Raid types, For details, see – QNAP TVS-472XT 4-Bay NAS Enclosure User Manual
Page 63
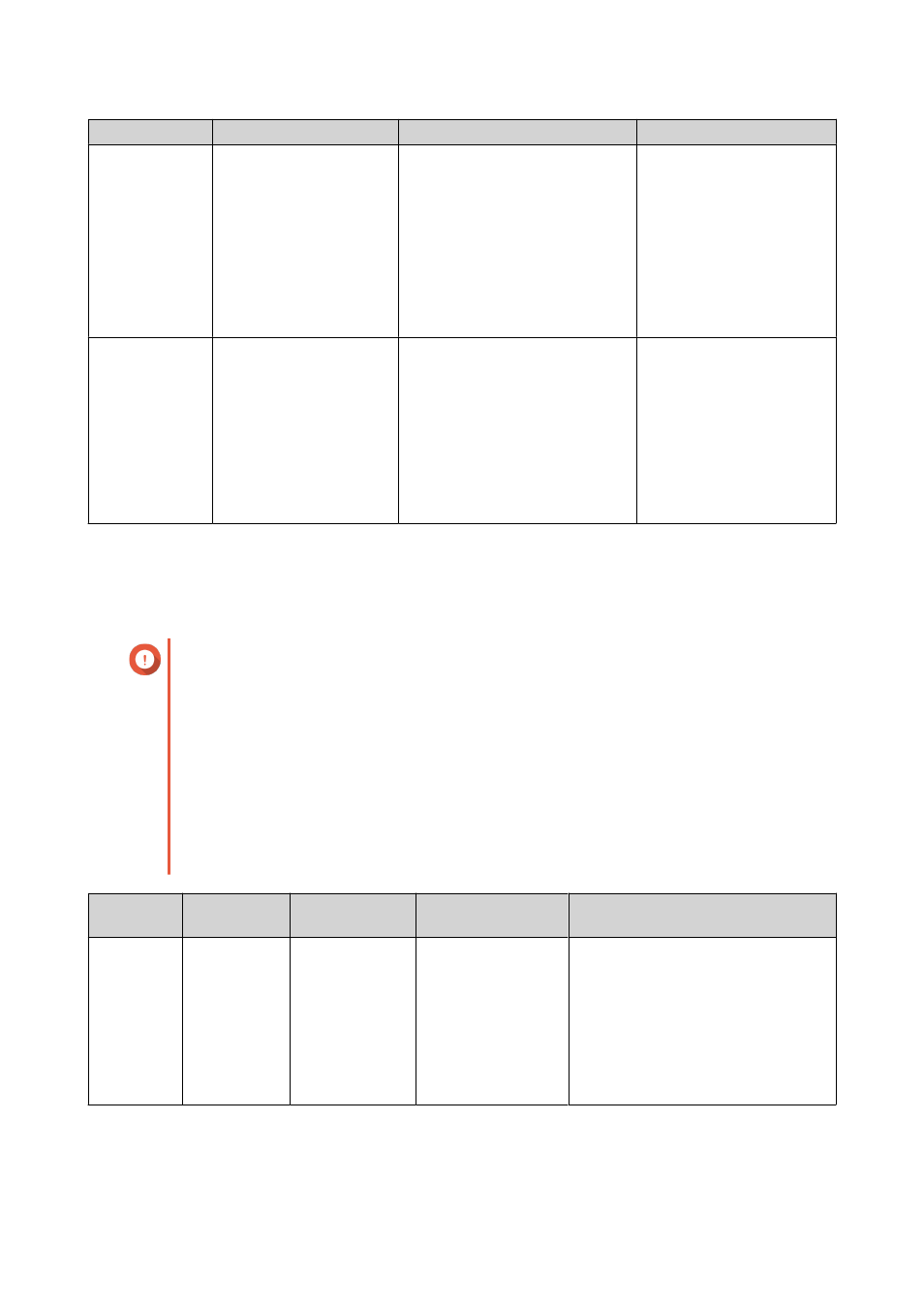
RAID Feature
Description
Advantages
Disadvantages
Striping
Data is split into smaller
pieces. Each piece is
stored on a different
disk in the RAID group.
QTS can then access that
data by reading from
or writing to multiple
disks simultaneously,
increasing read and write
speeds.
• Greater read/write speeds,
compared to a single disk
• Speeds can be increased
further by adding disks
If one disk in the RAID
group fails, and the RAID
group has no redundancy,
all data will be lost.
Redundancy
Each disk in the RAID
group can store the
following:
• Complete copy of the
stored data
• Metadata that allows
reconstruction of lost
data
• Disks can fail or be removed
from the RAID group without
any loss of data
• Users can access data
while failed disks are being
replaced
Total storage capacity of
the RAID group is reduced.
RAID Types
QTS supports several RAID types. Each type provides a different combination of performance and
redundancy.
Important
• If disks with different capacities are combined in one RAID group, all disks function
according to the capacity of the smallest disk. For example, if a RAID group contains
five 2 TB disks and one 1 TB disk, QTS detects six 1 TB disks.
QNAP recommends the following when mixing disks of different capacities.
a. Create a separate RAID group for each capacity.
b. Combine the RAID groups using storage pools.
• If different types of disk (HDD, SSD, SAS) are combined in one RAID group, the RAID
group will function according to the speed of the slowest disk.
RAID Type
Number of
Disks
Disk Failure
Tolerance
Capacity
Overview
Single
1
0
Total disk capacity
• Uses a single disk for storage.
• Provides no disk failure
protection or performance
benefits.
• Suitable for single disk
configurations that have a data
backup plan in place.
QTS 4.4.x User Guide
Storage & Snapshots
62
