Adjust effects – Adobe Premiere Pro CS6 User Manual
Page 392
Wipe transitions
Barn Doors Wipe transition
Gradient Wipe transition
Inset Wipe transition
Wipe transition
Transition effects
Adjust effects
Auto Color, Auto Contrast, and Auto Levels effects
The Auto Color, Auto Contrast, and Auto Levels effects make quick global adjustments to a clip. Auto Color adjusts contrast and color by
neutralizing the midtones and clipping the white and black pixels. Auto Contrast adjusts the overall contrast and mixture of colors, without
introducing or removing color casts. Auto Levels automatically corrects the highlights and shadows. Because Auto Levels adjusts each color
channel individually, it may remove or introduce color casts.
Each effect has one or more of the following settings:
Temporal Smoothing The range of adjacent frames, in seconds, analyzed to determine the amount of correction needed for each frame, relative
to its surrounding frames. If Temporal Smoothing is 0, each frame is analyzed independently, without regard for surrounding frames. Temporal
Smoothing can result in smoother looking corrections over time.
Scene Detect If this option is selected, frames beyond a scene change are ignored when the effect analyzes surrounding frames for temporal
smoothing.
Snap Neutral Midtones (Auto Color only) Identifies an average nearly neutral color in the frame and then adjusts the gamma values to make
the color neutral.
Black Clip, White Clip How much of the shadows and highlights are clipped to the new extreme shadow and highlight colors in the image. Be
careful of setting the clipping values too large, as doing so reduces detail in the shadows or highlights. A value between 0.0% and 1% is
recommended. By default, shadow and highlight pixels are clipped by 0.1%—that is, the first 0.1% of either extreme is ignored when the darkest
and lightest pixels in the image are identified; those pixels are then mapped to output black and output white. This clipping ensures that input black
and input white values are based on representative rather than extreme pixel values.
Blend With Original Determines the effect’s transparency. The result of the effect is blended with the original image, with the effect result
composited on top. The higher you set this value, the less the effect affects the clip. For example, if you set this value to 100%, the effect has no
visible result on the clip; if you set this value to 0%, the original image doesn’t show through.
Convolution Kernel effect
The Convolution Kernel effect changes the brightness values of each pixel in the clip according to a mathematical operation known as a
convolution. A convolution overlays a matrix of numbers onto a matrix of pixels, multiplies each underlying pixel's value by the number that
overlays it, and replaces the central pixel's value with the sum of all of these multiplications. This is performed for each pixel in the image.
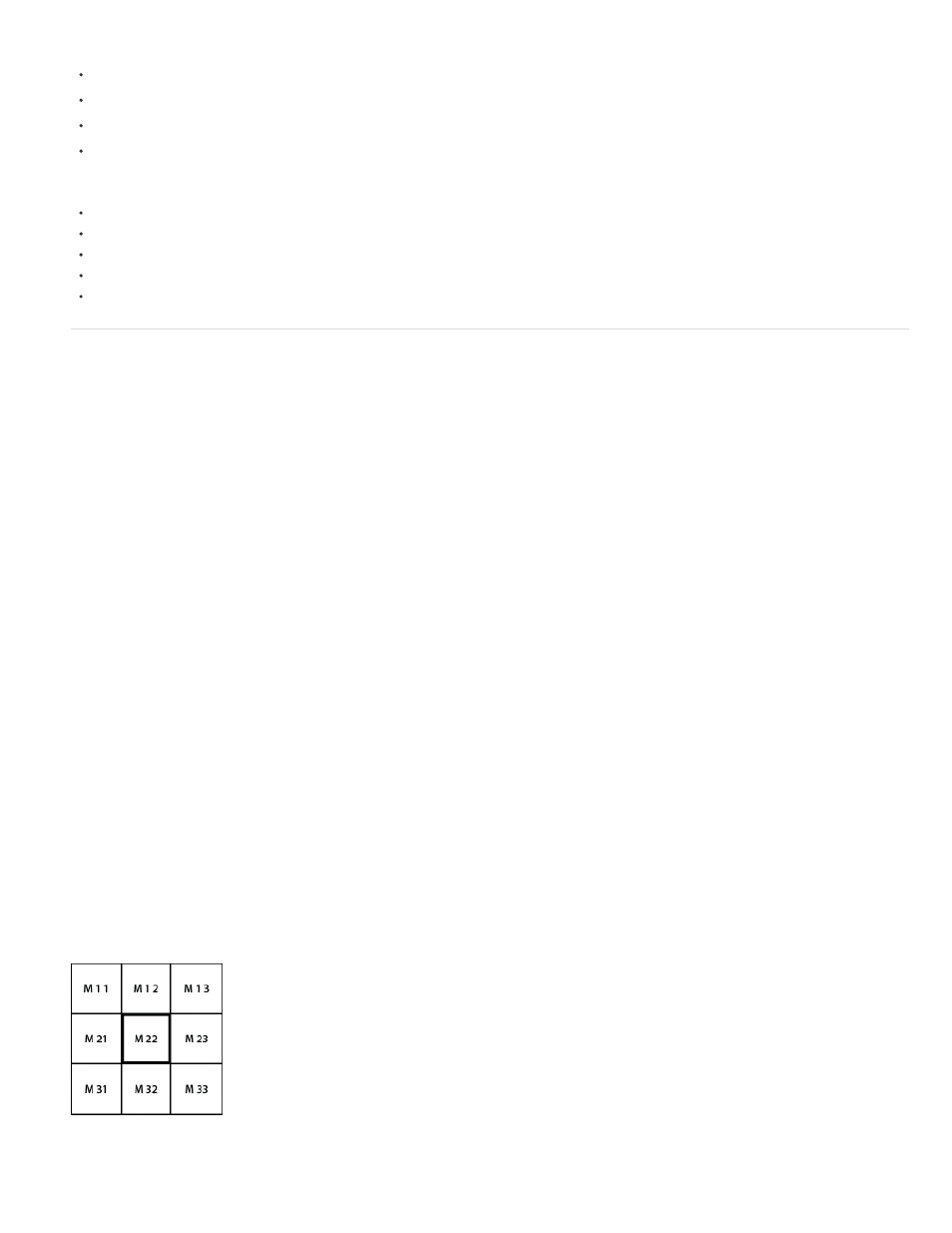
The Convolution Kernel Settings include a set of controls that represent cells in a 3x3 grid of pixel brightness multipliers. Labels on the controls,
which begin with the letter “M,” indicate their position in the matrix. The M11 control, for example, affects the cell in the first row and first column of
the grid; the M32 control affects the cell in the third row and second column. The pixel being evaluated falls in the center of the grid, at the M22
location. Use this effect for fine control over the properties of various emboss, blur, and sharpen effects. For a given effect, it is easier to apply one
of the Convolution Kernel presets and to modify it, than to create the effect from scratch using the Convolution Kernel effect itself.
Convolution Kernel pixel grid, showing the position of each control in the matrix
388
