Trigonometric functions -10, Overview -10, Trigonometric functions – HEIDENHAIN TNC 407 (280 580) ISO Programming User Manual
Page 199: 3 trigonometric functions, Bc a α
TNC 426/TNC 425/TNC 415 B/TNC 407
7 - 1 0
7
Programming with Q Parameters
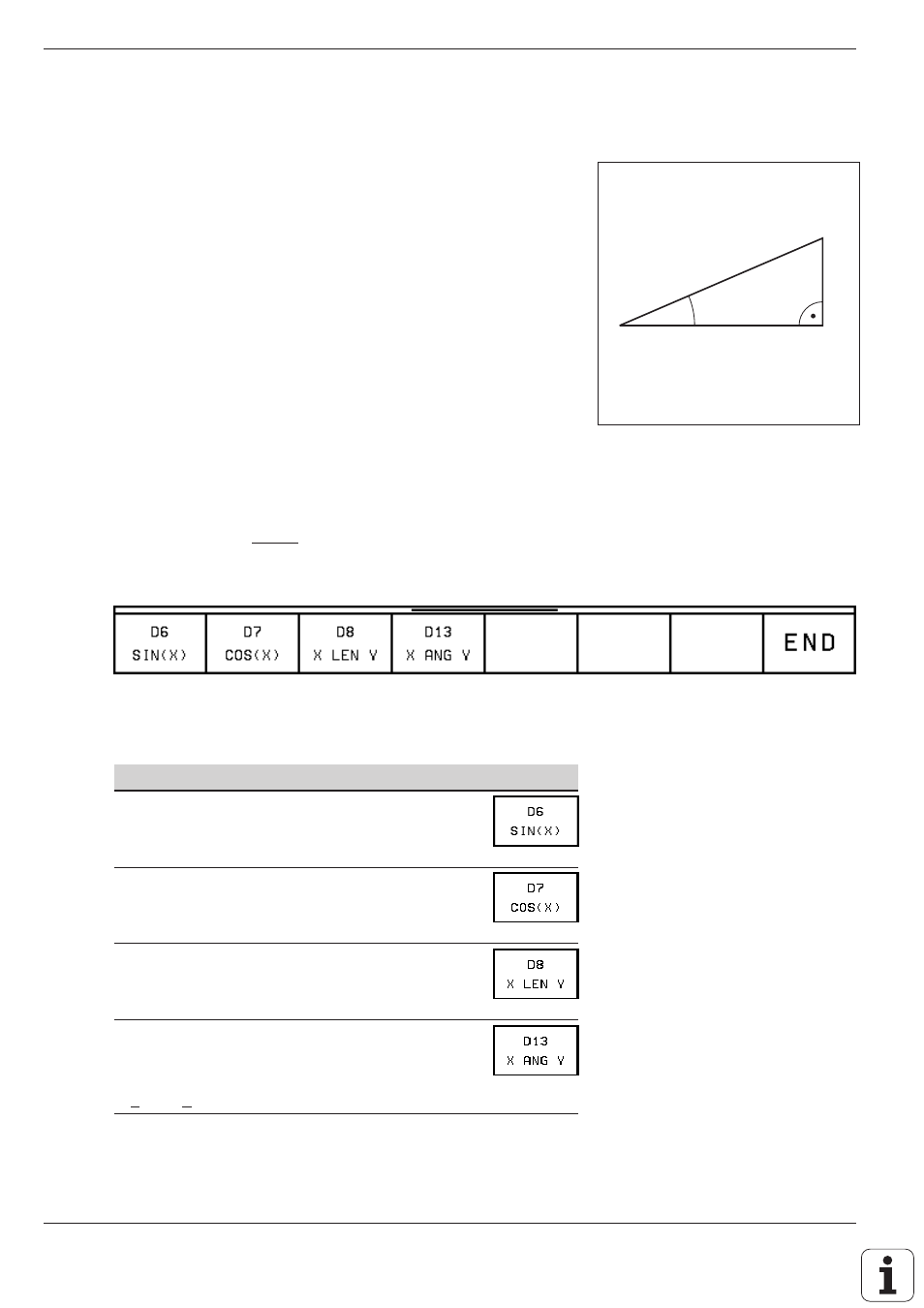
Fig. 7.3: Sides and angles on a right triangle
7.3 Trigonometric Functions
Sine, cosine and tangent are terms designating the ratios of the sides of
right triangles.
For a right triangle, the trigonometric functions of the angle
α
are defined
by the equations
sin
α
=
a/c,
cos
α
=
b/c,
tan
α
=
a/b = sin
α
/ cos
α
,
where
•
c is the side opposite the right angle
•
a is the side opposite angle
α
•
b the third side.
The angle can be found from the tangent:
α
= arc tan
α
= arc tan (
a/b) = arc tan (sin
α
/ cos
α
)
Example:
a = 10 mm
b = 10 mm
α
= arc tan (
a / b) = arc tan 1 = 45°
Furthermore,
a
2
+
b
2
=
c
2
(
a
2
=
a
.
a)
c =
√
a
2
+
b
2
Select the trigonometric functions to call the following options:
Overview
b
c
a
α
Soft key
D6: SINE
Example: D06 Q20 P01 –Q5
∗
Calculate the sine of an angle in degrees (°)
and assign it to a parameter
D7: COSINE
Example: D07 Q21 P01 –Q5
∗
Calculate the cosine of an angle in degrees (°)
and assign it to a parameter
D8: ROOT-SUM OF SQUARES
Example: D08 Q10 P01 +5 P02 +4
∗
Take the square root of the sum of two squared
numbers and assign it to a parameter
D13: ANGLE
Example: D13 Q20 P01 +10 P02 –Q1
∗
Calculate the angle from the arc tangent of two
sides or from the sine and cosine of the angle
(0 < angle < 360°) and assign it to a parameter
