Retrotec USACE User Manual
Page 336
G6 ENERGY & PROCESS ASSESSMENT PROTOCOL
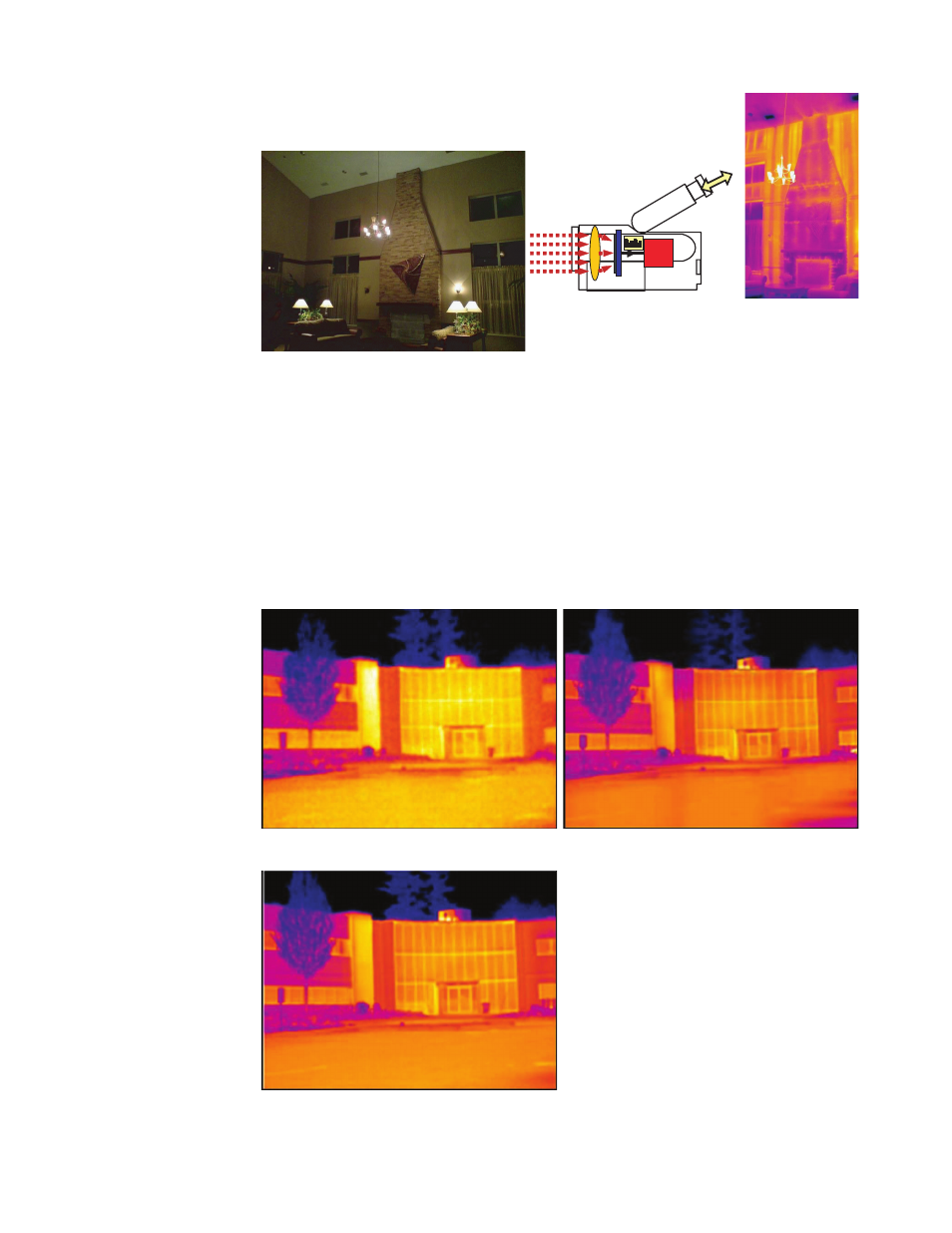
Figure G2. The IR camera converts invisible infrared radiation into a visible image.
A device that evaluates the IR radiation of an object is called an IR camera
(thermal scanner, thermal imager). It produces a thermograph (thermal image)
that refl ects both the temperature distribution and emissivity of the observed
object. The modern radiometric (temperature measuring) IR cameras are light
and small—as compact as standard camcorders (see Figure G2).
The thermal sensitivity is generally 0.1 °C (1.8 °F) or better, and the images
are saved on a memory card, along with (in some models) text or spoken com-
ments. The recorded thermal images can be postprocessed, tuned, and ana-
lyzed by specialized image-processing software. General considerations for
building application IR cameras are detector resolution (see Figure G3), ther-
160×120 pixel array 19,000 pixels
320×240 pixel array 76,800 pixels
Figure G3. Three IR thermographs showing
resolution differences. (Images from IR
Cameras and Building Insulation Performance,
Infrared Training Center, Jay Bowen, Robert
Madding, Paul Frisk.)
640×480 pixel array 307,200 pixels
