Rockwell Automation 1336E IMPACT Adjustable Frequency AC Drive User Manual V 1-4.XX User Manual
Page 118
7-6
Setting Up the Input/Output
4. Compare the output of the digital-to-analog conversion (C) with
the internal drive units (B).
In Figure 7.3, the values were different, so we used Step 5.
5. Calculate the scale. For example, if the output of the digital to
analog conversion is
±1024 and the internal drive units are ±4096,
the scale value should be 4 (4 x 1024 = 4096).
6. Enter the offset and scale values into the appropriate parameters.
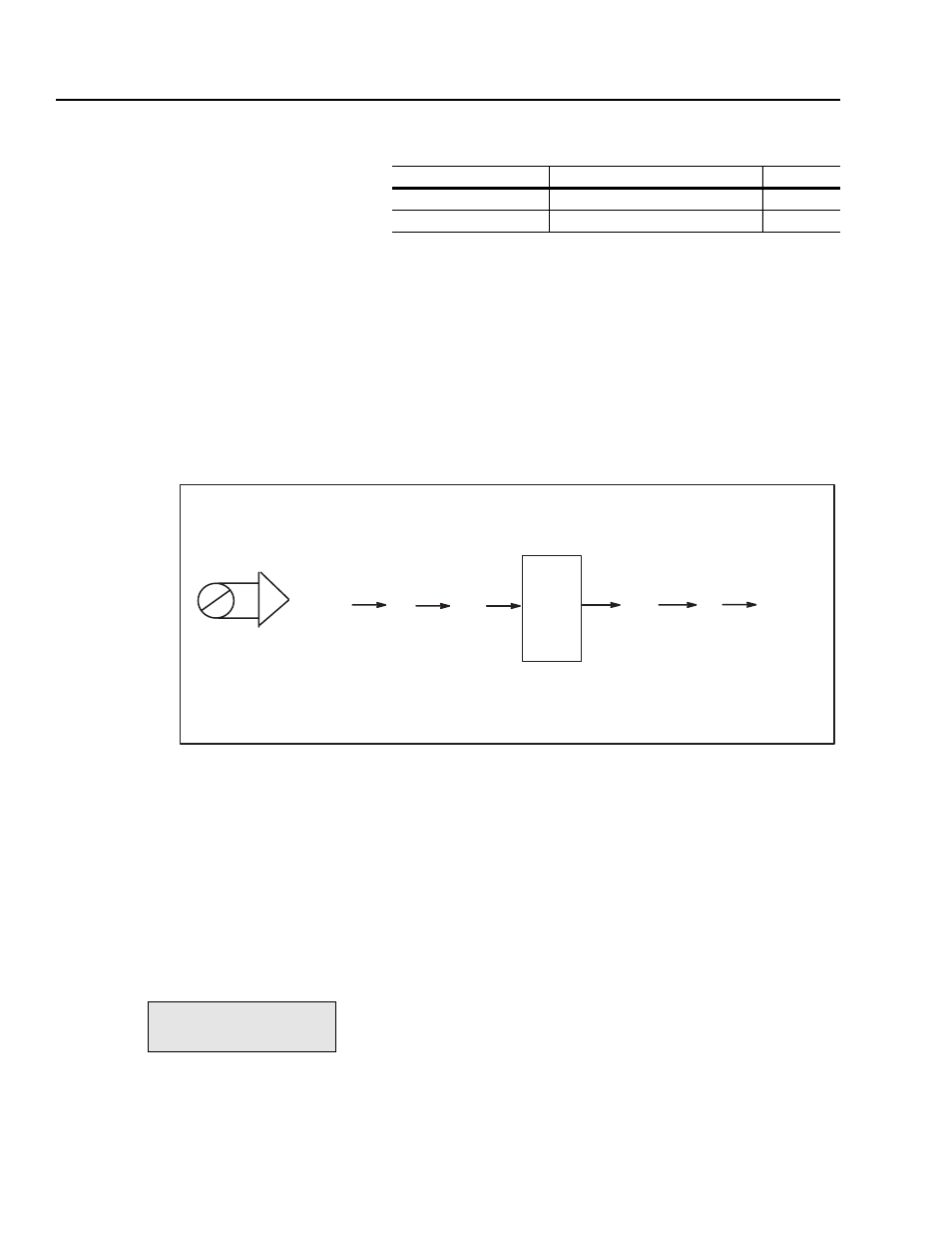
Figure 7.4 shows another example of an analog input. In this
example, you have an analog input range of
±10V and you want an
internal range of
±4096 (4096 = base motor speed).
Figure 7.4
Example of Offset and Scale for Analog Inputs
The offset is 0 because the analog input and the internal range are
both
± ranges. When the ±10V range is converted to internal units,
you get a range of
±2048. To get the internal range of ±4096, you can
use a scale factor of 2 (2 x 2048 = 4096).
The 1336 IMPACT drive provides analog input filter parameters for
you to use if the analog values are unstable. The filter parameters use
a low pass filter to create a more stable value. You will lose some of
the available bandwidth by using these parameters.
Determining the Offset and Scale Values for an Analog
Output
To determine the offset and scale values for an analog output, you
need to know the following:
•
the range that you want for the analog output (for example, -5V to
+5V or 0V to 10V)
•
the range that the drive is using for the internal units (for
example, -2048 to +2048 or 0 to 4096)
If the values are:
Then you:
Go to:
Identical
Do not need to scale the value
Different
Need to scale the value
Analog
Input
Offset
Scale
+10
–10
+10
–10
+2048
–2048
+4096
–4096
2
0
0
0
0
Analog to
Digital
Converter
±10 =
±2048
Drive Output
Range of the analog
input after the offset
is applied
Range of the analog
input in internal
drive units
±10V pot
Because you already have the
correct range (
± to ±), you do
not need an offset.
By multiplying
±2048 by 2,
you get the
±4096 range
you were looking for
.
file:
Interface/Comm
group:
Analog Outputs
