Iv-2 a/d converter, Features and structure of a/d converter – Epson S1C33210 User Manual
Page 433
IV ANALOG BLOCK: A/D CONVERTER
S1C33210 FUNCTION PART
EPSON
B-IV-2-1
IV-2 A/D CONVERTER
Features and Structure of A/D Converter
The Analog Block contains an A/D converter with the following features:
• Conversion method:
Successive comparison
• Resolution:
10 bits
• Input channels:
Maximum of 4
• Conversion time:
Maximum of 10
µ
s (when a 2-MHz input clock is selected)
• Conversion range:
Between V
SS
and AV
DD
• Two conversion modes can be selected:
Normal mode:
Conversion is completed in one operation.
Continuous mode: Conversion is continuous and terminated through software control.
Continuous conversion of multiple channels can be performed in each mode.
• Four types of A/D-conversion start triggers can be selected:
Triggered by the external pin (#ADTRG)
Triggered by the compare match B of the 16-bit programmable timer 0
Triggered by the underflow of the 8-bit programmable timer 0
Triggered by the software
• A/D conversion results can be read out from a 10-bit data register.
• An interrupt is generated upon completion of A/D conversion.
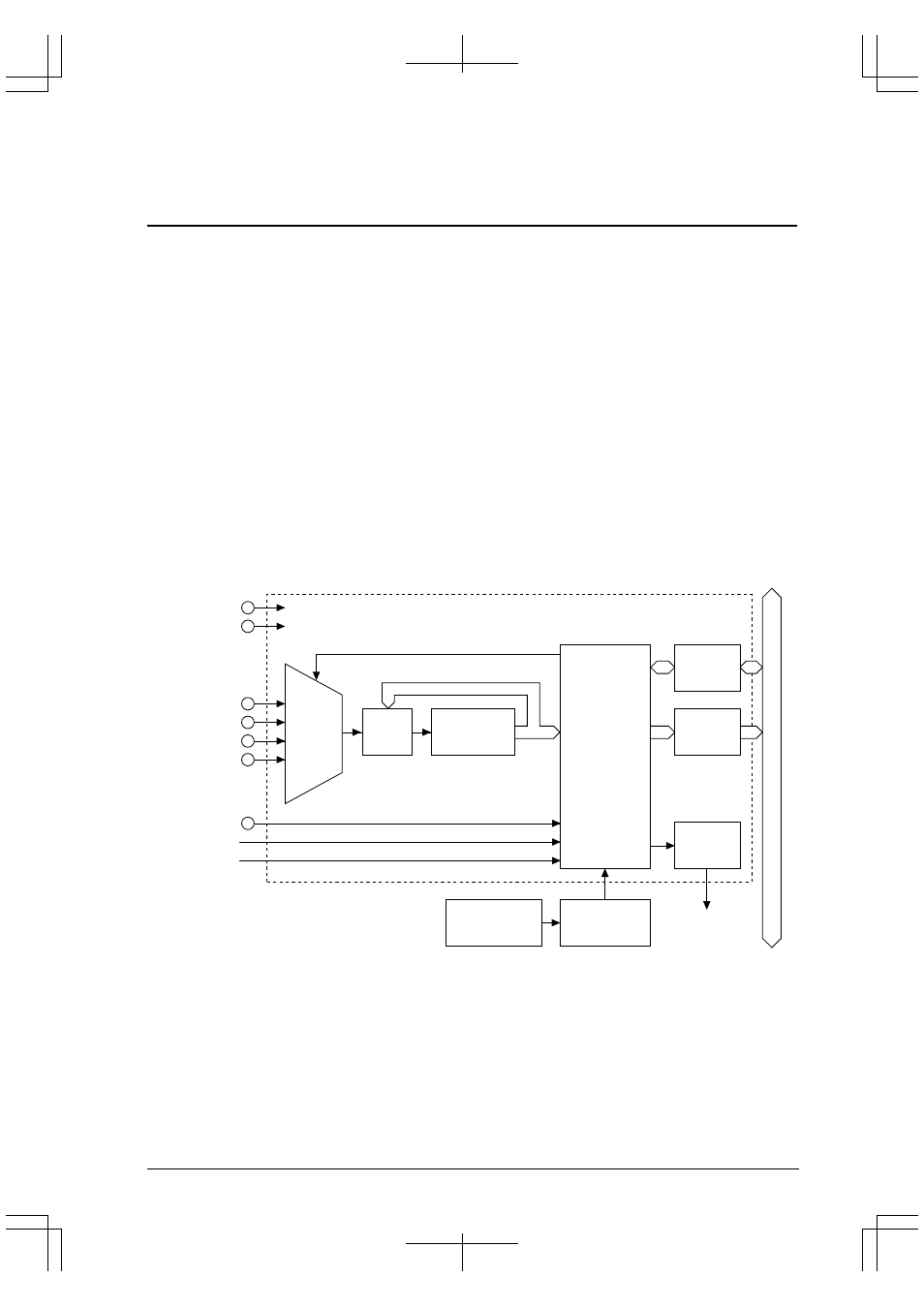
Figure 2.1 shows the structure of the A/D converter.
Internal data bus
AV
DD
V
SS
Analog
input
decoder
Control circuit
AD0
AD1
AD2
AD3
#ADTRG
8-bit timer 0
16-bit timer 0
Clock
generator
Prescaler
Interrupt request
Analog
block
Successive
approximation
block
Data
register
Interrupt
control
circuit
Control
registers
Figure 2.1 Structure of A/D Converter
