Apple Motion 5.1.1 User Manual
Page 930
Chapter 21
3D compositing
930
•
Viewpoint: Sets the camera origin at the center of projection.
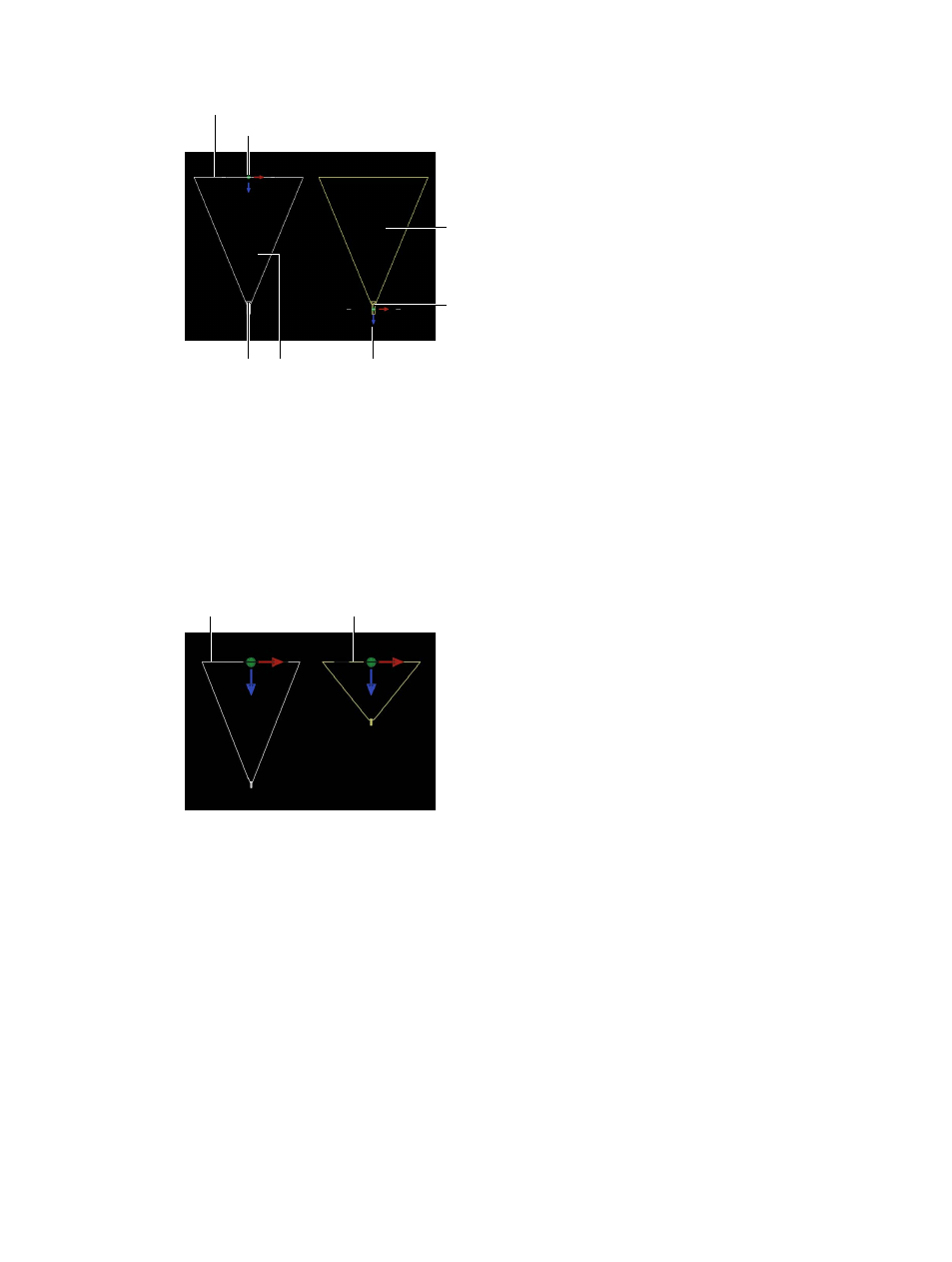
Framing
camera
Camera’s focal plane
Camera’s
angle of view
Viewpoint camera origin
Framing camera origin
Camera’s angle of view
Viewpoint
camera
Tip: The position of a Framing camera’s origin makes it useful for orbiting moves. Rotating the
camera causes it to orbit, whereas rotating a Viewpoint camera causes it to pivot—also known
as panning (horizontal) or tilting (vertical).
•
Angle of View: A slider that sets the angle of view of the camera, which is the number of
degrees in which the camera sees. Values range from 0 to 180 degrees.
Note: When you animate the Angle of View parameter on a Framing camera, the result is
an opposing dolly effect. An opposing dolly zooms in the opposite direction that the camera
moves. When you animate the Angle of View parameter on a Viewpoint camera, the result is a
regular camera zoom.
Angle of View = 45°
Angle of View = 80°
Framing camera
•
Near Plane: A slider that sets the distance where the camera begins to see objects. Objects
closer to the camera than this distance are not rendered from this camera’s point of view.
•
Far Plane: A slider that sets the distance where the camera ceases to see objects. Objects
further from the camera than this distance are not rendered from this camera’s point of view.
•
Near Fade: A slider that sets the softness factor for the near plane. The softness factor sets a
boundary range over which near objects fade in.
•
Far Fade: A slider that sets the softness factor for the far plane. The softness factor sets a
boundary range over which far objects fade out.
67% resize factor
