Ii-5 itc (interrupt controller), Outline of interrupt functions, Maskable interrupts – Epson S1C33210 User Manual
Page 199
II CORE BLOCK: ITC (Interrupt Controller)
S1C33210 FUNCTION PART
EPSON
B-II-5-1
II-5 ITC (Interrupt Controller)
The C33 Core Block contains an interrupt controller, making it possible to control all interrupts generated by the
internal peripheral circuits. This section explains the functions of this interrupt controller centering around the
method for controlling maskable interrupts. For details about the various factors and conditions under which
interrupts are generated, refer to the description of each peripheral circuit in this manual.
Outline of Interrupt Functions
Maskable Interrupts
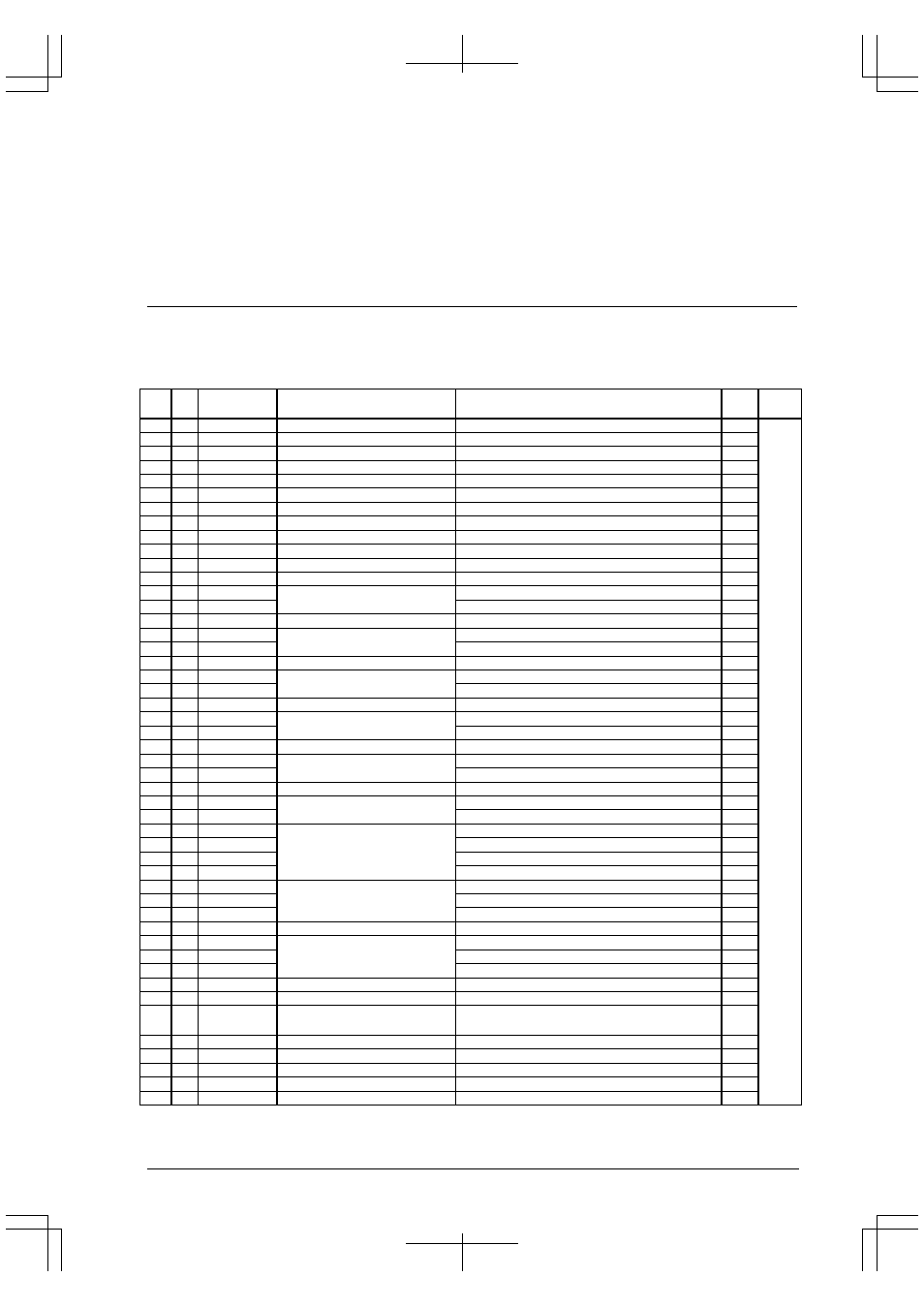
The ITC can handle 39 kinds of maskable interrupts as shown in the table below.
