Verifying the configuration, Network requirements, Configuation considerations – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 215: Configuring secpath a
203
[SecPathB-ipsec-policy-isakmp-use1-10] ike-peer peer
[SecPathB-ipsec-policy-isakmp-use1-10] quit
# Configure the IP address of the GigabitEthernet interface.
[SecPathB] interface GigabitEthernet 0/2
[SecPathB-GigabitEthernet0/2] ip address 2.2.3.1 255.255.255.0
# Apply the IPsec policy group to the interface.
[SecPathB-GigabitEthernet0/2] ipsec policy use1
Verifying the configuration
After the configuration, IKE negotiation will be triggered to set up SAs when there is traffic between
subnet 10.1.1.0/24 and subnet 10.1.2.0/24. If IKE negotiation is successful and SAs are set up, the traffic
between the two subnets will be IPsec protected.
IPsec with IPsec tunnel interfaces configuration example
Network requirements
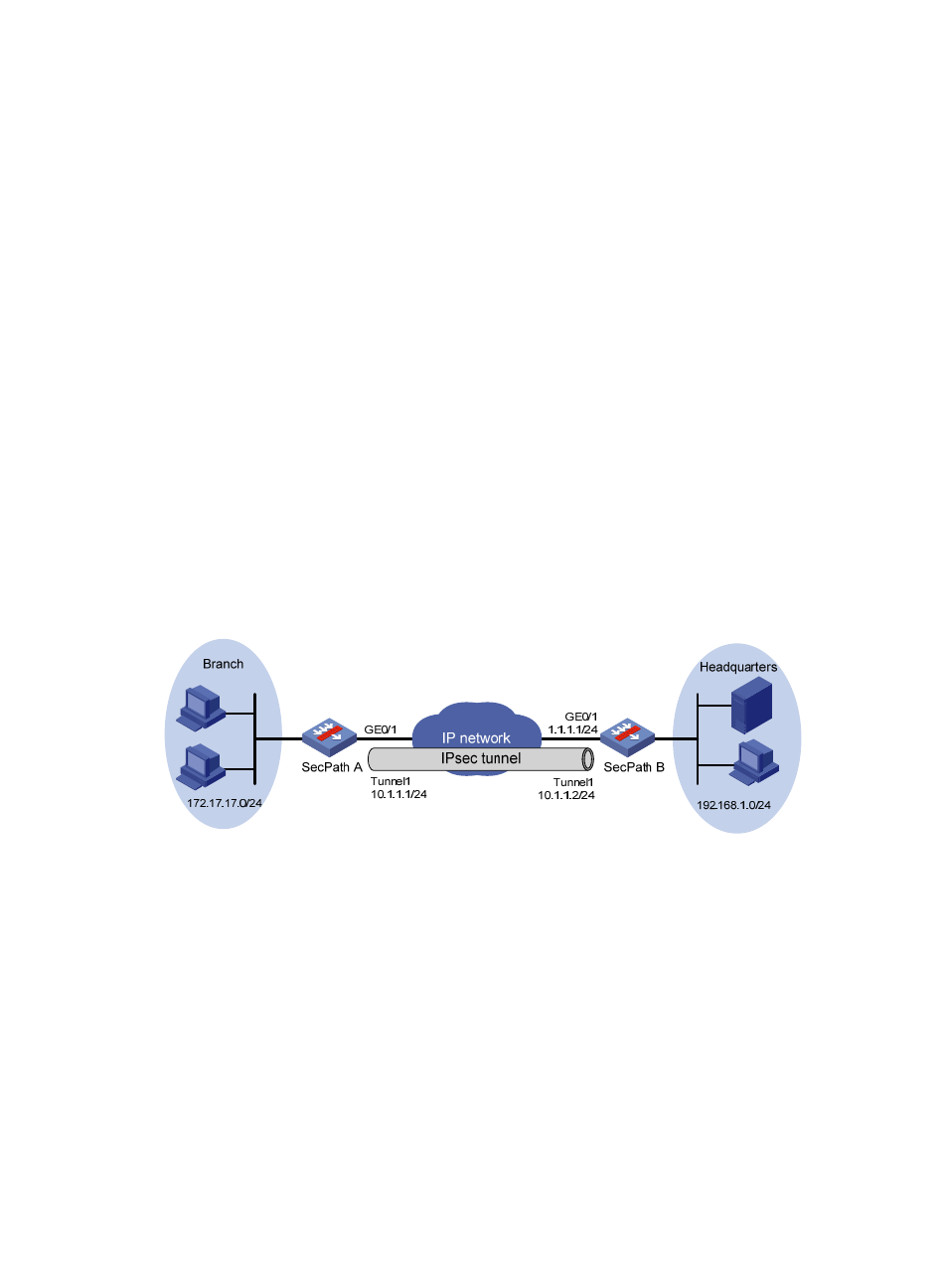
As shown in
, the gateway of the branch accesses the Internet through a dial-up line and
obtains the IP address dynamically. The headquarters accesses the Internet by using a fixed IP address.
Configure an IPsec tunnel to protect the traffic between the branch and the headquarters. Make sure that
the IPsec configuration of the headquarters’ gateway remains relatively stable despite of changes of the
branch's private IP address segment.
Figure 128 Network diagram
Configuation considerations
To meet the requirements, configure an IPsec tunnel interface on each SecPath and configure a static
route on each SecPath to route the packets destined to the peer to the IPsec tunnel interface for IPsec
protection.
Configuring SecPath A
# Name the local gateway SecPatha.
[SecPathA] ike local-name SecPatha
# Configure an IKE peer named atob. As the local peer obtains the IP address automatically, set the IKE
negotiation mode to aggressive.
[SecPathA] ike peer atob
[SecPathA-ike-peer-atob] exchange-mode aggressive
[SecPathA-ike-peer-atob] pre-shared-key simple aabb
- H3C SecPath F5000-A5 Firewall H3C SecPath F1000-A-EI H3C SecPath F1000-E-SI H3C SecPath F1000-S-AI H3C SecPath F5000-S Firewall H3C SecPath F5000-C Firewall H3C SecPath F100-C-SI H3C SecPath F1000-C-SI H3C SecPath F100-A-SI H3C SecBlade FW Cards H3C SecBlade FW Enhanced Cards H3C SecPath U200-A U200-M U200-S H3C SecPath U200-CA U200-CM U200-CS
