Brocade Multi-Service IronWare Administration Guide (Supporting R05.6.00) User Manual
Page 224
206
Multi-Service IronWare Administration Guide
53-1003028-02
IPv6 Traceroute over an MPLS network
6
IPv6 traceroute behavior is similar to IPv4 traceroute. However, unlike IPv4 traceroute, IPv6
traceroute has a new 6PE label added during each hop across the MPLS cloud. Based on the IP
header value, the node devices differentiate if the Internet Control Message Protocol version 6
(ICMPv6) echo request is from an IPv6 or IPv4 source device.
When the traceroute sends ICMPv6 echo request packets with a TTL value (hop limit) value of 1,
the first router in the path replies with the ttl-exceeded error message to the source. The next
packet has a TTL (hop limit) value of 2 and the second router replies with the ttl-exceeded error
message. This process continues till the destination host receives the packets and returns an
ICMPv6 Echo Reply message.
Based on the ttl-exceeded messages or the ICMPv6 Echo Reply messages received during the
traceroute operation, the source device obtains details such as the hop sequence, total hops taken
to complete the path, and the IPv4 or IPv6 addresses of devices that it passed during the path. For
each hop, the traceroute gathers information about the hop number, best hop time, and the TTL
value.
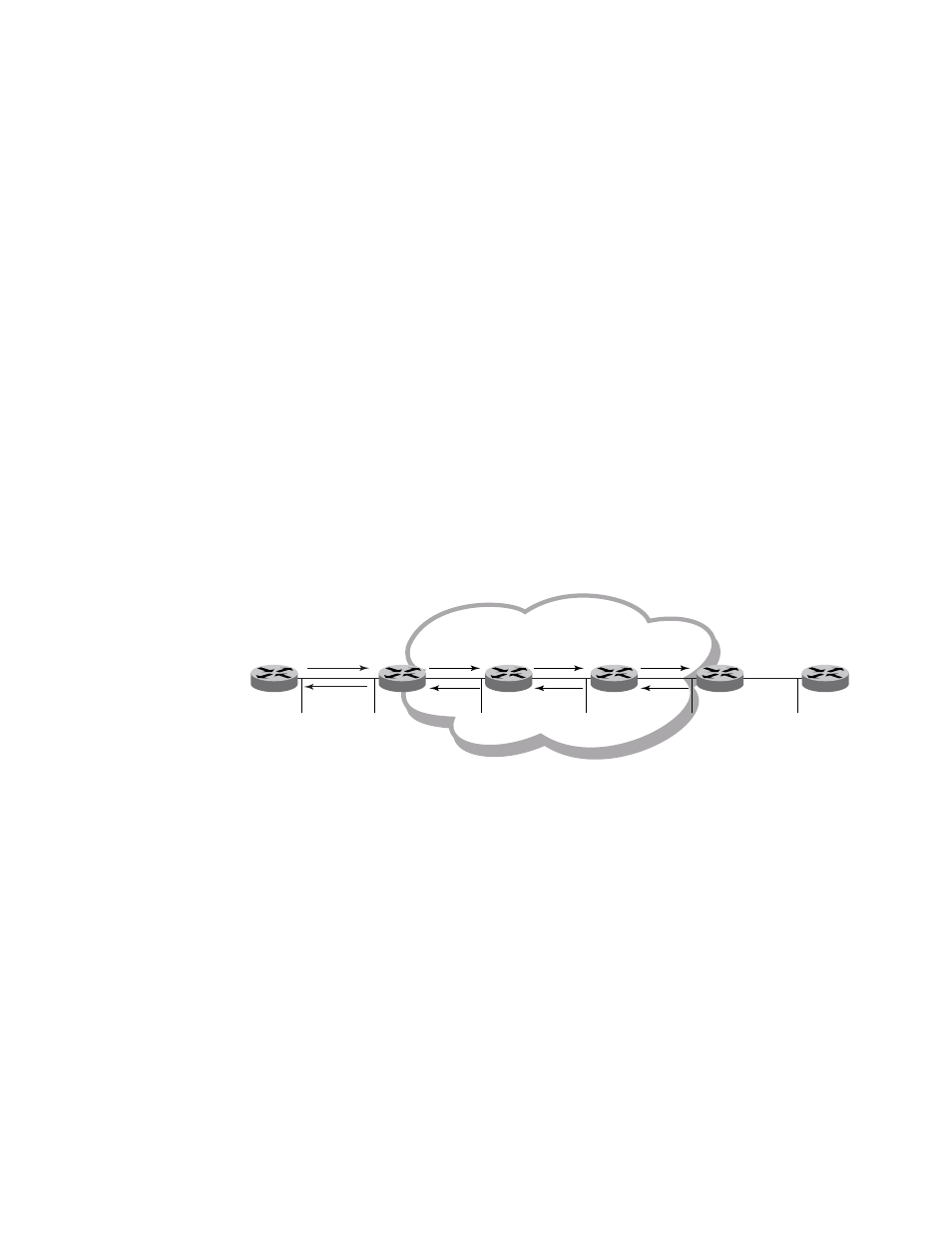
Tracing an IPv6 route through an MPLS domain
Figure 14
shows an MPLS-enabled provider network consisting of four LSRs. PE1 is the ingress PE
Label Edge Router (LER), P1 and P2 are transit LSRs, and PE2 is the egress provider edge LER. CE1
and CE2 are CE devices located in different geographical locations.
FIGURE 14
IPv6 Traceroute in an MPLS cloud
To understand the IPv6 traceroute behavior in an MPLS domain, assume the following:
•
Customer traffic is tunneled through a MPLS VPN network, and traffic within the MPLS core is
forwarded by label-switching only.
•
The CE1 router sends UDP packets from CE1 router towards the CE2 router.
•
Traceroute is configured to generate ICMPv6 messages per ICMP extensions and to use LSPs
to forward these messages. Refer to
“Configuring IPv6 Traceroute over MPLS”
on page 208 for
more information.
•
The PE routers are aware of the source and destination IPv6 addresses while the transit LSRs
have no such knowledge.
•
The traceroute command is issued from CE1 to CE2 and reports the following information:
Brocade# traceroute ipv6 2001:DB8:2::2
Type Control-c to abort
Tracing the route to IPv6 node 2001:DB8:2::2 from 1 to 30 hops
P2
PE2
CE2
P1
MPLS/IPv4 cloud
PE1
CE1
2001:DC8:200::3
2001:DB8:2::2
2001:DC8:200::3
2001:DD8:300::2
2001:DE8:300::2
2001:DB8:1::2
