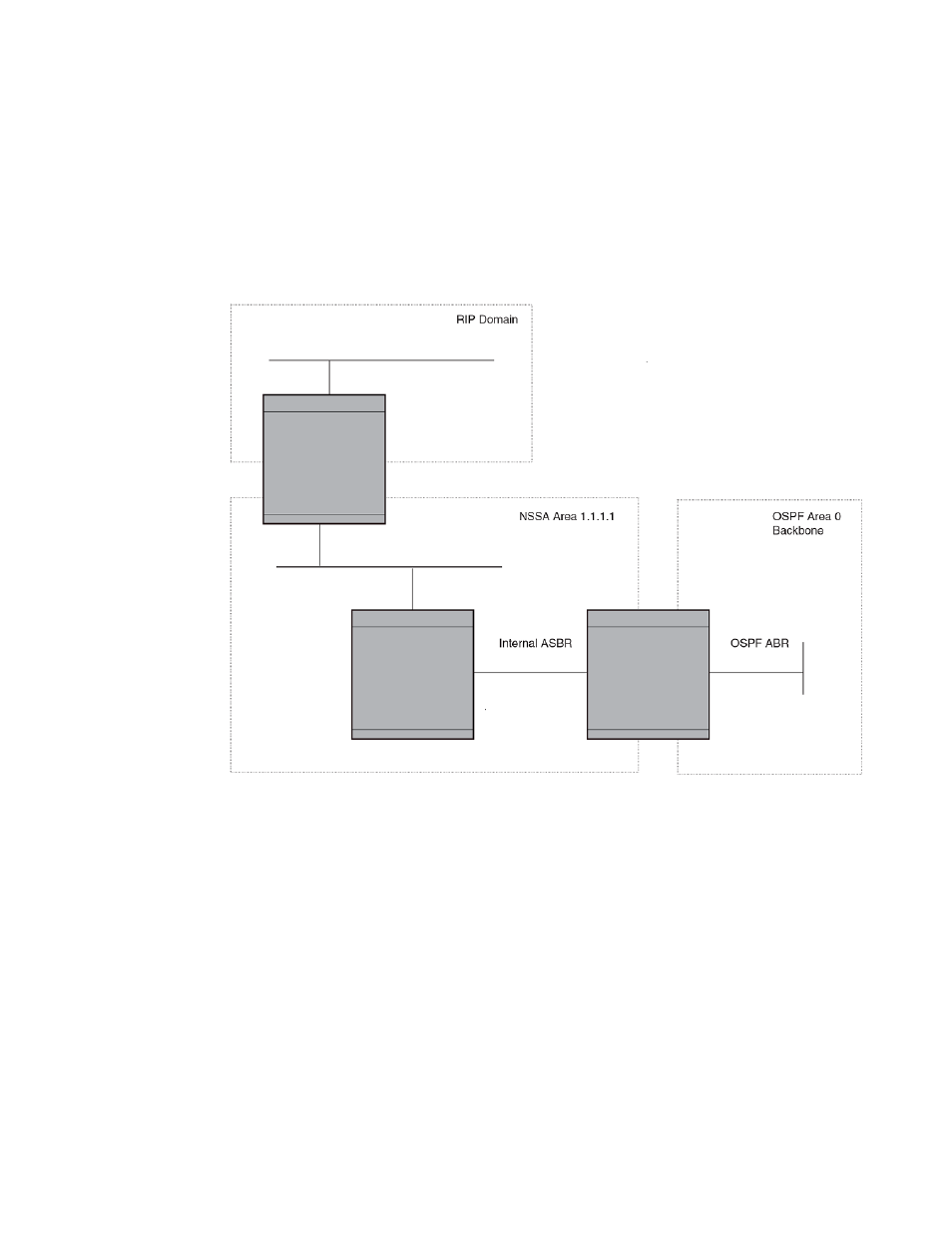
FIGURE 23 OSPF network containing an NSSA
This example shows two routing domains, a RIP domain and an OSPF domain. The ASBR inside the
NSSA imports external routes from RIP into the NSSA as Type-7 LSAs, which the ASBR floods
throughout the NSSA.
The ABR translates the Type-7 LSAs into Type-5 LSAs. If an area range is configured for the NSSA,
the ABR also summarizes the LSAs into an aggregate LSA before flooding the Type-5 LSAs into the
backbone.
Since the NSSA is partially "stubby" the ABR does not flood external LSAs from the backbone into the
NSSA. To provide access to the rest of the Autonomous System (AS), the ABR generates a default
Type-7 LSA into the NSSA.
Configuring an NSSA
To configure OSPF area 1.1.1.1 as an NSSA, enter the following commands.
device(config)# router ospf
device(config-ospf-router)# area 1.1.1.1 nssa 1
device(config-ospf-router)# write memory
OSPFv2
258
FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing Configuration Guide
53-1003087-04
