Features, Functional description, Transmit data storage – Rainbow Electronics DS3170 User Manual
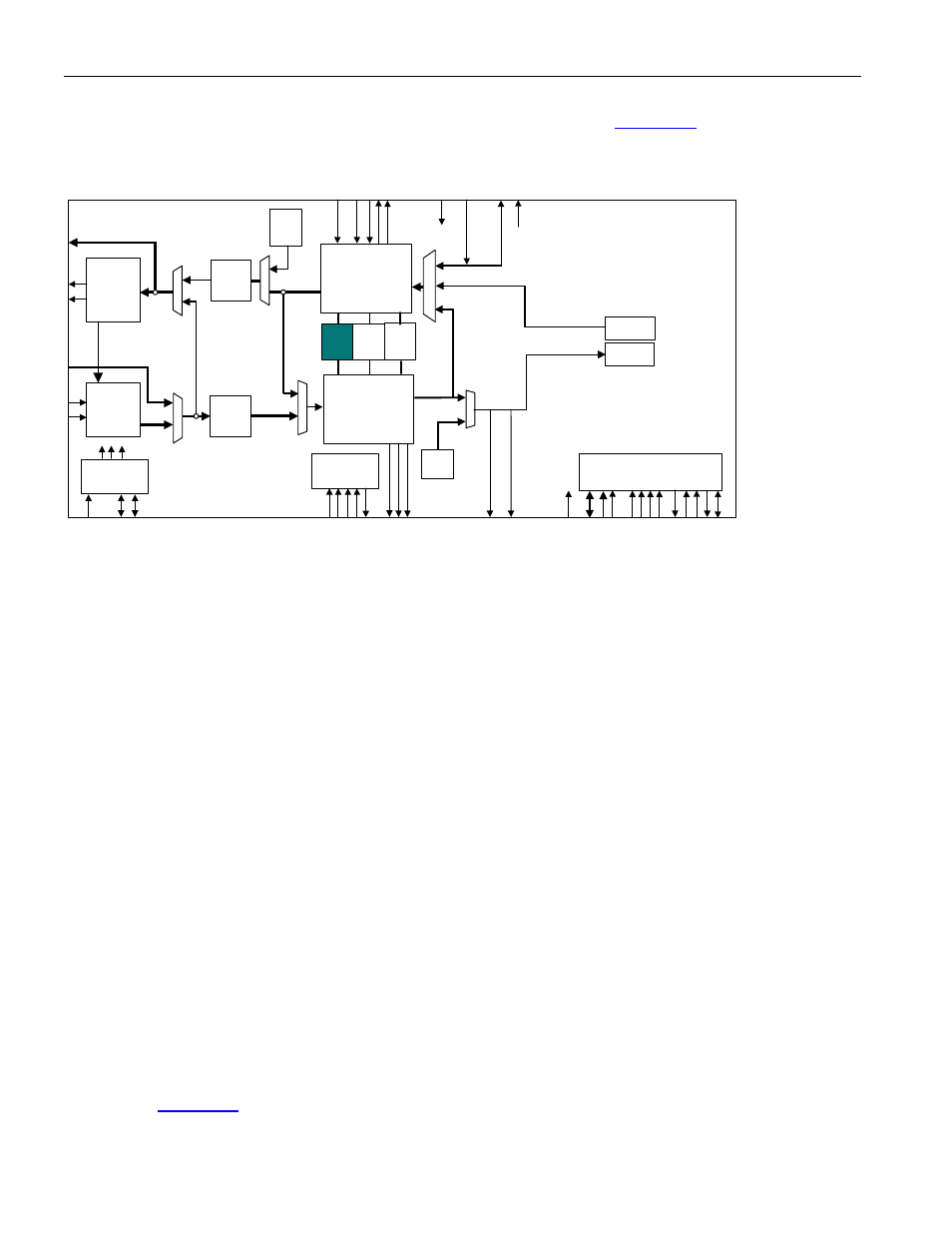
Page 103: Transmit feac processor, Figure 9-22. feac controller block diagram, 2 features, 3 functional description
DS3170 DS3/E3 Single-Chip Transceiver
103 of 233
The transmit direction inputs codewords from the microprocessor via the register interface and stores the
codewords. It removes the codewords and performs FEAC processing. See
for the location of the
FEAC Controller in the block diagram
Figure 9-22. FEAC Controller Block Diagram
DS3/E3
Transmit
LIU
IEEE P1149.1
JTAG Test
Access Port
Microprocessor
Interface
HDLC
FEAC
LLB
DL
B
DS3 / E3
Transmit
Formatter
DS3 / E3
Receive
Framer
Trail
Trace
Buffer
DS3/E3
Receive
LIU
TAIS
TUA1
Clock Rate
Adapter
TX BERT
RX BERT
PL
B
AL
B
UA1
GEN
B3ZS/
HDB3
Encoder
B3ZS/
HDB3
Decoder
9.9.2 Features
· Programmable dual codeword output – The transmit side can be programmed to output a single codeword
ten times, one codeword ten times followed by a second codeword ten times, or a single codeword
continuously.
· Four codeword receive FIFO
· Fully independent transmit and receive paths
· Fully independent Line side and register side timing – The FIFO can be read from or written to at the
register interface side while all line side clocks and signals are inactive, and read from or written to at the line
side while all register interface side clocks and signals are inactive.
9.9.3 Functional
Description
The bits in a code are received MSB first, LSB last. When they are output serially, they are output MSB first, LSB
last. The bits in a code in an incoming signal are numbered in the order they are received, 1 (MSB) to 6 (LSB).
However, when a code is stored in a register, the MSB is stored in the lowest numbered bit (0), and the LSB is
stored in the highest numbered bit (5). This is to differentiate between a code in a register and the corresponding
code in a signal.
9.9.3.1 Transmit Data Storage
The Transmit Data Storage block contains the registers for two FEAC codes (C{1:6]) and controller circuitry for
reading and writing the memory. The Transmit Data Storage receives data from the microprocessor interface, and
stores the data in memory. The Transmit FEAC Processor reads the data from the Transmit Data Storage.
9.9.3.2 Transmit
FEAC
Processor
The Transmit FEAC Processor accepts data from the Transmit Data Storage performs FEAC processing. The
FEAC codes are read from Transmit Data Storage with the MSB (C[1]) in TFCA[0] or TFCB[0], and the LSB (C[6])
in TFCA[5] or TFCB[5].
FEAC processing has four modes of operation (Idle, single code, dual code, and continuous code). In Idle mode, all
ones are output on the outgoing FEAC data stream. In single code mode, the code from TFCA[5:0] is inserted into
a codeword (
), and sent ten consecutive times. Once the ten codewords have been sent, all ones are
output. In dual code mode, the code from TFCA[5:0] is inserted into a codeword, and sent ten consecutive times.
Then the code from TFCB[5:0] is inserted into a codeword, and sent ten consecutive times. Once both codewords
