Tunnel establishment phase, Supported dvpn features, Nat traversal of dvpn packets encapsulated by udp – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 417
405
identity authentication request, indicating the required authentication algorithm. In the case of
CHAP authentication, a random number is also sent.
3.
The client submits its identity information to the server.
4.
After receiving the identity information of the client, the server sends an authentication request to
the AAA server and, after receiving the expected authentication acknowledgement, sends an
accounting request to the AAA server. When the server receives the accounting acknowledgement,
it sends the client a registration acknowledgement, telling the client information about the hubs in
the VPN.
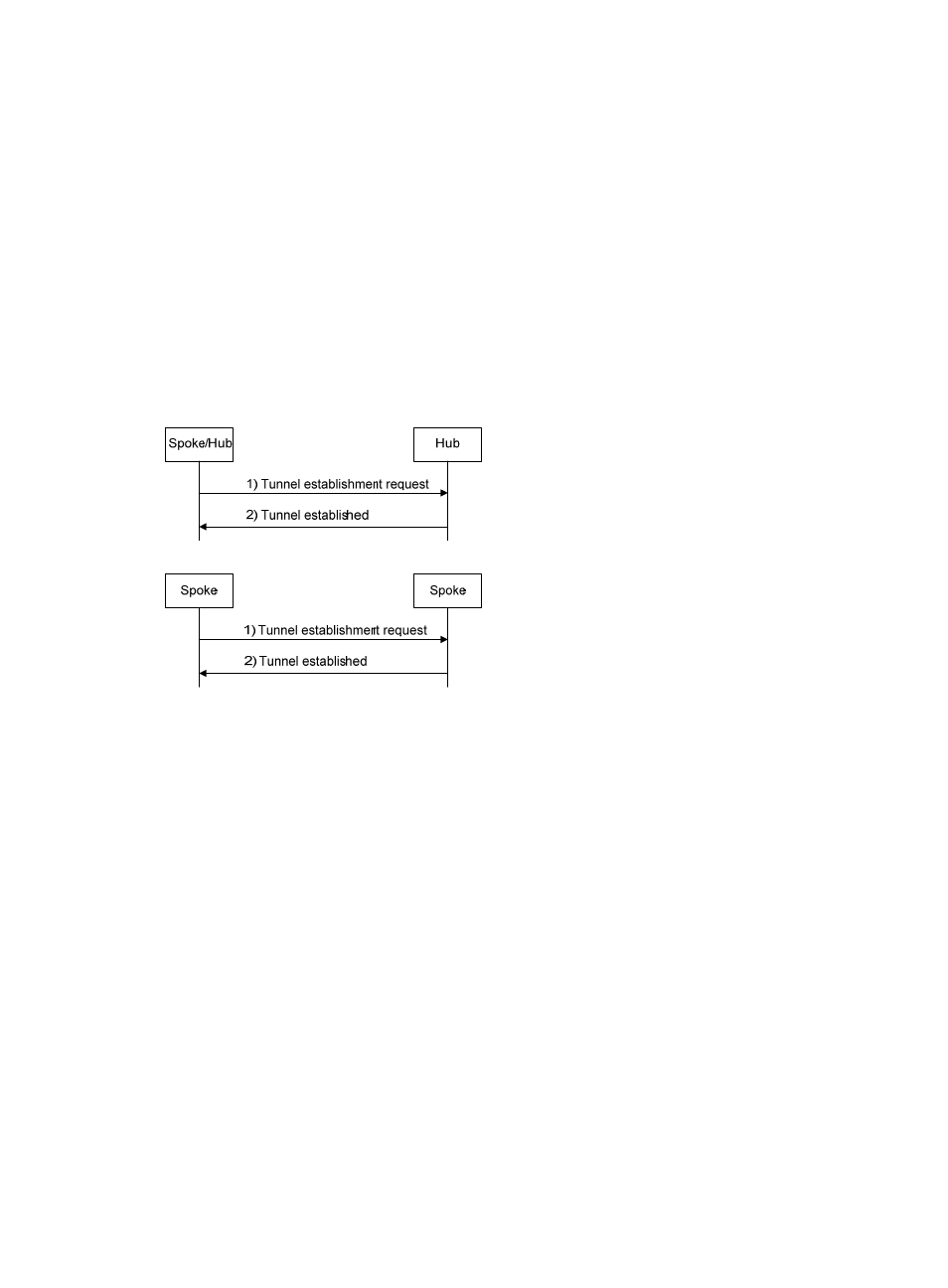
Tunnel establishment phase
After a spoke successfully registers itself, it needs to establish a permanent tunnel with a hub. A spoke can
establish permanent tunnels with up to two hubs. If there are two hubs in a VPN domain, a permanent
tunnel is required between the hubs.
shows the tunnel establishment process.
Figure 299 Tunnel establishment process
1.
The initiator originates a tunnel establishment request.
{
Hub-spoke tunnel: After a spoke registers itself successfully, it needs to establish a permanent
tunnel with each hub in the VPN. Upon receiving the registered information of the hubs from the
server, the spoke checks whether a tunnel is present to each hub. If no tunnel exists between the
spoke and a hub, the spoke sends a tunnel establishment request to the hub.
{
Hub-Hub tunnel: After a hub registers itself successfully, the server sends the registered
information of the other hubs in the VPN to the hub and the hub checks whether a tunnel exists
to each of its peer hubs. If not, the hub sends a tunnel establishment request to the peer hub.
{
Spoke-spoke tunnel: In a full mesh network, when a spoke receives a data packet but finds no
tunnel for forwarding the packet, it sends an address resolution request to the server and then,
after receiving the resolved address, sends a tunnel establishment request to the peer spoke.
2.
The tunnel establishment request receiver saves the tunnel establishment information and sends a
response to the sender. If the request sender receives the response, a tunnel is established.
Otherwise, tunnel establishment attempt fails.
Supported DVPN features
NAT traversal of DVPN packets encapsulated by UDP
When a spoke needs to communicate with another spoke, one of the following cases will occur:
- H3C SecPath F5000-A5 Firewall H3C SecPath F1000-A-EI H3C SecPath F1000-E-SI H3C SecPath F1000-S-AI H3C SecPath F5000-S Firewall H3C SecPath F5000-C Firewall H3C SecPath F100-C-SI H3C SecPath F1000-C-SI H3C SecPath F100-A-SI H3C SecBlade FW Cards H3C SecBlade FW Enhanced Cards H3C SecPath U200-A U200-M U200-S H3C SecPath U200-CA U200-CM U200-CS
