Ipsec for ripng configuration example, Network requirements, Configuation considerations – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 219: Configuring secpath a
207
Reply from 172.17.17.1: bytes=56 Sequence=3 ttl=255 time=10 ms
Reply from 172.17.17.1: bytes=56 Sequence=4 ttl=255 time=5 ms
Reply from 172.17.17.1: bytes=56 Sequence=5 ttl=255 time=4 ms
--- 172.17.17.1 ping statistics ---
5 packet(s) transmitted
5 packet(s) received
0.00% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max = 4/8/15 ms
Similarly, you can view the information on SecPath A. (Details not shown.)
IPsec for RIPng configuration example
NOTE:
The IPsec configuration procedures for protecting OSPFv3 and IPv6 BGP are similar. For more information
about RIPng, OSPFv3, and IPv6 BGP, see
Network Management Configuration Guide.
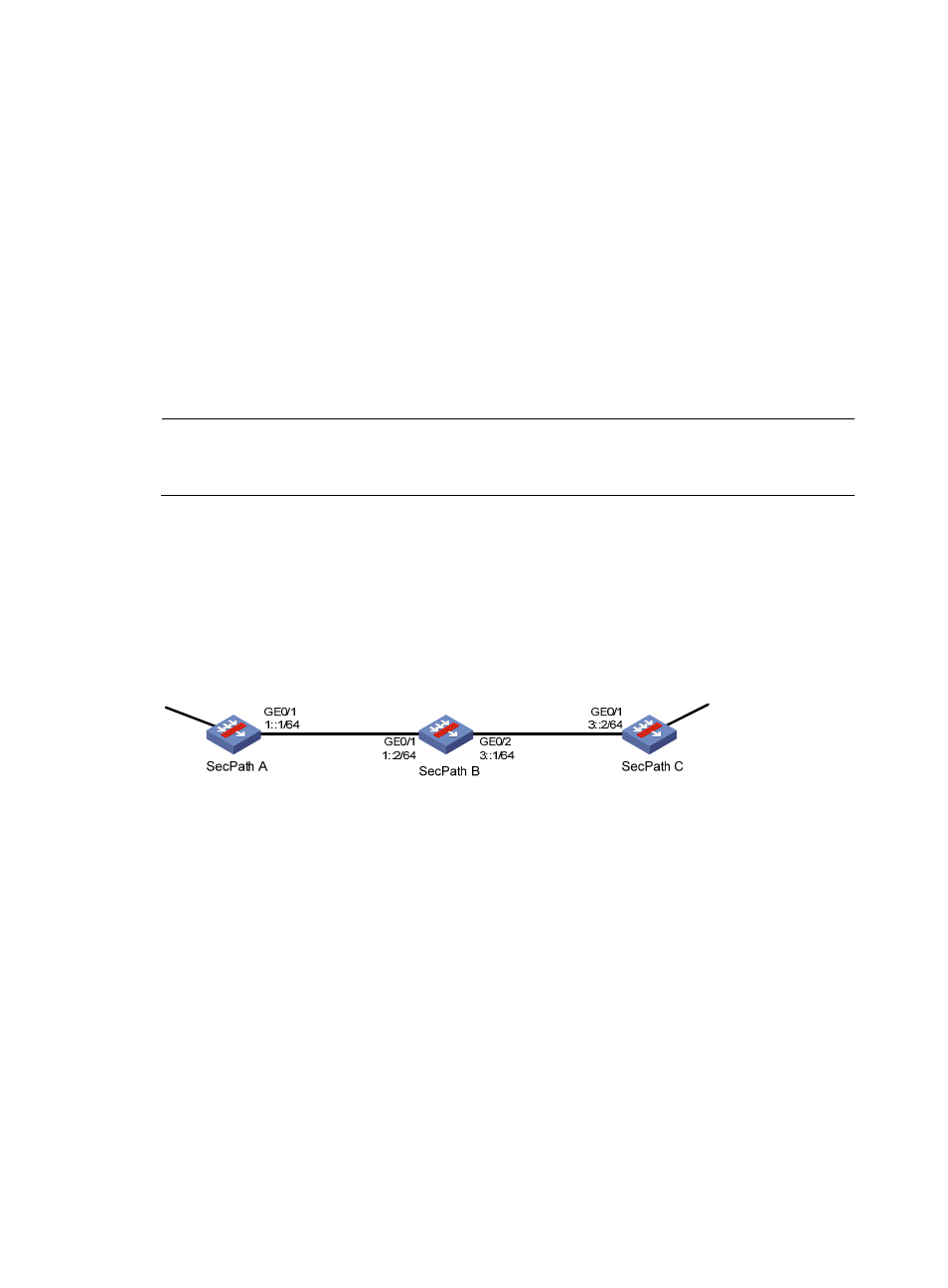
Network requirements
As shown in
, SecPath A, SecPath B, and SecPath C are connected. They learn IPv6 routing
information through RIPng.
Configure IPsec for RIPng so that RIPng packets exchanged between the routers are transmitted through
an IPsec tunnel. Configure IPsec to use the security protocol ESP, the encryption algorithm DES, and the
authentication algorithm SHA1-HMAC-96.
Figure 129 Network diagram
Configuation considerations
To meet the requirements, perform the following configuration tasks:
•
Configure basic RIPng parameters.
•
Configure a manual IPsec policy.
•
Apply the IPsec policy to a RIPng process to protect RIPng packets in this process or to an interface
to protect RIPng packets traveling through the interface.
Configuring SecPath A
# Assign an IPv6 address to each interface. (Details not shown.)
# Create a RIPng process and enable it on GigabitEthernet 0/1.
[SecPathA] ripng 1
[SecPathA-ripng-1] quit
[SecPathA] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1
[SecPathA-GigabitEthernet0/1] ripng 1 enable
- H3C SecPath F5000-A5 Firewall H3C SecPath F1000-A-EI H3C SecPath F1000-E-SI H3C SecPath F1000-S-AI H3C SecPath F5000-S Firewall H3C SecPath F5000-C Firewall H3C SecPath F100-C-SI H3C SecPath F1000-C-SI H3C SecPath F100-A-SI H3C SecBlade FW Cards H3C SecBlade FW Enhanced Cards H3C SecPath U200-A U200-M U200-S H3C SecPath U200-CA U200-CM U200-CS
