Epson S1C33210 User Manual
Page 324
III PERIPHERAL BLOCK: SERIAL INTERFACE
B-III-8-8
EPSON
S1C33210 FUNCTION PART
• Clock-synchronized master mode
The timing at which the device starts transmitting in the master mode is as follows:
When #SRDY is on a low level while TDBEx = "0" (the transmit-data register contains data written to it) or
when TDBEx is set to "0" (data has been written to the transmit-data register) while #SRDY is on a low level.
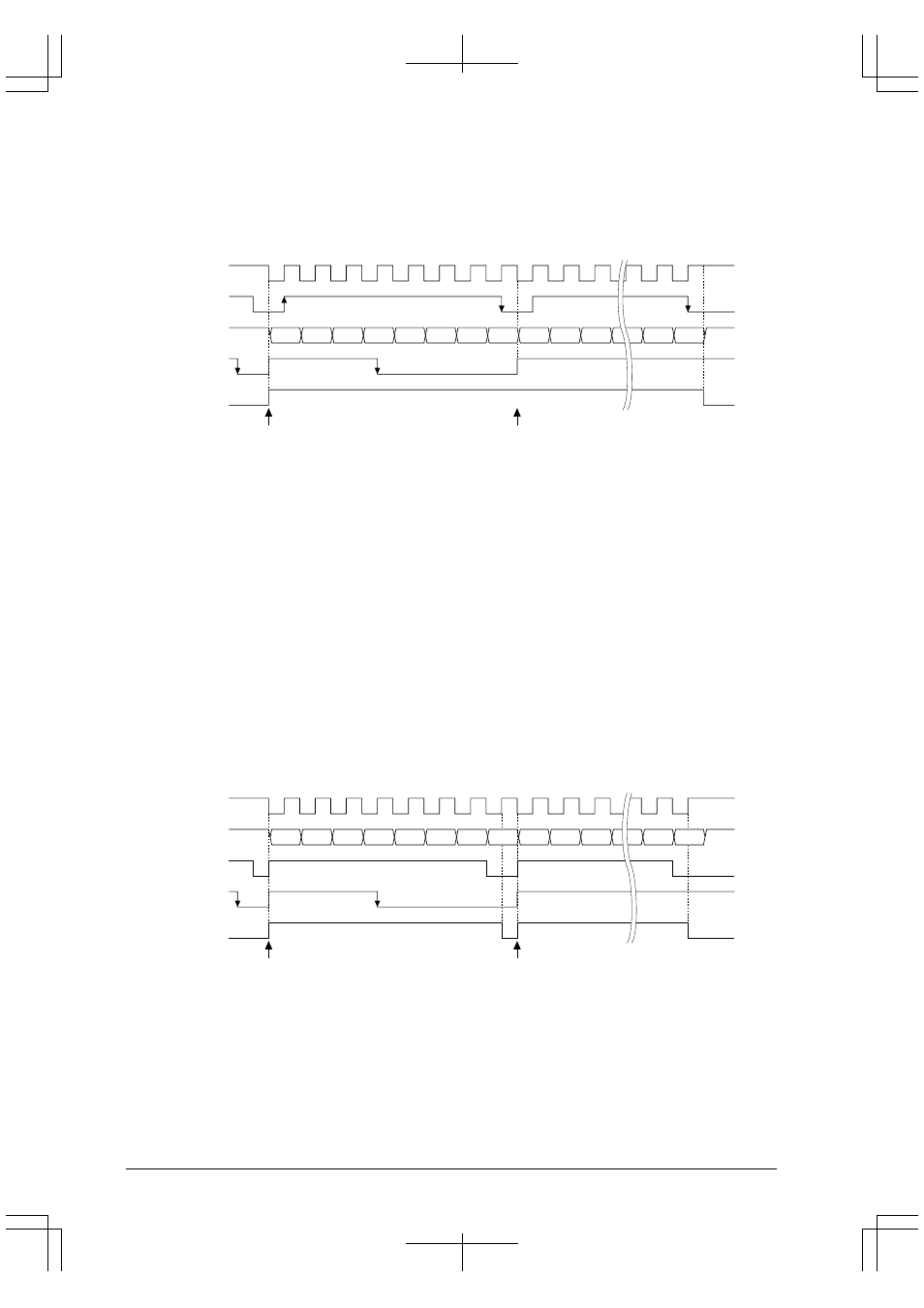
Figure 8.4 shows a transmit timing chart in the clock-synchronized master mode.
#SCLKx
#SRDYx
SOUTx
TDBEx
TENDx
Transmit-buffer empty
interrupt request
Transmit-buffer empty
interrupt request
A
B
Slave device receives the LSB.
Slave device receives the MSB.
C
D
First data is written.
Next data is written.
A
B
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
D6
D7
D0
D1
D2
B
C
D
Figure 8.4 Transmit Timing Chart in Clock-Synchronized Master Mode
1. If the #SRDYx signal from the slave is on a high level, the master waits until it is on a low level (ready to
receive).
2. If #SRDYx is on a low level, the synchronizing clock input to the serial interface begins. The synchronizing
clock is also output from the #SCLKx pin to the slave device.
3. The content of the data register is transferred to the shift register synchronously with the first falling edge of
the clock. At the same time, the LSB of the data transferred to the shift register is output from the SOUTx
pin.
4. The data in the shift register is shifted 1 bit by the next falling edge of the clock, and the bit following the
LSB is output from SOUTx. This operation is repeated until all 8 bits of data are transmitted.
The slave device must take in each bit synchronously with the rising edges of the synchronizing clock.
• Clock-synchronized slave mode
Figure 8.5 shows a transmit timing chart in the clock-synchronized slave mode.
Transmit-buffer empty
interrupt request
Transmit-buffer empty
interrupt request
A
B
First data is written.
Next data is written.
#SCLKx
SOUTx
#SRDYx
TDBEx
TENDx
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
D6
D7
D0
D1
D2
A
B
Figure 8.5 Transmit Timing Chart in Clock-Synchronized Slave Mode
1. After setting the #SRDYx signal to a low level (ready to transmit), the slave waits for clock input from the
master.
2. When the synchronizing clock is input from the #SCLKx pin, the content of the data register is transferred to
the shift register synchronously with the first falling edge of the clock. At the same time, the LSB of the data
transferred to the shift register is output from the SOUTx pin.
