Table 23 interpreting npd/id numbers – Nortel Networks NN43001-106 User Manual
Page 421
Feature interactions
421
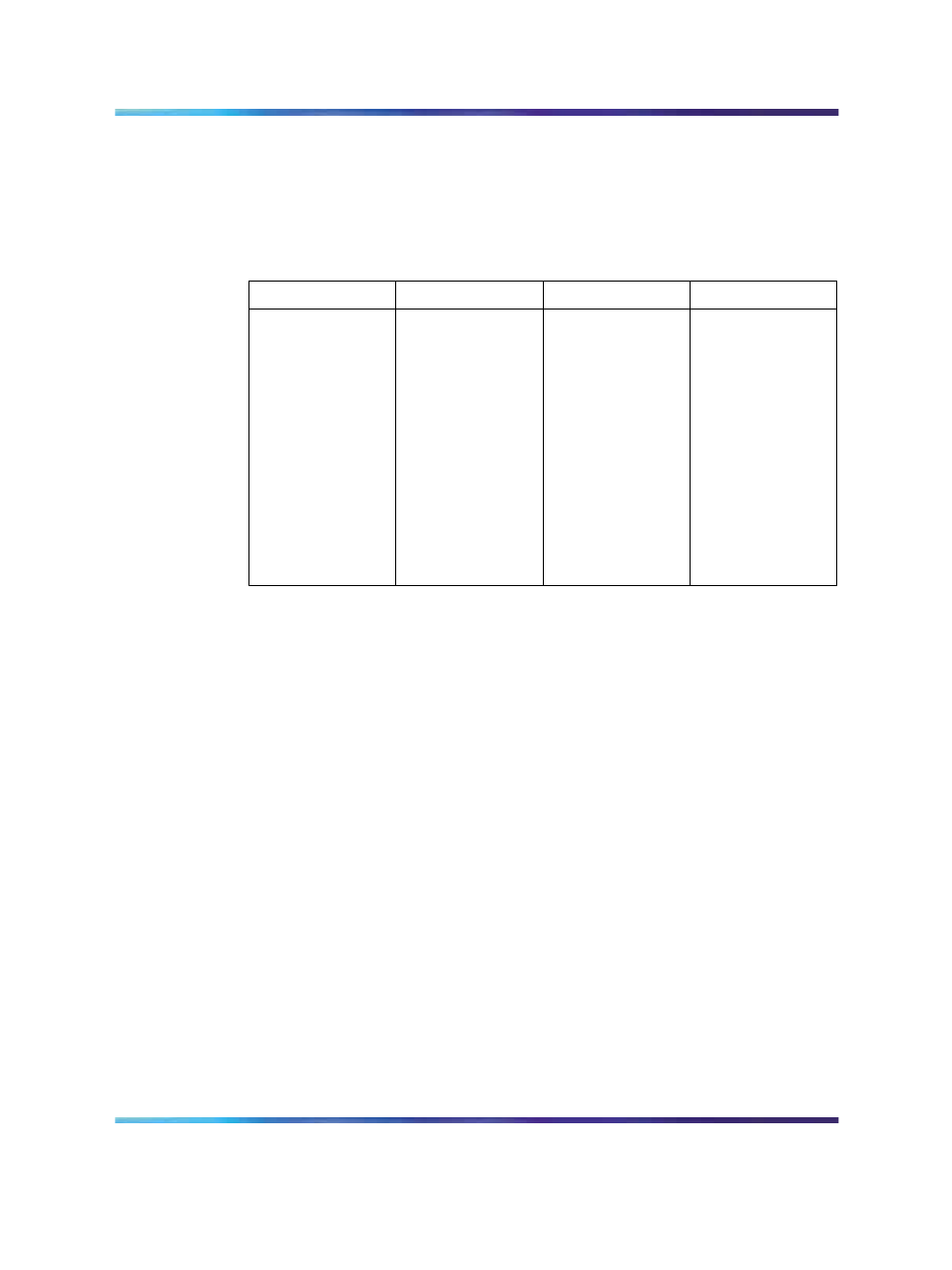
Table 23 "Interpreting NPD/ID numbers" (page 421)
shows an example of
an NPID table. The last two fields, ANI Failure and Test Calls, are mutually
exclusive. If the NPD/ID digit 0 is interpreted as ANI failure, it cannot also
be interpreted as a test call.
Table 23
Interpreting NPD/ID numbers
NPI/Info Digit
NPA
ANI Failure
Test Call
0
408
No
No
1
415
No
No
2
NONE
No
No
3
NONE
No
No
4
NONE
No
No
5
NONE
No
No
6
NONE
No
No
7
NONE
Yes
No
8
NONE
No
Yes
9
NONE
No
No
If the NPA is not specified (NPA = NONE), the NPD/ID digit appears on the
telephone. Otherwise, the NPA appears on the telephone for calls with
a valid ANI.
Seven zeros indicate a failure (for example, MF receive fault, garbled tones
or a timeout). After all ANI digits are received or a timeout occurs, the
system processes the call.
A test call has no display.
Trunk route assignments
The 911 trunk must auto-terminate to a Controlled Directory Number (CDN)
defined in LD 23. The start arrangement must be WINK and the Class
of Service must be defined as Priority Trunk (APY) and Multifrequency
Receiver (MFR).
ANI failure
If ANI information is incorrectly delivered, the call may not have a valid ANI,
as indicated by the seven zeros in the display.
ANI failure affects the incoming call’s Application Module Link (AML)
message, which informs the application with a special DN type value. The
911 caller’s DN type Information Element (IE) contains one of these types:
ANI with NPD, ANI with ID or ANI failure.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
Features and Services - Book 1 of 6 (A to B)
NN43001-106
01.04
Standard
Release 5.0
27 July 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks
.
