5 spanning tree protocol (stp), Spanning tree protocol (stp) – FUJITSU XG Series P3NK-4452-01ENZD User Manual
Page 71
XG Series User's Guide
Chapter 4 Switch Functions and their Configuration
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
71
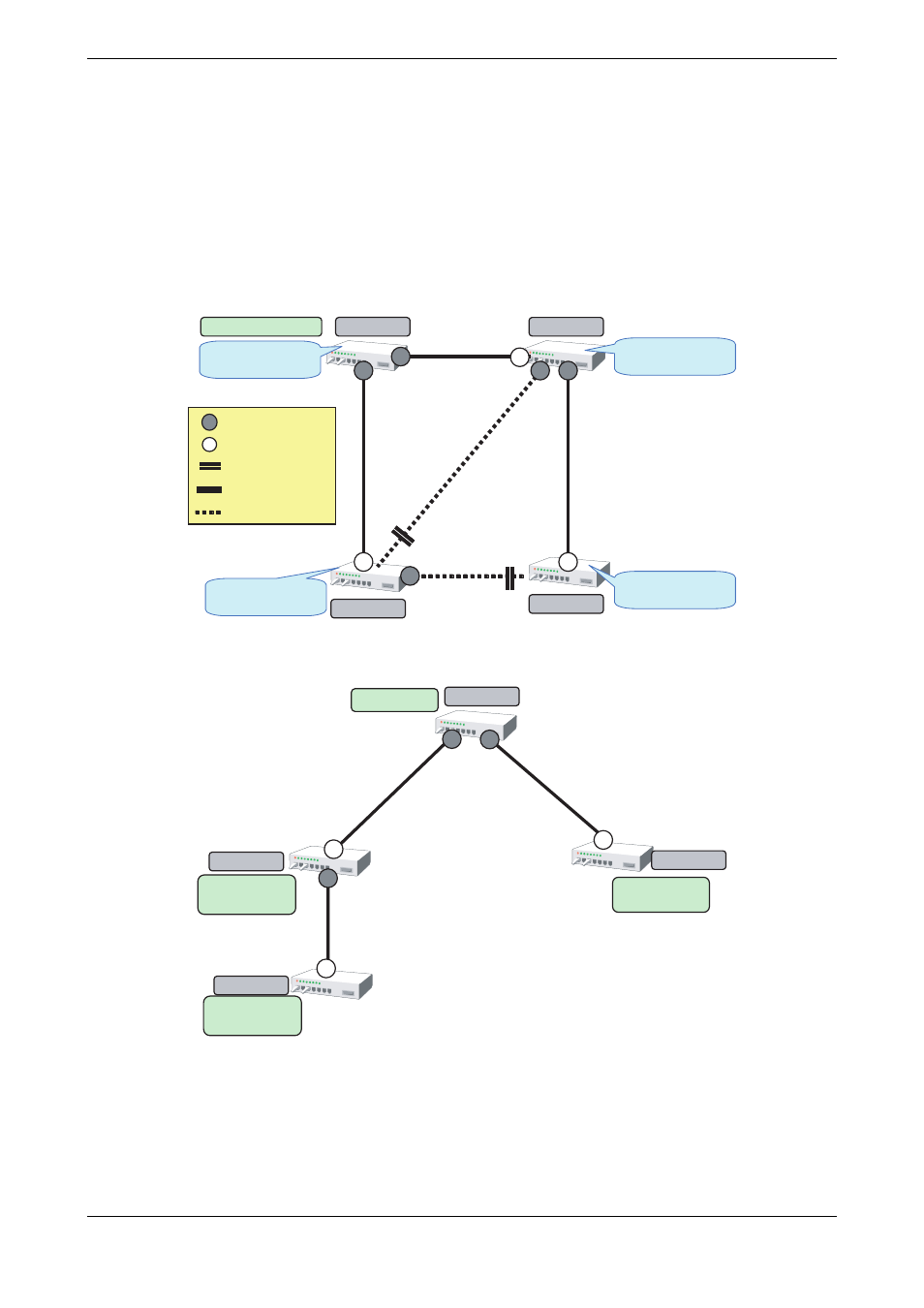
4.5 Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a function that prevents loops from occurring on a network. It is also possible to
provide network redundancy by intentionally creating a loop.
STP exclusively uses only one active path between network devices, and shuts out other paths, to avoid network loops. An
active path is selected by comparing path costs defined on each path. After the comparison, the lowest cost path will be
selected. If the selected path becomes disabled, STP will activate the lowest cost path amongst the paths remaining.
The device supports IEEE802.1w RSTP (Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol). The RSTP is upward compatible with
IEEE802.1D STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) and serves as a STP if the destination device only supports STP.
Switch Priority = 10
Switch A
Switch B
Switch C
Switch D
Switch Priority = 20
Switch Priority = 30
Switch Priority = 40
Designated port
Route port
Blocking port
Forwarding pass
Blocking pass
Path Cost = 10
Path
Co
st
=
20
Path
Co
st
=
15
Path Cost = 10
Pass Cos
t = 15
Route Switch
Physical Topology
Switch A
Switch B
Switch C
Switch D
Route
Path Cost = 20
Route Switch
Route
Path Cost = 10
Route
Path Cost = 25
Path Cos
t =
20
Path Cost
= 10
Path Cost =
15
Logical Topology by STP
