Ipv6 over ipv6 tunneling – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 97
85
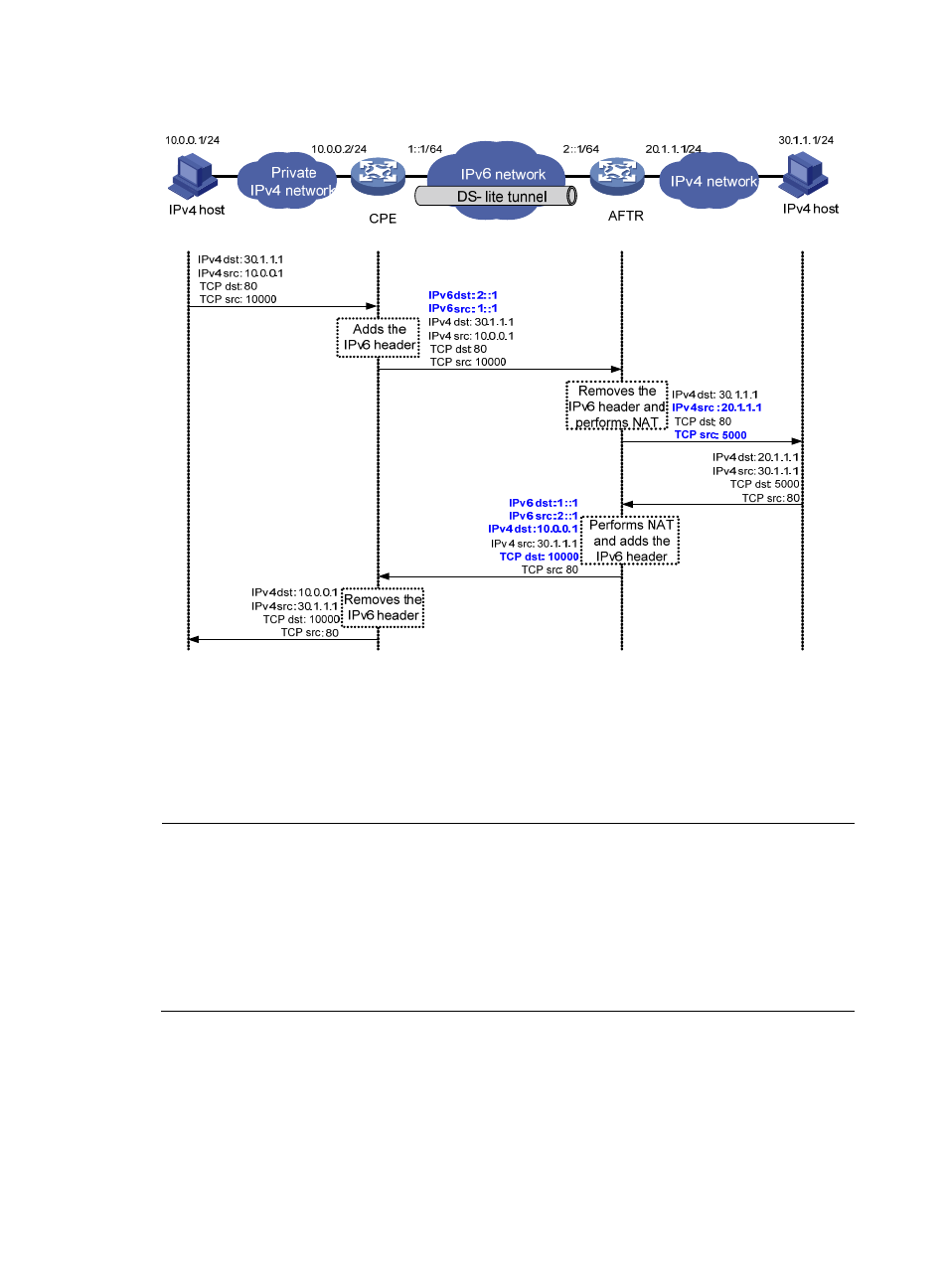
Figure 70 Packet forwarding process in DS-Lite
When a gateway serves as the CPE, the changes of source and destination IP addresses and port
numbers are illustrated in
. The entire process is summarized as follows:
•
The CPE and AFTR encapsulate and de-encapsulate packets.
•
The AFTR performs NAT.
When a host serves as the CPE, the process is similar and therefore not shown.
NOTE:
•
NAT supports both basic address translation between private and public addresses and Network
Address Port Translation (NAPT), which translates both IP address (private or public) and port
shows an example of NAPT. For more information about NAT, see
NAT
Configuration Guide.
•
DS-Lite tunnel supports only an IPv4 host in a private network initiating communication with an IPv4 host
on the Internet and does not support an IPv4 host on the Internet initiating communication with an IPv4
host in a private network.
IPv6 over IPv6 tunneling
IPv6 over IPv6 tunneling (specified in RFC 2473) is developed for IPv6 data packet encapsulation so that
encapsulated packets can be transmitted over an IPv6 network. The encapsulated packets are IPv6
tunnel packets.
- H3C SecPath F5000-A5 Firewall H3C SecPath F1000-A-EI H3C SecPath F1000-E-SI H3C SecPath F1000-S-AI H3C SecPath F5000-S Firewall H3C SecPath F5000-C Firewall H3C SecPath F100-C-SI H3C SecPath F1000-C-SI H3C SecPath F100-A-SI H3C SecBlade FW Cards H3C SecBlade FW Enhanced Cards H3C SecPath U200-A U200-M U200-S H3C SecPath U200-CA U200-CM U200-CS