Table 5.1 List of Maskable Interrupts
No.
HEX
No.
Vector number
(Hex address)
Interrupt system
(Peripheral circuit)
Interrupt factor
IDMA
Ch.
Priority
1
10 16(Base+40)
Port input interrupt 0
Edge (rising or falling) or level (High or Low)
1
High
2
11 17(Base+44)
Port input interrupt 1
Edge (rising or falling) or level (High or Low)
2
↑
3
12 18(Base+48)
Port input interrupt 2
Edge (rising or falling) or level (High or Low)
3
4
13 19(Base+4C)
Port input interrupt 3
Edge (rising or falling) or level (High or Low)
4
5
14 20(Base+50)
Key input interrupt 0
Rising or falling edge
–
6
15 21(Base+54)
Key input interrupt 1
Rising or falling edge
–
7
16 22(Base+58)
High-speed DMA Ch.0
High-speed DMA Ch.0, end of transfer
5
8
17 23(Base+5C)
High-speed DMA Ch.1
High-speed DMA Ch.1, end of transfer
6
9
18 24(Base+60)
High-speed DMA Ch.2
High-speed DMA Ch.2, end of transfer
–
10
19 25(Base+64)
High-speed DMA Ch.3
High-speed DMA Ch.3, end of transfer
–
11
1A 26(Base+68)
IDMA
Intelligent DMA, end of transfer
–
–
27–29
reserved
–
–
12
1E 30(Base+78)
16-bit programmable timer 0
Timer 0 comparison B
7
13
1F 31(Base+7C)
Timer 0 comparison A
8
–
32–33
reserved
–
–
14
22 34(Base+88)
16-bit programmable timer 1
Timer 1 comparison B
9
15
23 35(Base+8C)
Timer 1 comparison A
10
–
36–37
reserved
–
–
16
26 38(Base+98)
16-bit programmable timer 2
Timer 2 comparison B
11
17
27 39(Base+9C)
Timer 2 comparison A
12
–
40–41
reserved
–
–
18
2A 42(Base+A8)
16-bit programmable timer 3
Timer 3 comparison B
13
19
2B 43(Base+AC)
Timer 3 comparison A
14
–
44–45
reserved
–
–
20
2E 46(Base+B8)
16-bit programmable timer 4
Timer 4 comparison B
15
21
2F 47(Base+BC)
Timer 4 comparison A
16
–
48–49
reserved
–
–
22
32 50(Base+C8)
16-bit programmable timer 5
Timer 5 comparison B
17
23
33 51(Base+CC)
Timer 5 comparison A
18
24
34 52(Base+D0)
8-bit programmable timer
Timer 0 underflow
19
25
35 53(Base+D4)
Timer 1 underflow
20
26
36 54(Base+D8)
Timer 2 underflow
21
27
37 55(Base+DC)
Timer 3 underflow
22
28
38 56(Base+E0)
Serial interface Ch.0
Receive error
–
29
39 57(Base+E4)
Receive buffer full
23
30
3A 58(Base+E8)
Transmit buffer empty
24
–
59
reserved
–
–
31
3C 60(Base+F0)
Serial interface Ch.1
Receive error
–
32
3D 61(Base+F4)
Receive buffer full
25
33
3E 62(Base+F8)
Transmit buffer empty
26
–
63
reserved
–
–
34
40 64(Base+100)
A/D converter
A/D converter, end of conversion
27
35
41 65(Base+104)
Clock timer
Falling edge of 32 Hz, 8 Hz, 2 Hz or 1 Hz signal
1-minute, 1-hour or specified time count up
–
–
66–67
reserved
–
–
36
44 68(Base+110)
Port input interrupt 4
Edge (rising or falling) or level (High or Low)
28
37
45 69(Base+114)
Port input interrupt 5
Edge (rising or falling) or level (High or Low)
29
38
46 70(Base+118)
Port input interrupt 6
Edge (rising or falling) or level (High or Low)
30
↓
39
47 71(Base+11C) Port input interrupt 7
Edge (rising or falling) or level (High or Low)
31
Low
