13 interrupt handling – Avago Technologies LSI53C825AE User Manual
Page 59
PCI Cache Mode
2-35
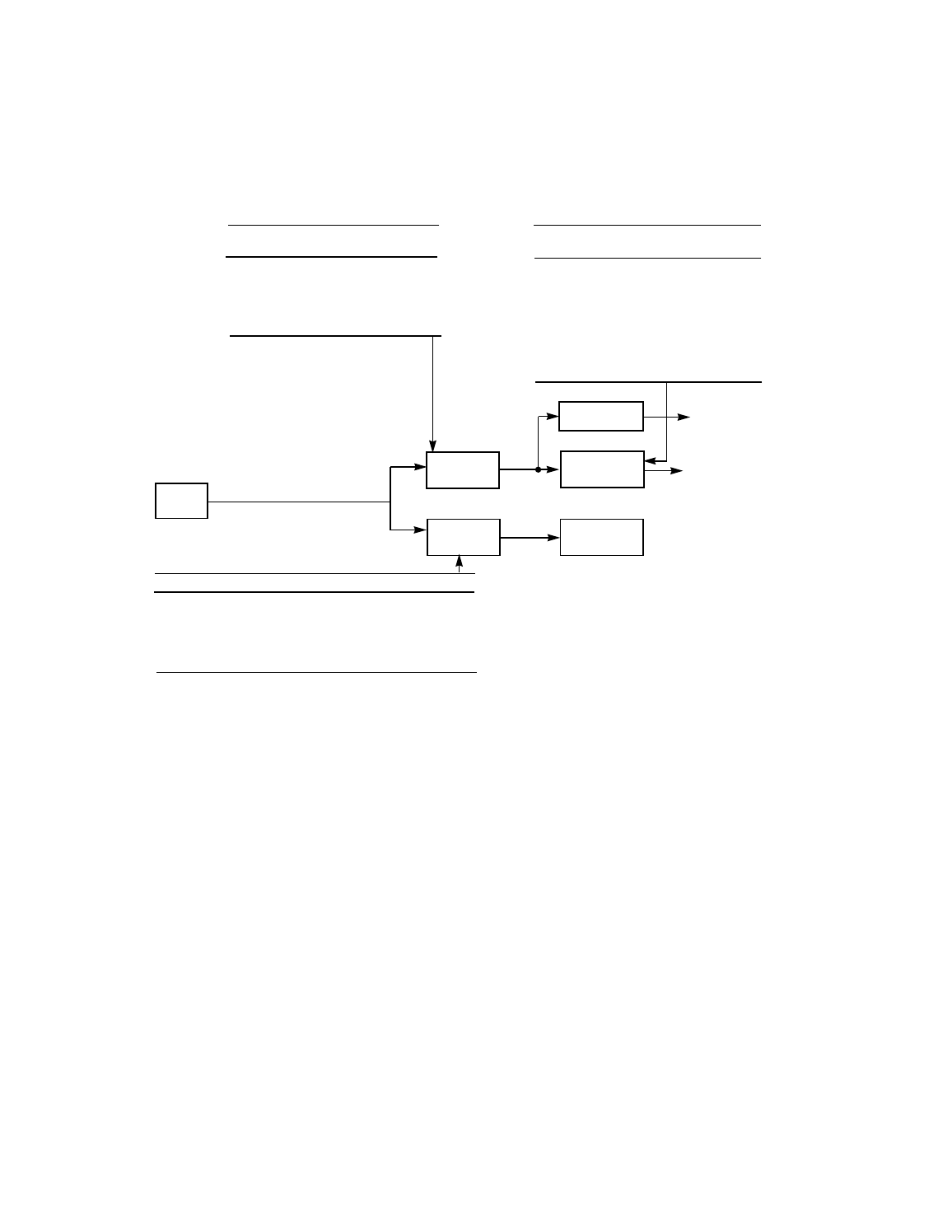
Figure 2.5
Determining the Synchronous Transfer Rate
2.4.13 Interrupt Handling
The SCRIPTS processor in the LSI53C825A performs most functions
independently of the host microprocessor. However, certain interrupt
situations must be handled by the external microprocessor. This section
explains all aspects of interrupts as they apply to the LSI53C825A.
2.4.13.1 Polling and Hardware Interrupts
The external microprocessor is informed of an interrupt condition by
polling or hardware interrupts. Polling means that the microprocessor
must continually loop and read a register until it detects a bit set that
indicates an interrupt. This method is the fastest, but it wastes CPU time
that could be used for other system tasks. The preferred method of
SCLK
SCF
Divider
CCF
Divider
Synchronous
Divider
Asynchronous
SCSI Logic
Divide by 4
SCF2
SCF1
SCF0
SCF
Divisor
0
0
1
1
0
1
0
1.5
0
1
1
2
1
0
0
3
0
0
0
3
TP2
TP1
TP0
XFERP
Divisor
0
0
0
4
0
0
1
5
0
1
0
6
0
1
1
7
1
0
0
8
1
0
1
9
1
1
0
10
1
1
1
11
CCF2
CCF1
CCF0
Divisor
0
0
1
1
0
1
0
1.5
0
1
1
2
1
0
0
3
0
0
0
3
Example:
SCLK = 40 MHz, SCF = 1, XFERP = 4,
SCSI transfer rate = 10 MHz, CCF = 2
This point
must not
exceed
50 MHz
Receive
Clock
Send Clock
(to SCSI Bus)
This point
must not
exceed
25 MHz
(40 MHz
÷
1 = synchronous core rate)
(40 MHz
÷
4 = 10 MHz synchronous rate =
10 Mbytes/s on an 8-bit SCSI bus)
