L2tp tunnel modes and tunnel establishment process, Typical l2tp tunnel modes – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 249
237
Control messages and data messages share the same header structure. An L2TP header contains a
tunnel ID and a session ID, which are used to identify the tunnel and session respectively. Packets with the
same tunnel ID but different session IDs are multiplexed to the same tunnel. The tunnel ID and session ID
in a header are those of the intended receiver, not the sender.
L2TP tunnel modes and tunnel establishment process
Typical L2TP tunnel modes
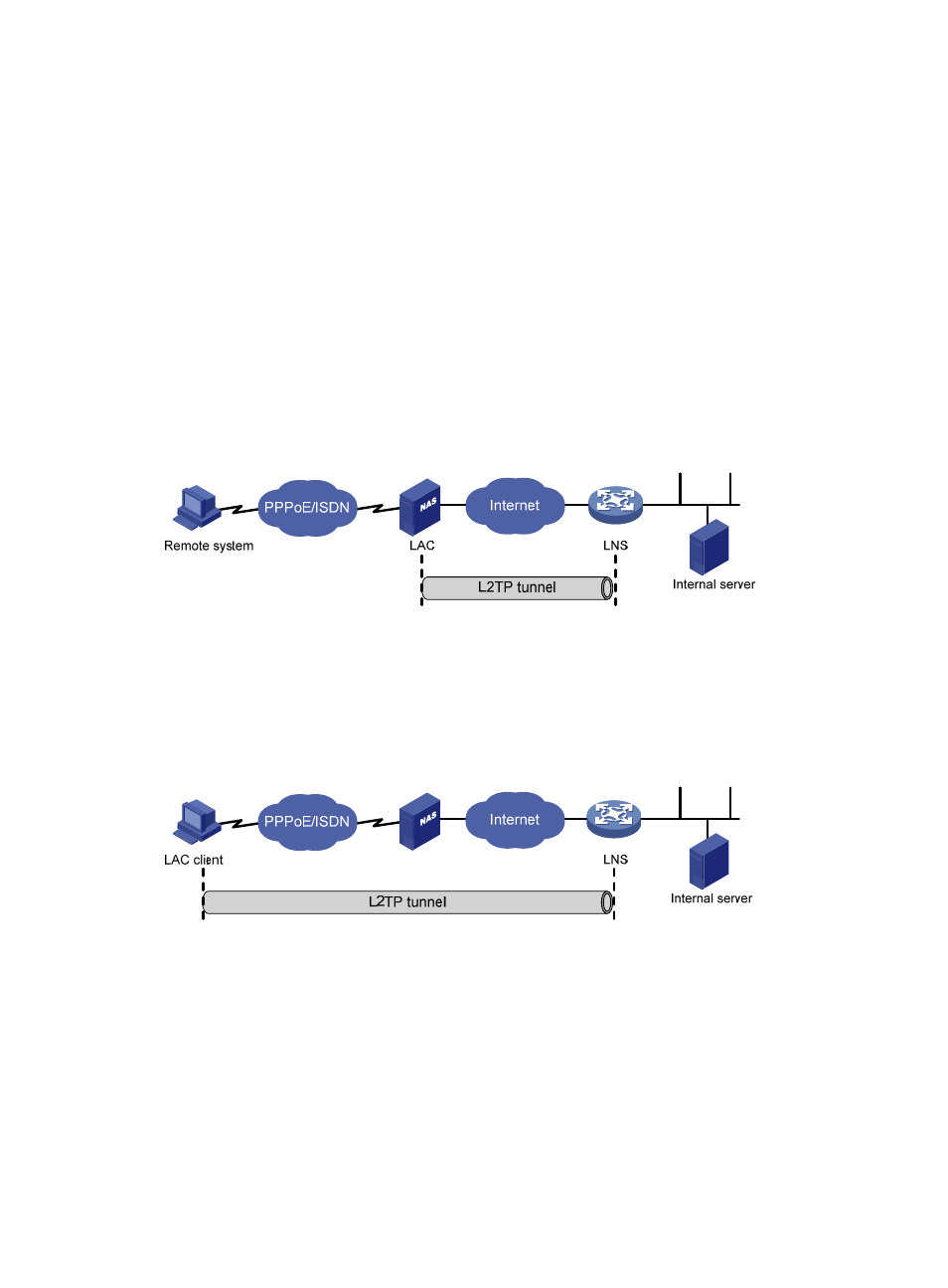
Typical L2TP tunnel modes include NAS-initiated, client-initiated, and LAC-Auto-Initiated.
•
NAS-initiated
In this mode, a remote system dials in the LAC through a PPPoE/ISDN network, and the LAC
initiates a tunneling request to the LNS over the Internet, as shown in
assign the remote system a private IP address. Authentication and accounting of the remote system
can be implemented on the LAC by an agent or on the LNS.
Figure 149 NAS-initiated tunnel mode
•
Client-initiated
In this mode, after obtaining the access right to the Internet, a remote system running the L2TP client
software (LAC client) initiates a tunneling request to the LNS directly without requiring a separate
LAC. The LNS will assign the LAC client a private IP address. An LAC client needs a public IP
address to communicate with the LNS directly through the Internet.
Figure 150 Client-initiated tunnel mode
•
LAC-auto-initiated
In NAS-initiated mode, a remote system must successfully dial in to the LAC through PPPoE or ISDN
to trigger the LAC to initiate a tunneling request to the LNS.
In LAC-auto-initiated mode, you can create a virtual PPP user and execute the l2tp-auto-client
enable command on the LAC. Then, the LAC automatically initiates a tunneling request to the LNS
to establish an L2TP tunnel for the virtual PPP user. Then, when a remote system accesses the
internal network, the LAC forwards data through the L2TP tunnel. In this mode, the connection
between a remote system and the LAC is not confined to a dial-up connection and can be any
IP-based connection.
- H3C SecPath F5000-A5 Firewall H3C SecPath F1000-A-EI H3C SecPath F1000-E-SI H3C SecPath F1000-S-AI H3C SecPath F5000-S Firewall H3C SecPath F5000-C Firewall H3C SecPath F100-C-SI H3C SecPath F1000-C-SI H3C SecPath F100-A-SI H3C SecBlade FW Cards H3C SecBlade FW Enhanced Cards H3C SecPath U200-A U200-M U200-S H3C SecPath U200-CA U200-CM U200-CS
