Figure 16-1. in-circuit debugger -2, Maxq family user’s guide – Maxim Integrated MAXQ Family User Manual
Page 160
16-2
MAXQ Family User’s Guide
SECTION 16: IN-CIRCUIT DEBUG MODE
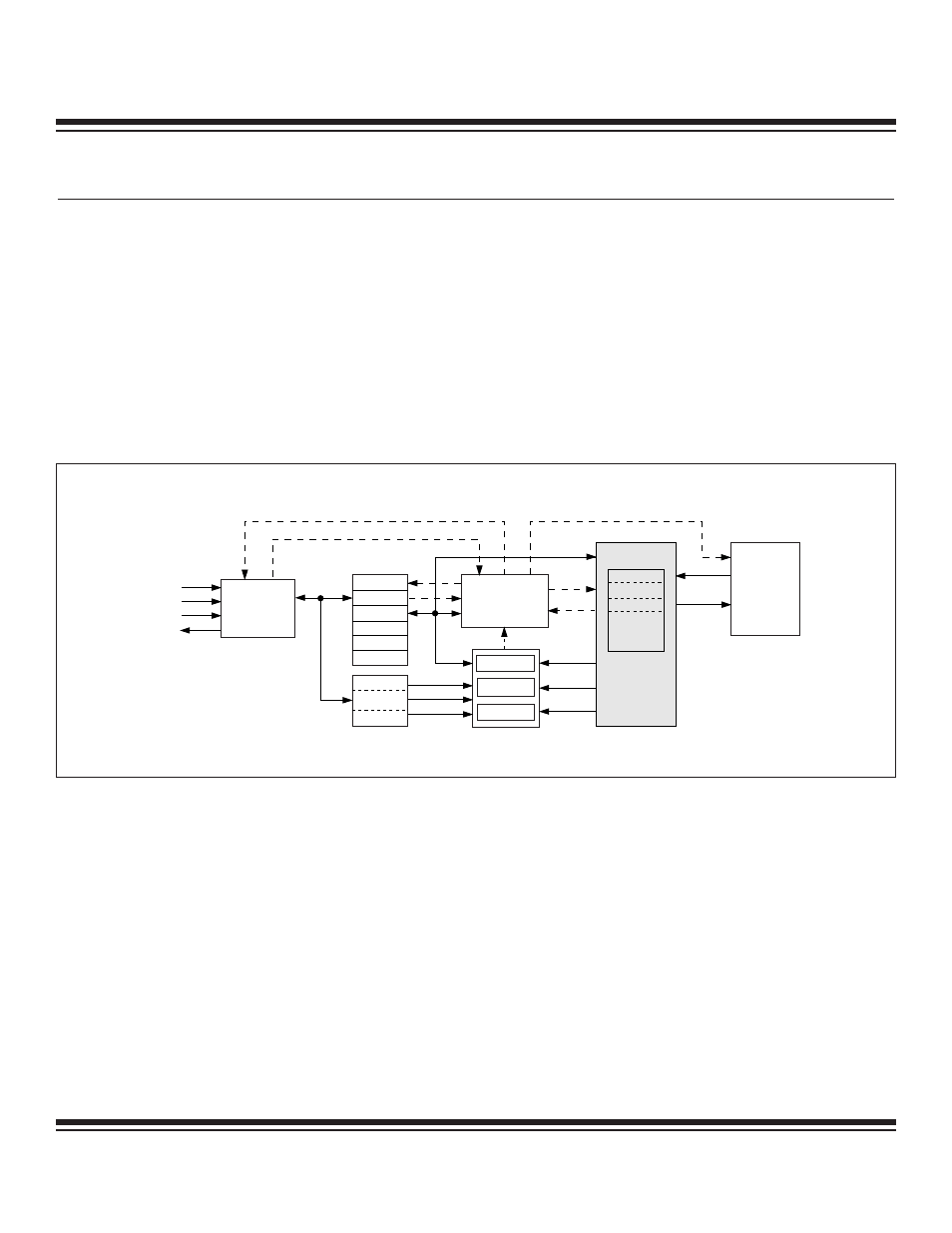
Most MAXQ microcontroller devices are equipped with embedded debug hardware and embedded ROM firmware developed for the
purpose of providing in-circuit debugging capability to the user application. The in-circuit debug mode uses the JTAG-compatible TAP
as its means of communication between the host and MAXQ microcontroller. Figure 16-1 shows a block diagram of the in-circuit debug-
ger. The in-circuit debug hardware and software features include:
• a debug engine
• a set of registers providing the ability to set breakpoints on register, code, or data
• a set of debug service routines stored in a ROM
Collectively, these hardware and software features allow two basic modes of in-circuit debugging:
• Background mode allows the host to configure and set up the in-circuit debugger while the CPU continues to execute the normal
program. Debug mode can be invoked from Background mode.
• Debug mode allows the debug engine to take control of the CPU, providing read-write access to internal registers and memory, and
single-step trace operation.
The embedded hardware debug engine is implemented as a stand-alone hardware block in the MAXQ microcontroller. The debug
engine can be enabled for monitoring internal activities and interacting with selected internal registers while the CPU is executing user
code. This capability allows the user to employ the embedded debug engine to debug the actual system, in place of the in-circuit emu-
lator that uses external hardware to duplicate operation of the microcontroller outside of the real application environment.
To enable a communication link between the host and the microcontroller debug engine, the Debug instruction (010b) must be loaded
into the TAP instruction register using the IR-Scan sequence. Once the instruction is latched in the instruction parallel buffer (IR2:0)
and is recognized by the TAP controller in the Update-IR state, the 10-bit data shift register is activated as the communication chan-
nel for DR-Scan sequences. The TAP instruction register retains the Debug instruction until a new instruction is shifted via an IR-Scan
or the TAP controller returns to the Test-Logic-Reset state.
TMS
TDO
TDI
TCK
CPU
ROM
DEBUG
ENGINE
BREAKPOINT
BREAK
ICDB
ICDF
ICDC
COMPARATOR
COMPARATOR
COMPARATOR
CODE ADDR
DATA ADDR
REG DATA
IP
IR
DATA
ADDR
ENABLE
ICDA
ICDD
ICDTn
TAP
CONTROLLER
Figure 16-1. In-Circuit Debugger
Maxim Integrated
