Managing certificates and private keys, 7 managing certificates and private keys – B&B Electronics WLNN-AN(ER,SE,SP.EK)-DP551 - Manual User Manual
Page 65
Airborne Enterprise CLI Reference Manual
65
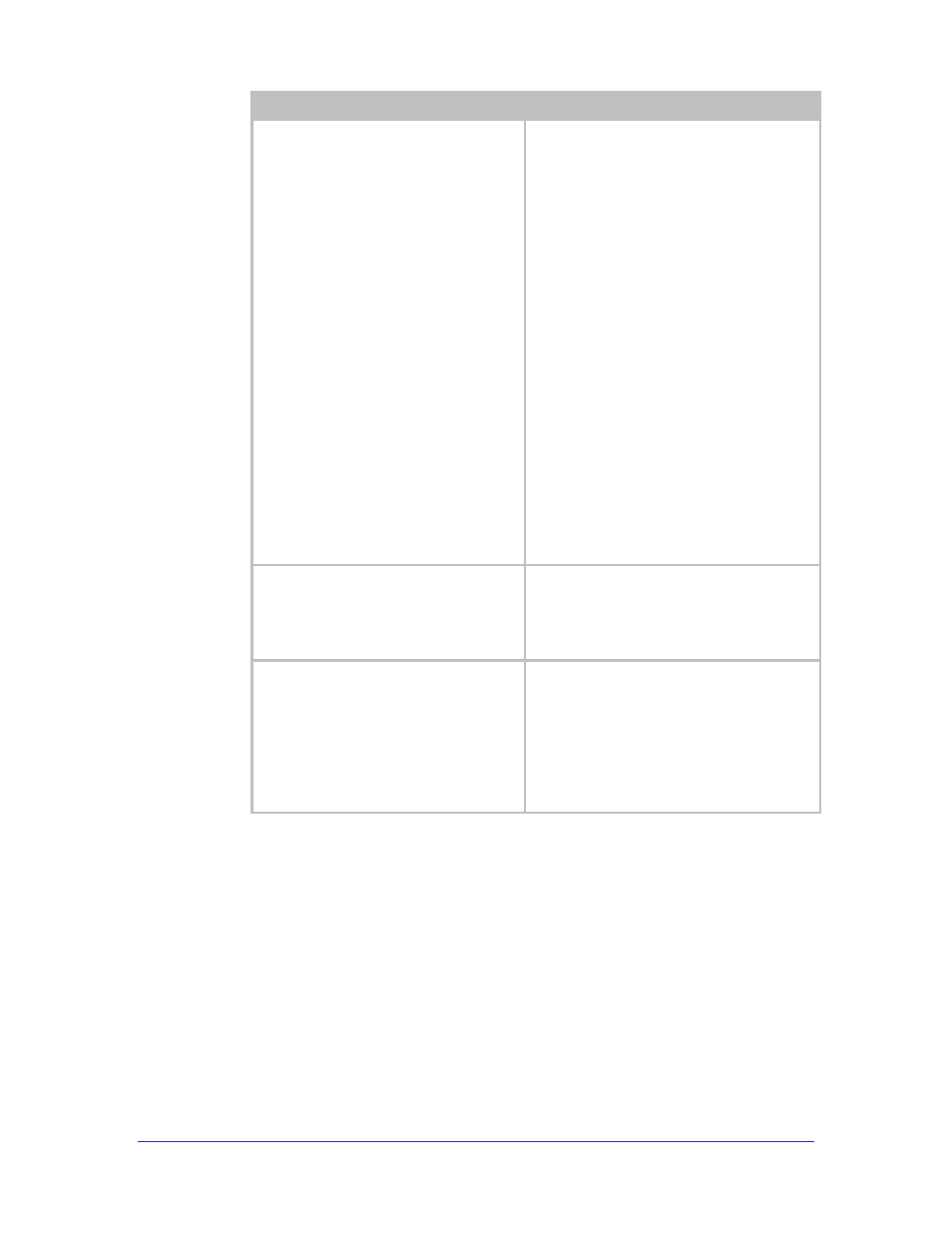
Command
Description
eap-fast-provisioning
Determines the method by which the EAP-FAST
credentials (PAC) are provisioned between the
module and the AAA server.
The
automatic provisioning of the modules credentials
by the AAA server. The options are:
authenticated
The AA server‟s identity is validated by the module
before the credentials are provisioned.
unauthenticated
The AA server‟s identity is not validated by the
module before the credentials are provisioned.
either
The module will attempt to use the
authenticated
method first; if this is not
possible then the module will use the
unauthenticated
.
If using authenticated or either the ca-
cert-filename
must be set for the AAA server
to be authenticated during the provisioning
process. If no ca-cert-filename is set the
provisioning process will not fail.
To use the ca-cert-filename the certificate
must be stored on the module.
eap-fast-max-pac-list <#ofServers>
Configures the number of AAA server credentials
that can be held by the module.
Changing the default value can impact memory
resources, although the memory will only be used
if the credentials are installed.
ca-cert-filename [CA root cert
name].pem
Identifies the CA root certificate name to be used
for authentication. Replace [CA root cert
name].pem
with the required filename (no
parenthesis).
The certificate must be saved to the module with
the name identified by this command.
If no CE root certificate is being used the file
name must be blank.
10.7 Managing Certificates and Private Keys
Since certificates are used by most of the supported EAP protocols it is
necessary to upload these files to the module before attempting to configure the
device for WPA2-Enterprise security.
The module supports both pushing and pulling of certificates and private key files
to the device, utilizing FTP and Xmodem transfer protocols. The different
methods can be seen in Figure 8.
The CLI commands that manage the delivery process are described in Table 21.
