6 – transmitting data, Transmitting data, Transmitting byte receiving byte – Maxim Integrated DS4830 Optical Microcontroller User Manual
Page 91: Receiving slave address
DS4830 User’s Guide
91
Transmitting
Byte
Receiving
Byte
Y
Receive
Addr[6:0] + R/W
Match
I2CSLA_S[7:1]
?
Transmit
I2CACK
I2CBUSY=0
N
I2CAMI=1
Set
I2CMODE
According to R/W
Detect START
I2CSRI=1
I2CBUS=1
I2CBUSY=1
I2CNACKI =
ACKNOWLEDGE
Transmit Shift
Register Byte,
MSB First
N
Y
I2CBUSY=1
8 Bits
Transmit
?
I2CTXI=1
I2CBUSY=0
Write to
I2CBUF_S
Receive a Bit into
Shift Register
,
MSB first
N
Y
I2CBUSY=1
8 Bits
Received
?
Load Shift
Register into
I2CBUF_S
I2CRXI=1
Send
I2CACK
Y
N
I2CROI=1
Receiver
Full
?
Detect 1
st
SCL
Rising Edge
I2CBUSY=0
Receiving Slave
Address
RECEIVE
ACKNOWLEDGE
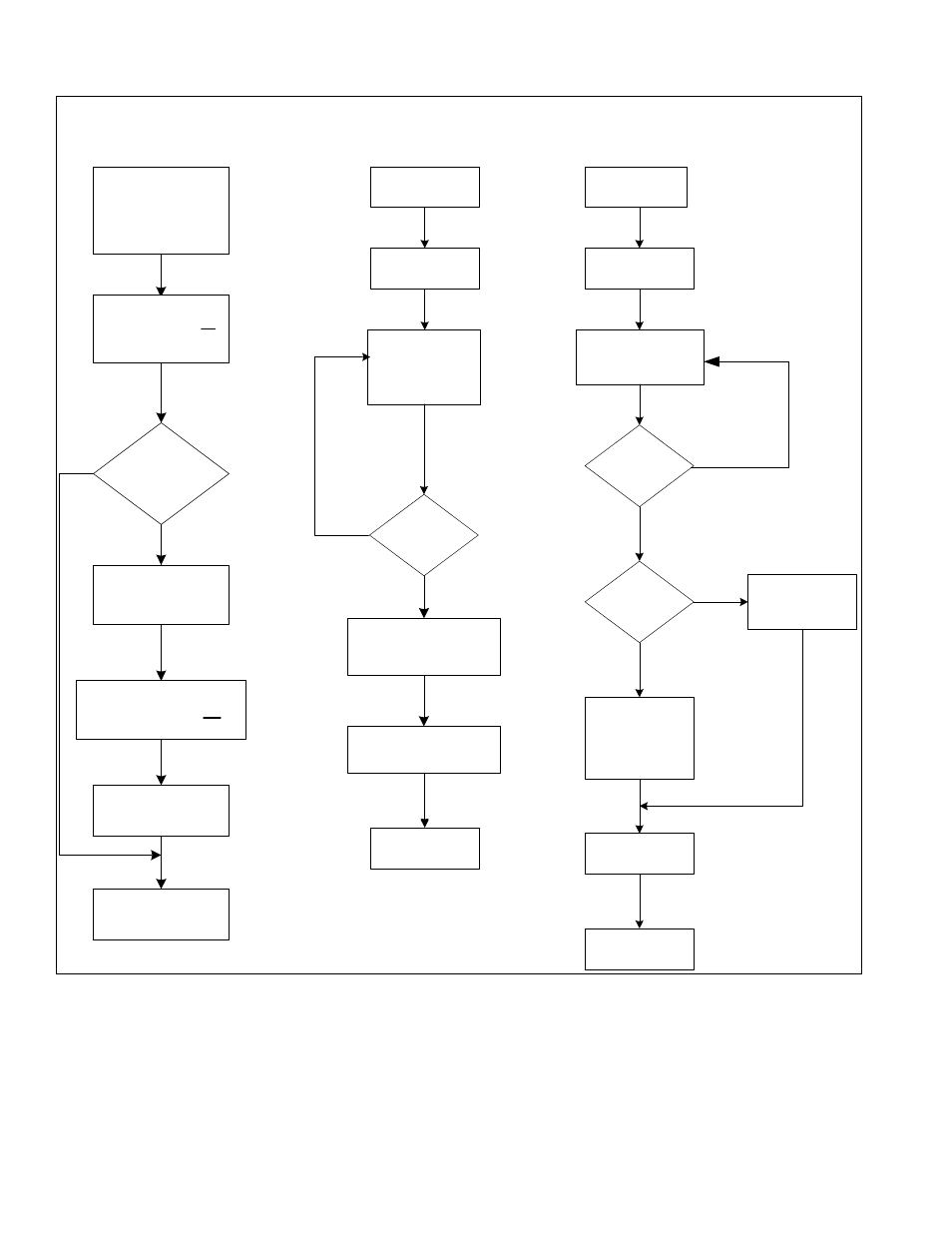
Figure 11-2: Slave I
2
C Data Flow
11.1.6
– Transmitting Data
The DS4830 I
2
C Slave Controller enters into data transmission mode after receiving a matching slave address with the
R/W bit set to a 1. The steps of data transmission are shown in Figure 11-2. Data transmission is started by software
loading a byte of data into the I2CBUF_S register. Loading I2CBUF_S causes the I2CBUSY bit in I2CST_S to be set.
Once set, a write to I2CBUF_S will be ignored. The first bit of data (most significant bit) will be shifted to SDA when SCL
is low. Each of the next seven bits will then be shifted following high to low transitions of SCL.
