Aft operation, Communication initiated by an ipv6 host – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 75
63
AFT operation
AFT allows an IPv6 host to initiate communication with any IPv4 host, but allows an IPv4 host to initiate
communication with only IPv6 hosts whose addresses are IVI addresses. The address translation process
for communication initiated by an IPv6 host is different from that for communication initiated by an IPv4
host.
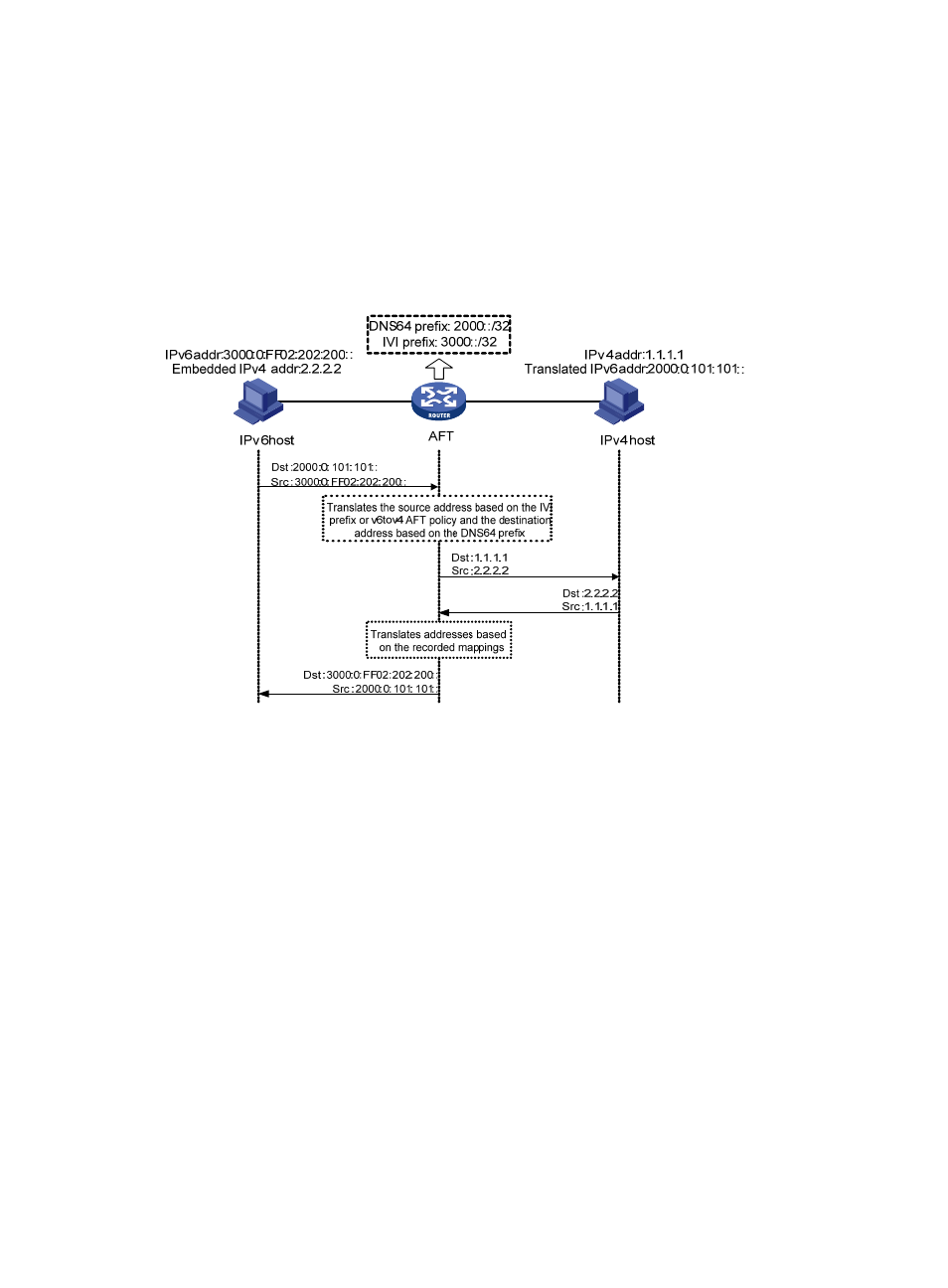
Communication initiated by an IPv6 host
Figure 59 AFT process when communication is initiated by an IPv6 host
AFT operates in the following steps:
1.
Determines whether address translation is needed. Upon receiving a packet from an IPv6 host, the
AFT checks whether the prefix of the destination IPv6 address is a predefined DNS64 prefix. If yes,
the packet is destined to an IPv4 host and address translation is needed.
2.
Translates the source IP address. If the source IPv6 address of the packet matches the IVI format, the
AFT uses the IPv4 address embedded in the source IPv6 address as the translated source IPv4
address of the packet. If not, the AFT translates the source IPv6 address into an IPv4 address based
on the 6to4 AFT policy.
3.
Translates the destination IP address. The AFT extracts the embedded IPv4 address from the
destination IPv6 address based on the length of the DNS64 prefix and uses the IPv4 address as the
translated destination IPv4 address.
4.
Forwards the packet and records the mapping. The AFT performs protocol translation such as
changing the IPv6 header to the IPv4 header, forwards the packet, and records the IPv4-IPv6
mappings.
5.
Translates and forwards the response packet. Upon receiving a response from the IPv4 host, the
AFT replaces the IPv4 addresses in the packet header with IPv6 addresses based on the recorded
address mappings and forwards the packet to the IPv6 host.
- H3C SecPath F5000-A5 Firewall H3C SecPath F1000-A-EI H3C SecPath F1000-E-SI H3C SecPath F1000-S-AI H3C SecPath F5000-S Firewall H3C SecPath F5000-C Firewall H3C SecPath F100-C-SI H3C SecPath F1000-C-SI H3C SecPath F100-A-SI H3C SecBlade FW Cards H3C SecBlade FW Enhanced Cards H3C SecPath U200-A U200-M U200-S H3C SecPath U200-CA U200-CM U200-CS
