Code for constrained random generation – Altera Video and Image Processing Suite User Manual
Page 284
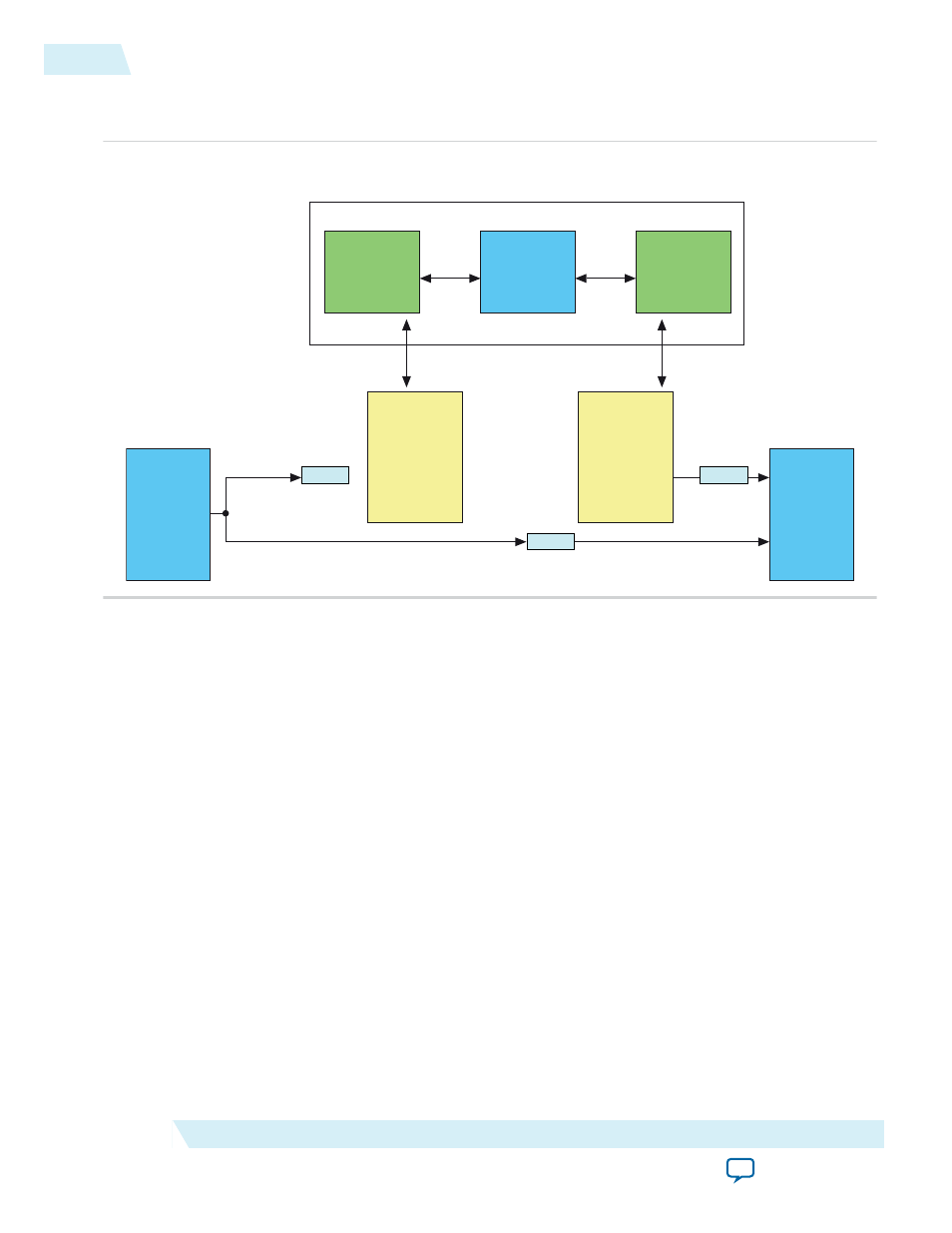
Figure A-6: Example of a Constrained Random Test Environment
The figure below shows the constrained random test environment structure.
Avalon-ST
Source BFM
module
Avalon-ST
Video Source
BFM
object
Avalon-ST
Video Sink BFM
object
DUT
Avalon-ST
Sink BFM
module
tb.v (netlist)
tb_test.v (test environment)
AV-ST
bus
function call
interface
m_video_items_for_src_bfm
m_video_items_
for_sink_bfm
m_video_items_for_scoreboard
function call
interface
AV-ST
bus
Random
video item
generation
Scoreboard
mailbox
mailbox
mailbox
The randomized video and control and user packets are generated using the SystemVerilog’s built-in
constrained random features. The DUT processes the video packets and the scoreboard determines a test
pass or fail result.
Code for Constrained Random Generation
fork
`SOURCE.start();
`SINK.start();
forever
begin
// Randomly determine which packet type to send :
r = $urandom_range(100, 0);
if (r>67)
begin
video_data_pkt1.set_max_length(100);
video_data_pkt1.randomize();
video_data_pkt1.populate();
// Send it to the source BFM :
m_video_items_for_src_bfm.put(video_data_pkt1);
// Copy and send to scoreboard :
video_data_pkt2 = new();
video_data_pkt2.copy(video_data_pkt1);
A-16
Code for Constrained Random Generation
UG-VIPSUITE
2015.05.04
Altera Corporation
Avalon-ST Video Verification IP Suite
