4 hitless protection switching (hps), Hitless protection switching (hps), Figure 9-25. hps block diagram – Rainbow Electronics DS26519 User Manual
Page 101
DS26519 16-Port T1/E1/J1 Transceiver
101 of 310
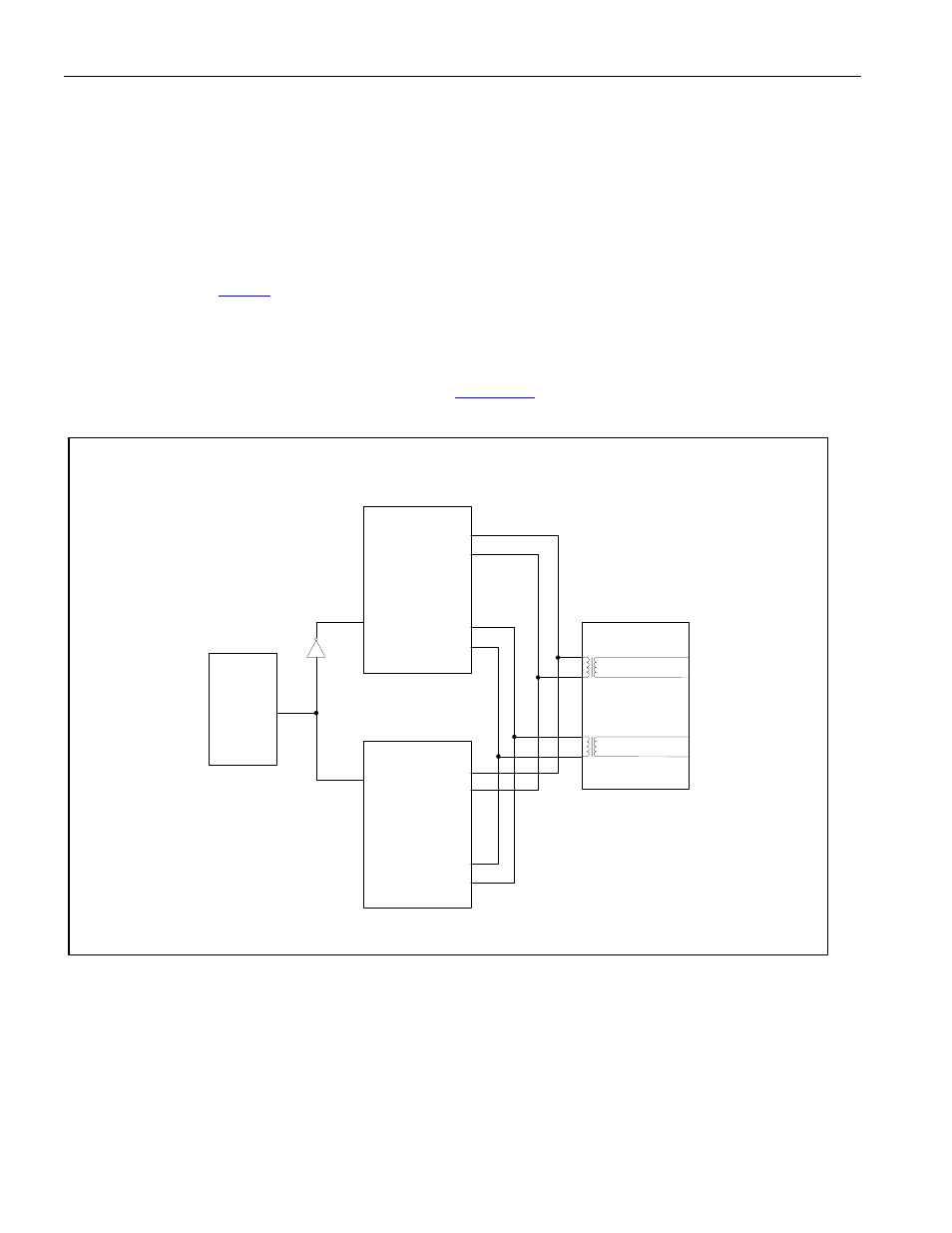
9.12.4 Hitless Protection Switching (HPS)
Many current redundancy protection implementations use mechanical relays to switch between primary and
backup boards. The switching time in relays is typically in the milliseconds, making T1/E1 HPS impossible. The
switching event will likely cause frame-synchronization loss in any equipment downstream, affecting the quality of
service. The same is also true for tri-stating mechanisms that use software or inactive clocks for the triggering of
HPS.
The DS26519 LIUs feature fast tristatable outputs for TTIPn and TRINGn and fast disabling of internal impedance
matching for RTIPn and RRINGn within one-bit period. The TXENABLE pin is used for hitless protection circuits in
combination with the
.RHPM bit. When low, the TXENABLE pin tri-states all 16 transmitters, providing a
high-impedance state on TTIPn and TRINGn. If the RHPM bit is set, the TXENABLE pin, when low, will also
disable the internal termination on RTIPn and RRINGn on a per-port basis, providing a high impedance to the
receive line.
This is a very useful function in that control can be done through a hardware pin, allowing a quick switch to the
backup system for both the receiver and the transmitter.
shows a typical HPS application.
Figure 9-25. HPS Block Diagram
PRIMARY
BOARD
BACKUP
BOARD
SWITCHING
CONTROL
TXENABLE
TRING
RTIP
TTIP
RRING
TRING
RTIP
TTIP
RRING
LINE
INTERFACE
CARD
RX
TX
TXENABLE
