Raid 6 – Avago Technologies 3ware SAS 9750-16i4e User Manual
Page 20
Chapter 1. Introducing the LSI 3ware SATA+SAS RAID Controller Card
8
3ware SATA+SAS RAID Controller Card Software User Guide, Version 10.2
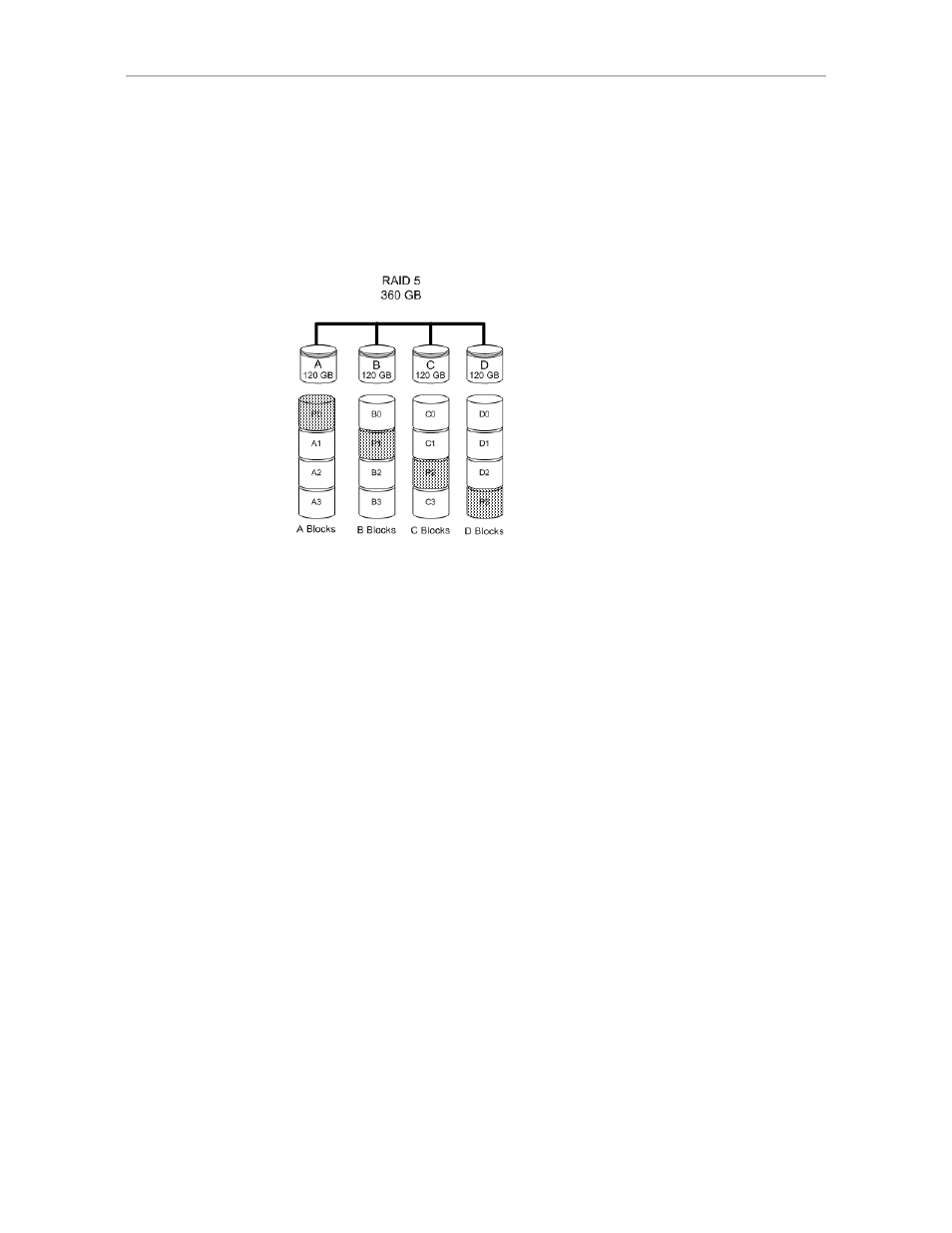
Parity information is distributed across all of the drives in a unit rather than
being concentrated on a single disk (see Figure 4). This method avoids
throughput loss due to contention for the parity drive.
RAID 5 can tolerate one drive failure in the unit.
Figure 4. RAID 5 Configuration Example
RAID 6
RAID 6 provides greater redundancy and fault tolerance than RAID 5. It is
similar to RAID 5 but, instead of a single block, RAID 6 has two blocks of
parity information (P+Q) distributed across all the drives of a unit (see
Figure 5).
Due to the two parities, a RAID 6 unit can tolerate two hard drives failing
simultaneously. This also means that a RAID 6 unit can be in two different
states at the same time. For example, one subunit can be degraded while
another is rebuilding, or one subunit can be initializing while another is
verifying.
The 3ware implementation of RAID 6 requires a minimum of five drives.
Performance and storage efficiency also increase as the number of drives
increase.
(480 GB - 120 GB for parity)
- 3ware SAS 9750-24i4e 3ware SAS 9750-4i 3ware SAS 9750-4i4e 3ware SAS 9750-8e 3ware SAS 9750-8i 3ware 8006-2LP 3ware 8006-2LP (Channel) 3ware 9550SXU-4LP 3ware 9550SXU-4LP (Channel) 3ware 9550SXU-8LP 3ware 9550SXU-8LP (Channel) 3ware 9650SE-12ML 3ware 9650SE-12ML (Channel) 3ware 9650SE-16ML 3ware 9650SE-16ML (Channel) 3ware 9650SE-24M8 3ware 9650SE-24M8 (Channel) 3ware 9650SE-2LP 3ware 9650SE-2LP (Channel) 3ware 9650SE-4LPML 3ware 9650SE-4LPML (Channel) 3ware 9650SE-8LPML 3ware 9650SE-8LPML (Channel) 3ware 9690SA-4I 3ware 9690SA-4I (Channel) 3ware 9690SA-4I4E 3ware 9690SA-4I4E (Channel) 3ware 9690SA-8E 3ware 9690SA-8E (Channel) 3ware 9690SA-8I 3ware 9690SA-8I (Channel)
