How dhcp assist works – Brocade FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing Configuration Guide User Manual
Page 109
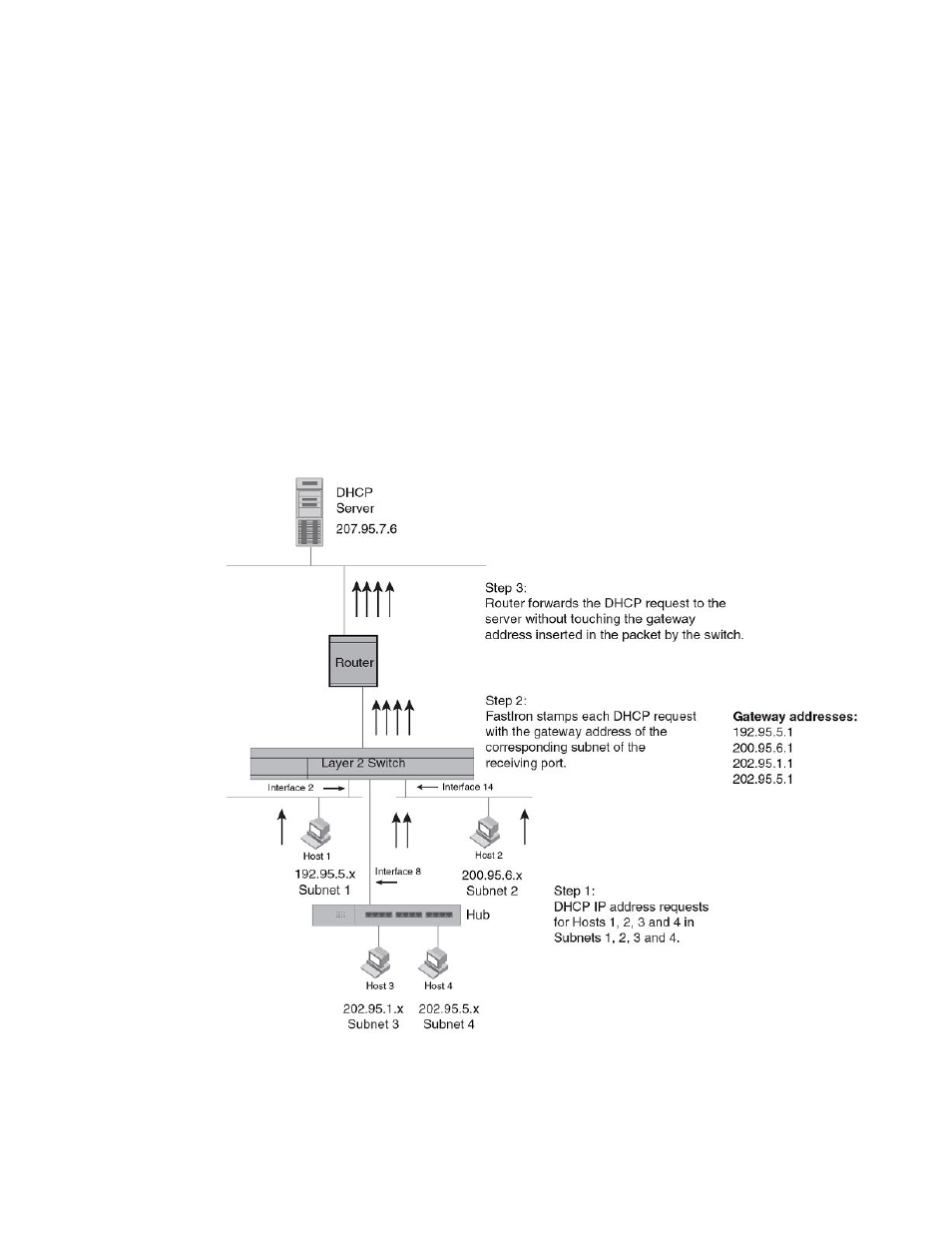
In the example figure, a host from each of the four subnets supported on a Layer 2 switch requests an
IP address from the DHCP server. These requests are sent transparently to the router. Because the
router is unable to determine the origin of each packet by subnet, it assumes the lowest IP address or
the ‘primary address’ is the gateway for all ports on the Layer 2 switch and stamps the request with that
address.
When the DHCP request is received at the server, it assigns all IP addresses within that range only.
With DHCP Assist enabled on a BrocadeLayer 2 switch, correct assignments are made because the
Layer 2 switch provides the stamping service.
How DHCP Assist works
Upon initiation of a DHCP session, the client sends out a DHCP discovery packet for an address from
the DHCP server. When the DHCP discovery packet is received at a BrocadeLayer 2 switch with the
DHCP Assist feature enabled, the gateway address configured on the receiving interface is inserted into
the packet. This address insertion is also referred to as stamping.
FIGURE 12 DHCP requests in a network with DHCP Assist operating on a FastIron Switch
When the stamped DHCP discovery packet is then received at the router, it is forwarded to the DHCP
server. The DHCP server then extracts the gateway address from each request and assigns an
available IP address within the corresponding IP subnet. The IP address is then forwarded back to the
workstation that originated the request.
How DHCP Assist works
FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing Configuration Guide
109
53-1003087-04
