Functions – H3C Technologies H3C Intelligent Management Center User Manual
Page 234
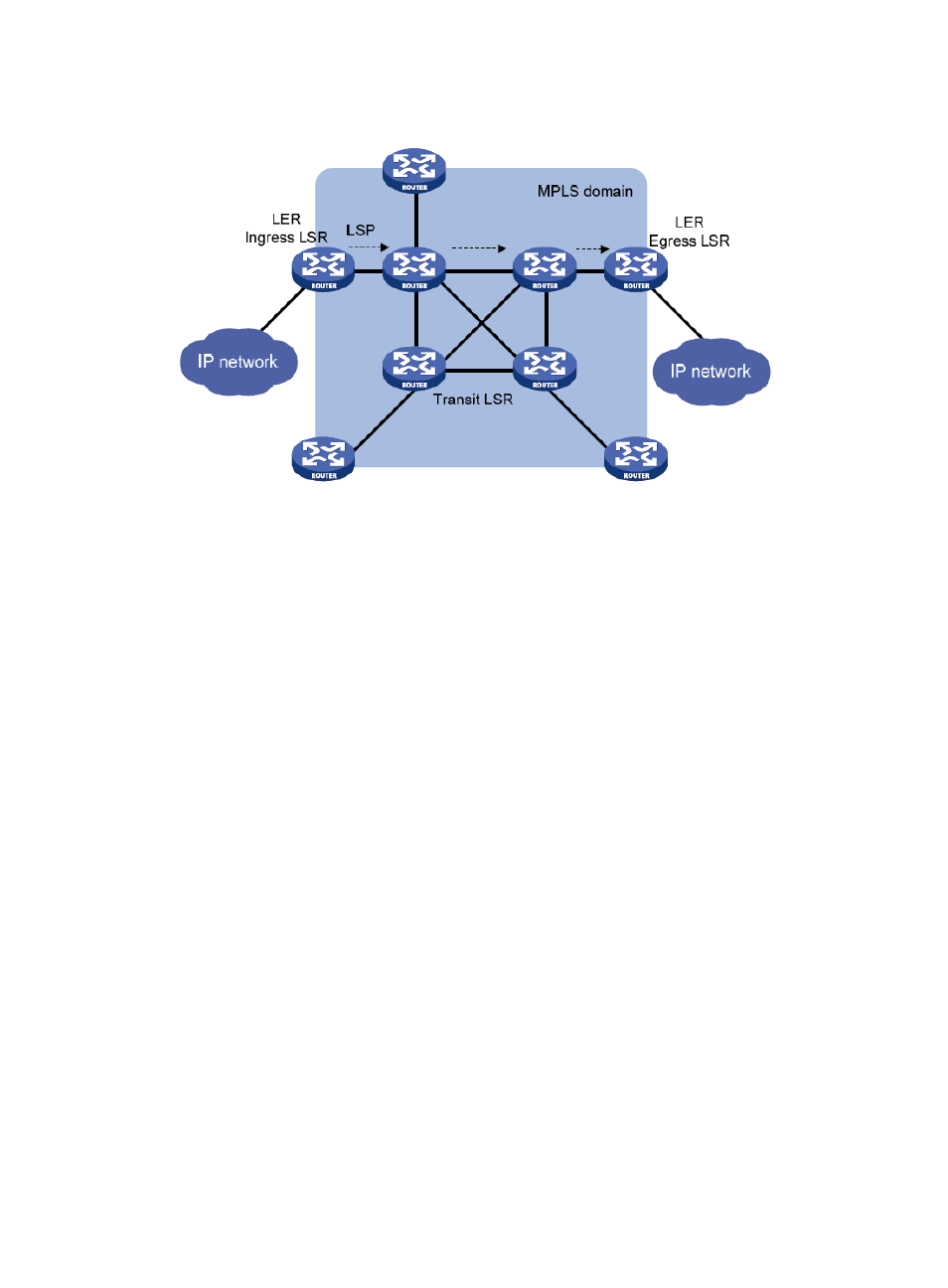
Figure 119 Diagram for the MPLS network structure
An MPLS domain consists of the following types of LSRs:
•
Ingress LSRs for receiving and labeling packets coming into the MPLS domain.
•
Transit LSRs for forwarding packets along LSPs to their egress LERs according to the labels.
•
Egress LSRs for removing labels from packets and IP forwarding the packets to their destination
networks.
In other words, transit LSRs perform MPLS forwarding based on labels of packets, and the ingress and
egress LSRs deal with the switch-over between MPLS and IP forwarding.
Functions
To access main functions, click the Service tab from the tabular navigation system on the top of the IMC
main page, and then select MPLS Management > Quick Start from the left navigation tree. Main
functions appear in the Quick Start page.
•
Device Management—Allows operators to import devices from the IMC platform to the MPLS
management component, to configure device LSR IDs, and to enable MPLS or MPLS LDP for devices
and interfaces. Provides batch operations to facilitate device and interface management.
•
LDP Management—Allows operators to manually create remote LDP peers and view session
information between peers. In addition, the system can automatically discover local peers.
•
LSP Management—Allows operators to manually add static LSPs on the topology, deploy, undeploy,
delete, and audit LSPs. The system can also automatically add static LSPs and automatically
discover LSPs.
•
Topology Management—Displays the MPLS global network topology and LSPs between devices,
and highlights LSPs.
224
