Incremental dimensions, Yx z, Absolute workpiece positions – HEIDENHAIN TNC 407 (280 580) ISO Programming User Manual
Page 33: Incremental workpiece positions
TNC 426/TNC 425/TNC 415 B/TNC 407
1-15
1
Introduction
Fig. 1.16:
Position definition through
incremental coordinates
Fig. 1.15:
Position definition through
absolute coordinates
I
Z=–15mm
Y
X
Z
2
10
5
5
15
20
10
10
I
X=10mm
I
Y=10mm
3
0
0
Y
X
Z
1
20
10
Z=15mm
X=20mm
Y=10mm
15
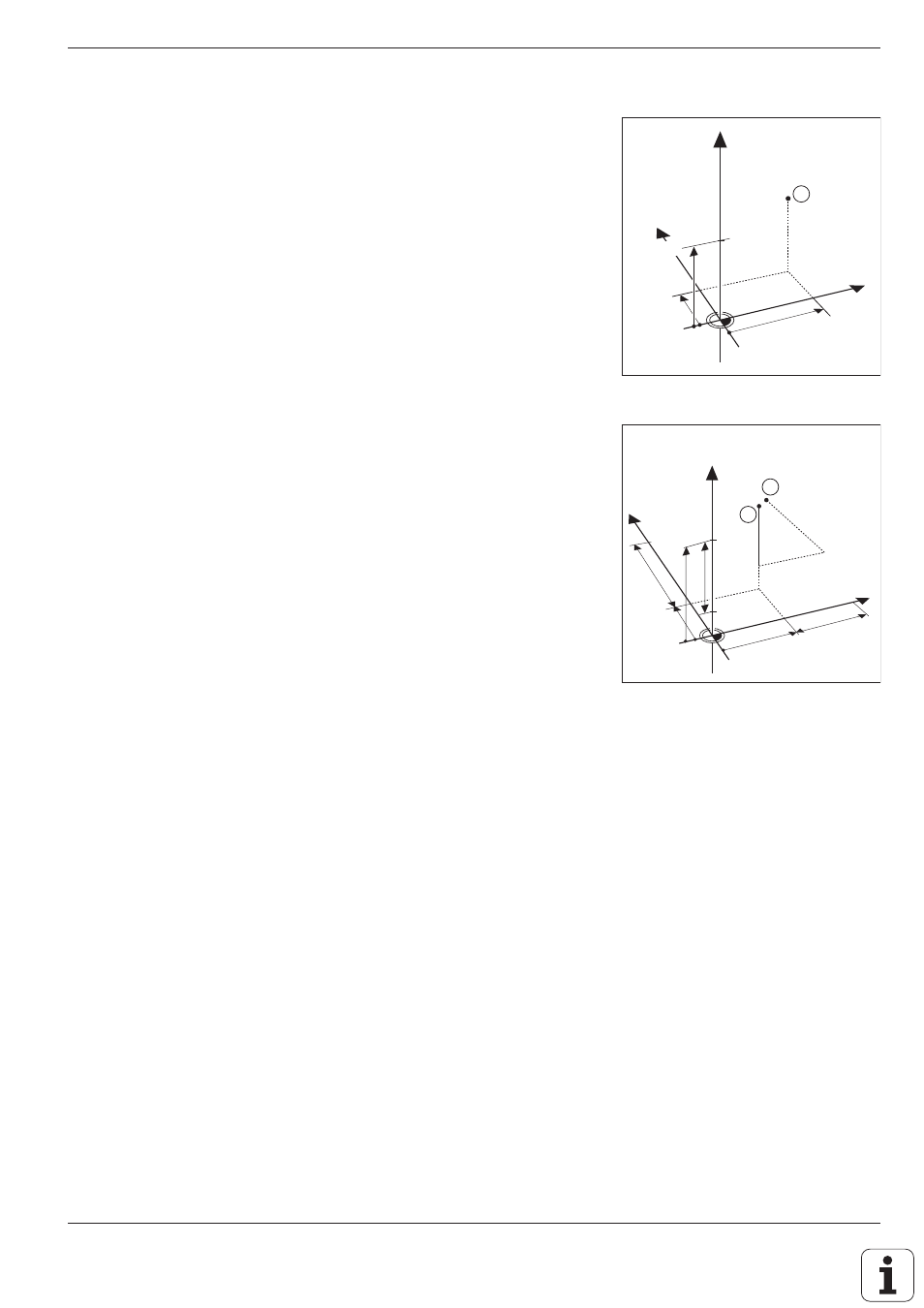
Absolute workpiece positions
Each position on the workpiece is uniquely defined by its absolute
coordinates.
Example:
Absolute coordinates of position ➀:
X = 20 mm
Y = 10 mm
Z = 15 mm
If you are drilling or milling a workpiece according to a workpiece drawing
with absolute coordinates, you are moving the tool to the value of the
coordinates.
Incremental workpiece positions
A position can also be referenced to the preceding nominal position. In
this case the relative datum is always the last programmed position. Such
coordinates are referred to as incremental coordinates (increment =
increase). They are also called chain dimensions (since the positions are
defined as a chain of dimensions). Incremental coordinates are designated
with the prefix I.
Example:
Incremental coordinates of position ➂ referenced to position ➁
Absolute coordinates of position ➁ :
X = 10 mm
Y = 5 mm
Z = 20 mm
Incremental coordinates of position ➂ :
IX = 10 mm
IY = 10 mm
IZ = –15 mm
If you are drilling or milling a workpiece according to a drawing with
incremental coordinates, you are moving the tool
by the value of the
coordinates.
An incremental position definition is therefore a specifically
relative
definition. This is also the case when a position is defined by the
distance-to-go to the nominal position. The distance-to-go has a negative
sign if the target position lies in the negative axis direction from the actual
position.
