Adobe Premiere Pro CS6 User Manual
Page 46
For an overview of the Premiere Pro workflow,
.
To get started editing quickly with Premiere Pro,
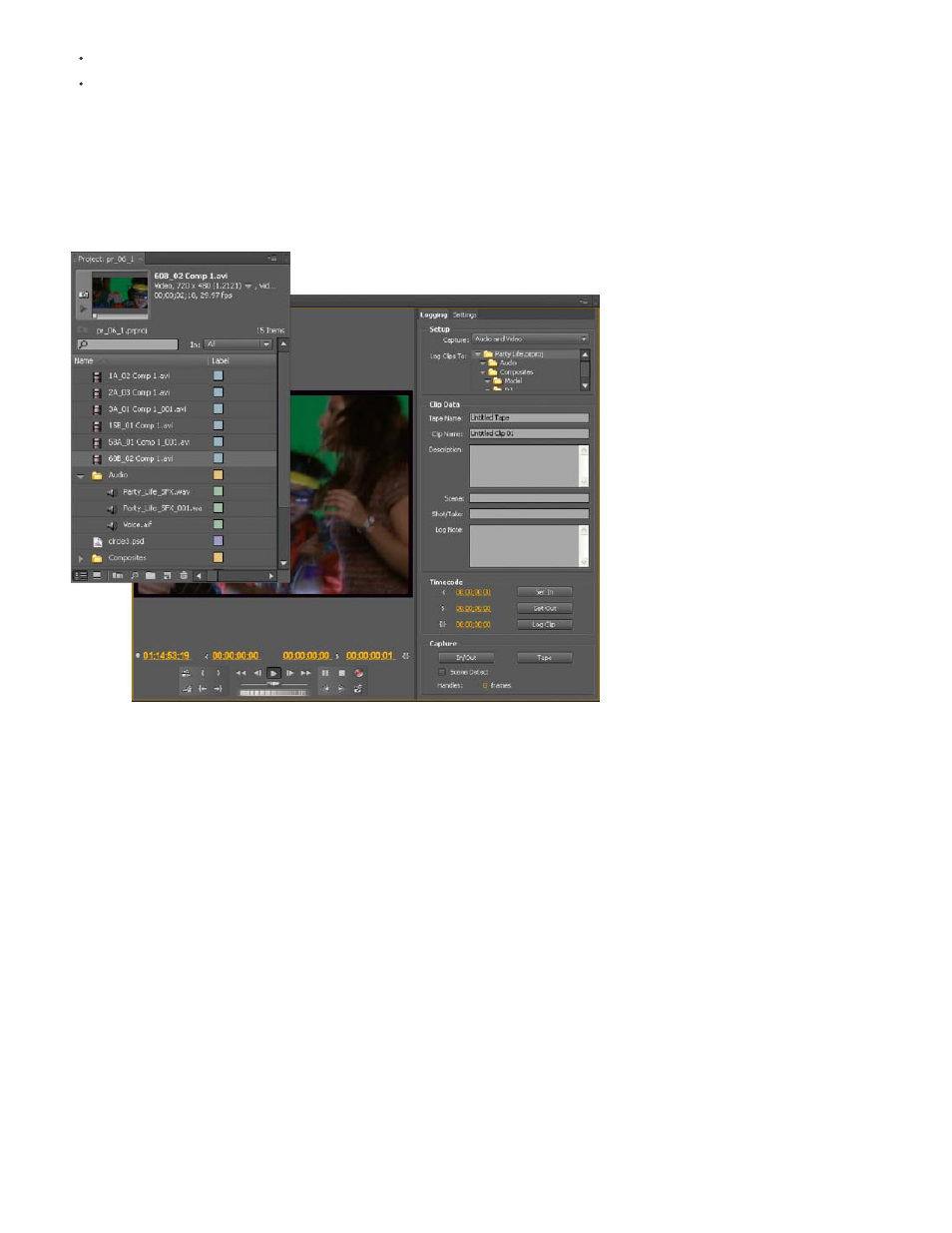
2. Capture and import video and audio
For file-based assets, using the Media Browser you can import files from computer sources in any of the leading media formats. Each file you
capture or import automatically becomes a clip in the Project panel.
Alternatively, using the Capture panel, capture footage directly from a camcorder or VTR. With the proper hardware, you can digitize and capture
other formats, from VHS to HDTV.
Optionally, if you import an Adobe OnLocation project into Premiere Pro, metadata from Adobe OnLocation makes it easy to create a preliminary
rough cut. Use Speech Search to synchronize the script to footage, and then edit based on the dialogue transcript.
Project panel and Capture panel
You can also import various digital media, including video, audio, and still images. Premiere Pro also imports Adobe® Illustrator® artwork or
Photoshop® layered files, and it translates After Effects® projects for a seamless, integrated workflow. You can create synthetic media, such as
standard color bars, color backgrounds, and a countdown. (See About capturing and digitizing.)
You can also use Adobe® Bridge to organize and find your media files. Then use the Place command in Adobe Bridge to place the files directly
into Premiere Pro.
In the Project panel, you can label, categorize, and group footage into bins to keep a complex project organized. You can open multiple bins
simultaneously, each in its own panel, or you can nest bins, one inside another. Using the Project panel Icon view, you can arrange clips in
storyboard fashion to visualize or quickly assemble a sequence.
Note: Before capturing or importing audio, ensure that Preferences>Audio>Default Track Format is set to match the desired channel format.
3. Assemble and refine a sequence
Using the Source Monitor, you can view clips, set edit points, and mark other important frames before adding clips to a sequence. For
convenience, you can break a master clip into any number of subclips, each with its own In and Out points. You can view audio as a detailed
waveform and edit it with sample-based precision. (See Source Monitor and Program Monitor overview.)
42
