2 mass spectrometer – INFICON HAPSITE Smart Plus Chemical Identification System User Manual
Page 35
1 - 7
IP
N 07
4-
47
2-
P1
C
HAPSITE Smart Plus Operating Manual
In the Survey mode of operation, in which air samples are passed directly to the
mass spectrometer, the sample pump draws the air sample directly across the
membrane with the isolation valve in the open position.
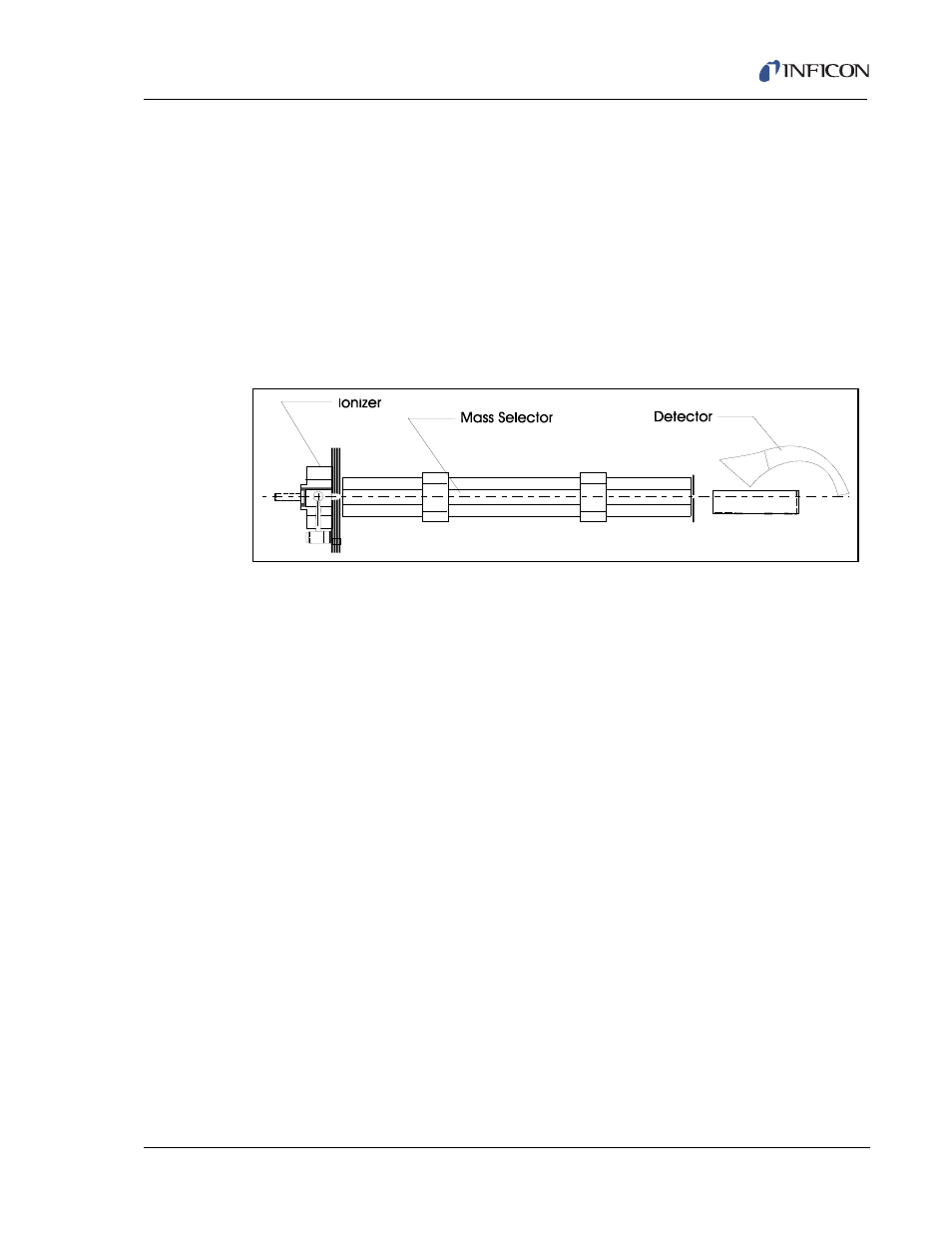
1.6.2 Mass Spectrometer
The Mass Spectrometer is comprised of three basic physical systems: the Ionizer,
the Mass Selector, and the Ion Detector. These are mounted together in a vacuum
manifold which also includes an inlet, two vacuum pumps, and a portion of the
Vacuum Interconnect Valve, as shown in
Figure 1-1 on page 1-4
.
Figure 1-3
is a
representation of the three sub-systems of the mass spectrometer.
Figure 1-3 Three Subsystems of the Mass Spectrometer
The inlet flow from the membrane isolation valve is brought directly to the Ionizer.
Within the ionizer, the component introduced from the inlet flow is subjected to a
bombardment of electrons which are boiled off the hot filament. Collisions with the
energetic electrons remove one electron from some of the gas molecules, leaving
them with a net positive charge. This process is termed ionization. Other gas
molecules are fractured into smaller molecules, some of which are also ionized.
The remaining stream of gas continues out the far side of the ion volume and is
pumped away by the vacuum pump system.
The ionized molecules, or ions, are driven from the ionizer toward the mass
selector by the different voltages on the ion volume and the focusing plates. As the
ions move through the holes in these plates, the ions are formed into a nearly
parallel beam of mixed ions of nearly the same energy.
The Mass Selector (or mass filter) is a quadrupole analyzer. The quadrupole
analyzer is comprised of four parallel rods, mounted with precise alignment and
spacing. Opposite rods are electrically connected together. The two pairs of rods
are connected to a radio frequency (RF) voltage 180
o
out of phase with each other.
In addition, the two pairs of rods have a direct current (DC) voltage applied to them;
positive on one pair, negative on the other.
The Ion Beam is directed down the center of the array of rods. At any specific
combination of RF and DC fields, some ions are light enough to oscillate
harmonically with the RF field. This oscillation causes them to pick up energy and
increase speed until the ions impact one of the rods and are neutralized. The DC
field acts upon the heavier ions resulting in their movement from the center towards
