IAI America SSEL User Manual
Page 203
181
Part 2 Programs
z PATH (Move along path)
Command, declaration
Extension condition
(LD, A, O, AB, OB)
Input condition
(I/O, flag)
Command,
declaration
Operand 1
Operand 2
Output
(Output, flag)
Optional Optional
PATH
Start
position
number
End
position
number
PE
[Function] Move continuously from the position specified in operand 1 to the position specified in
operand 2.
The output type in the output field can be set using an actuator-declaration command POTP.
Increasing the acceleration will make the passing points closer to the specified positions.
If invalid data is set for any position number between the start and end position numbers, that
position number will be skipped during continuous movement.
(Note 1)
Multi-dimensional movement can be performed using a PATH command.
In this case, input in operand 1 the point number of the next target, instead of the predicted
current position upon execution of the applicable command.
(Inputting a point number corresponding to the predicted current position will trigger movement
to the same point during continuous movement, thereby causing the speed to drop.)
(Note 2)
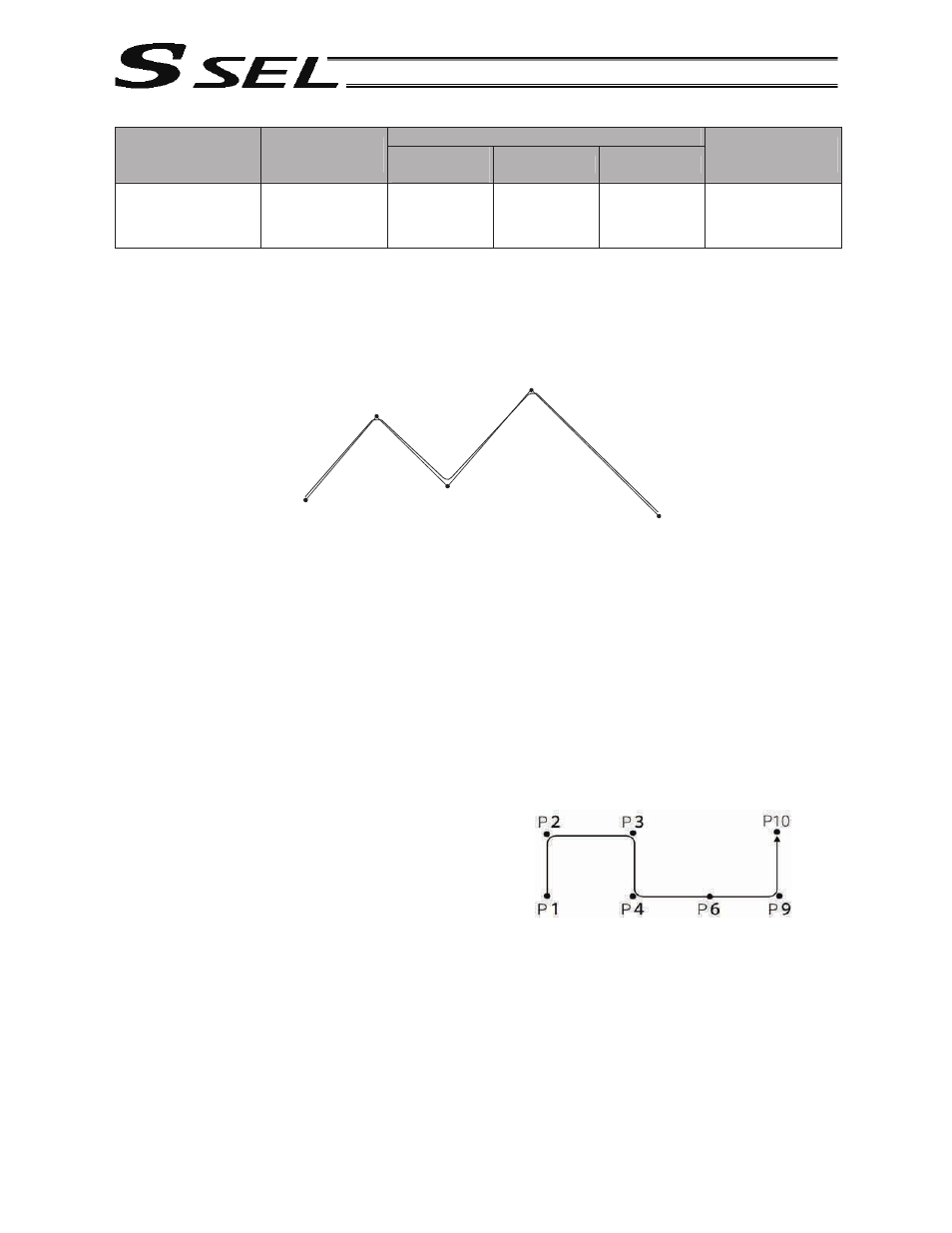
Continuous movement is possible even when the positions are discontinuous.
As shown in the example, specify the number corresponding to the discontinuous position for
both the start position number and end position number in the PATH command. In the
example, this position is No. 6.
[Example]
The actuator moves continuously in the sequence of position Nos. 1
o 2 o 3
o 4 o 6 o 9 o 10.
PATH
1
4
PATH
6
6 (discontinuous position)
PATH
9
10
[Example 1]
VEL
100
Set the speed to 100 mm/s.
PATH
100
120
Move continuously from position Nos. 100 to 120.
[Example 2]
VEL
100
Set the speed to 100 mm/s.
LET
1
50
Assign 50 to variable 1.
LET
2
100
Assign 100 to variable 2.
PATH
*1
*2
Move continuously along the positions from the content of
variable 1 (position No. 50) to the content of variable 2
(position No. 100).
Start position
Position origin
End position
