Snubber resistance (sgct device) – Rockwell Automation 7000 PowerFlex Medium Voltage AC Drive (B Frame) - ForGe Control (PanelView 550) User Manual
Page 270
270
Rockwell Automation Publication 7000-UM151E-EN-P - January 2013
Appendix C Snubber Testing
An SGCT when not gated on is an open circuit. A healthy device resistance value
should be close to the value of the sharing resistor, however due to parallel
resistances in the firing card, the resistance value will be slightly lower.
Example: The resistance across the anode-to-cathode of a 800 amp device may be
57 kΩ even though the sharing resistor is 80 kΩ.
You can detect SGCT failures by measuring a lower than normal resistance value;
one device in the converter may read 15 kΩ whereas the rest of the devices in the
converter measure close to 60 kΩ. This indicates a partially shorted device. A
fully shorted device will read closer to 0 Ω and is easily identified. If the SGCT is
out of tolerance, refer to
Component Definition and Maintenance on page 23
detailed instructions on how to replace the SGCT assembly.
Damage to a sharing resistor is detectable if the SGCT is replaced and the anode-
to-cathode resistance remains abnormal. If the resistor is found to be out of
tolerance, refer to
Component Definition and Maintenance on page 23
detailed instructions on how to replace the snubber/sharing resistor assembly.
Snubber Resistance (SGCT Device)
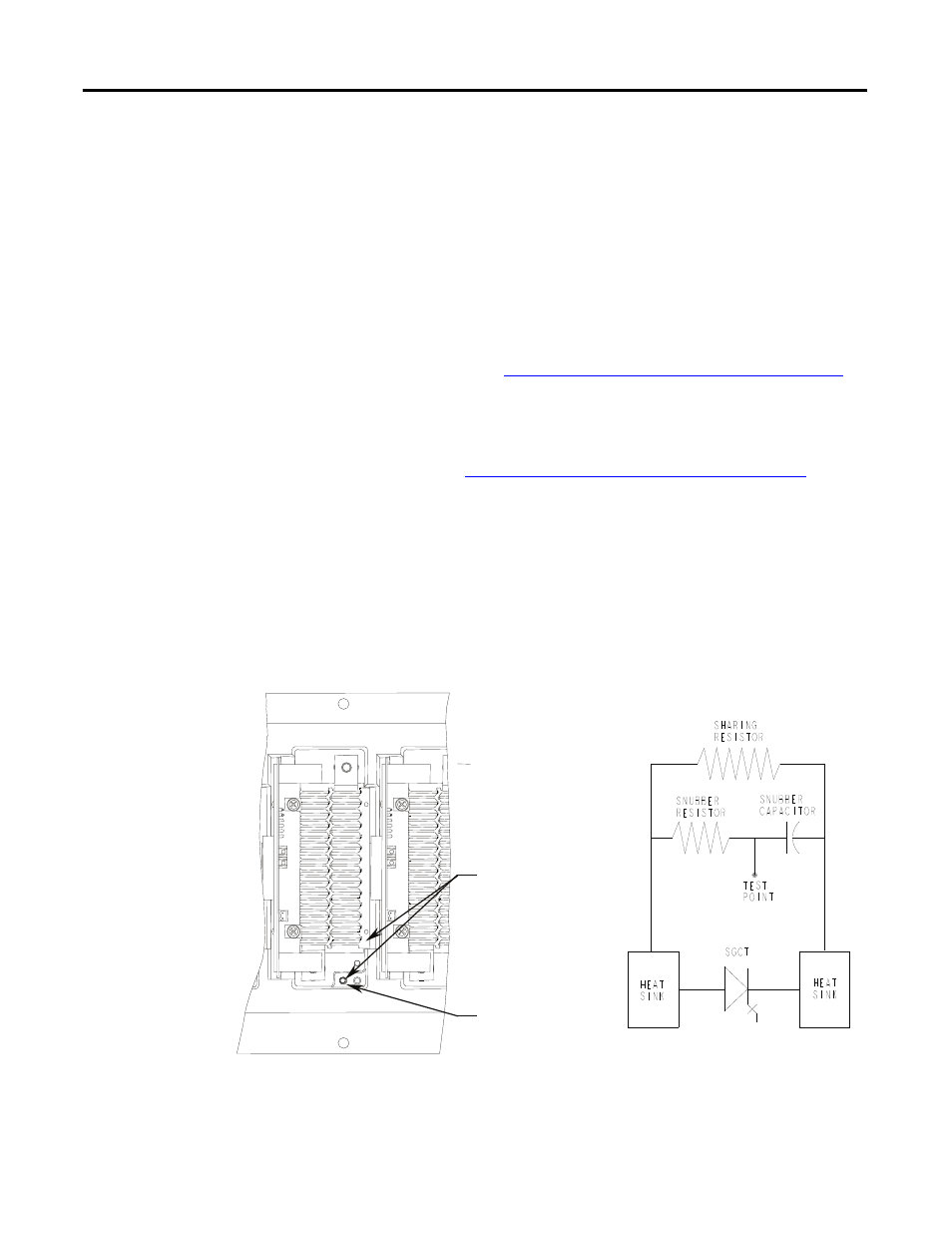
Access to the snubber resistor is not required to test the resistance. The snubber
circuit test point is located within the PowerCage under the heatsinks. For each
device, there is one test point. To verify the resistance, measure the resistance
between the test point and the heatsink above.
Figure 254 - Snubber resistor test
Measure resistance
between heatsink
and test point.
Snubber test point
