Integrator time, Integrator time -31, Figure 5.12 sh – Rockwell Automation 2092-DAx Ultra1500 User Manual User Manual
Page 111
Publication 2092-UM001D-EN-P — July 2005
Ultra1500 Application Examples
5-31
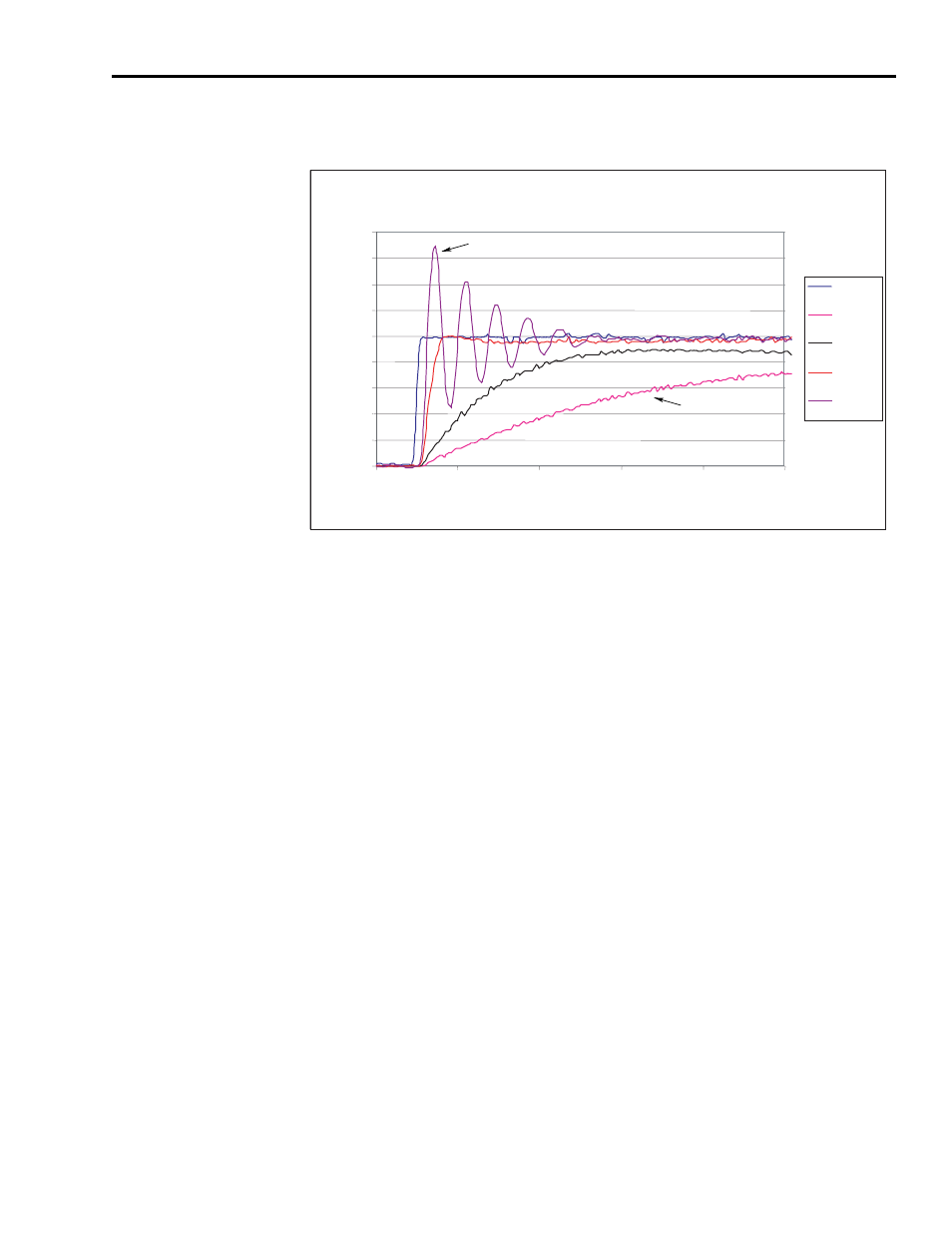
Figure 5.12
Velocity Regulator Step Response with Varying P Gain.
Integrator Time
The Integrator Time parameter sets the integral response of the velocity
regulator. It can be in the range 0–60,000. This parameter setting has an
inverse relationship to amount of Integral Gain in the regulator. Smaller values
result in more Integral Gain and less stability. Larger values result in less
Integral Gain and more stability. However, a value of zero results in zero
Integral Gain, effectively disabling the velocity loop integrator.
Integration in the regulator forces the feedback velocity to track the command
velocity when the velocity command is constant (so called “steady state” or
“zero frequency”), and the load in not changing. Excessive regulator
integration can result in oscillatory responses and system instability.
Figure 5.13 shows the effect of varying the Integrator Time parameter to the
velocity step response with the P Gain set to 30 and the D Gain set to zero.
The response becomes more oscillatory as the Integral Time is decreased, (and
the Integral Gain is effectively increased).
Velocity
Command
P = 20
P = 40
P = 200
P = 500
P Gain = 20
P Gain = 500
Time (msec)
0
5
10
15
20
25
0
50
100
150
200
450
400
350
300
250
V
elocity (RPM)
