Double buffering, Triple buffering, Double buffering -2 – Altera Video and Image Processing Suite User Manual
Page 199: Triple buffering -2
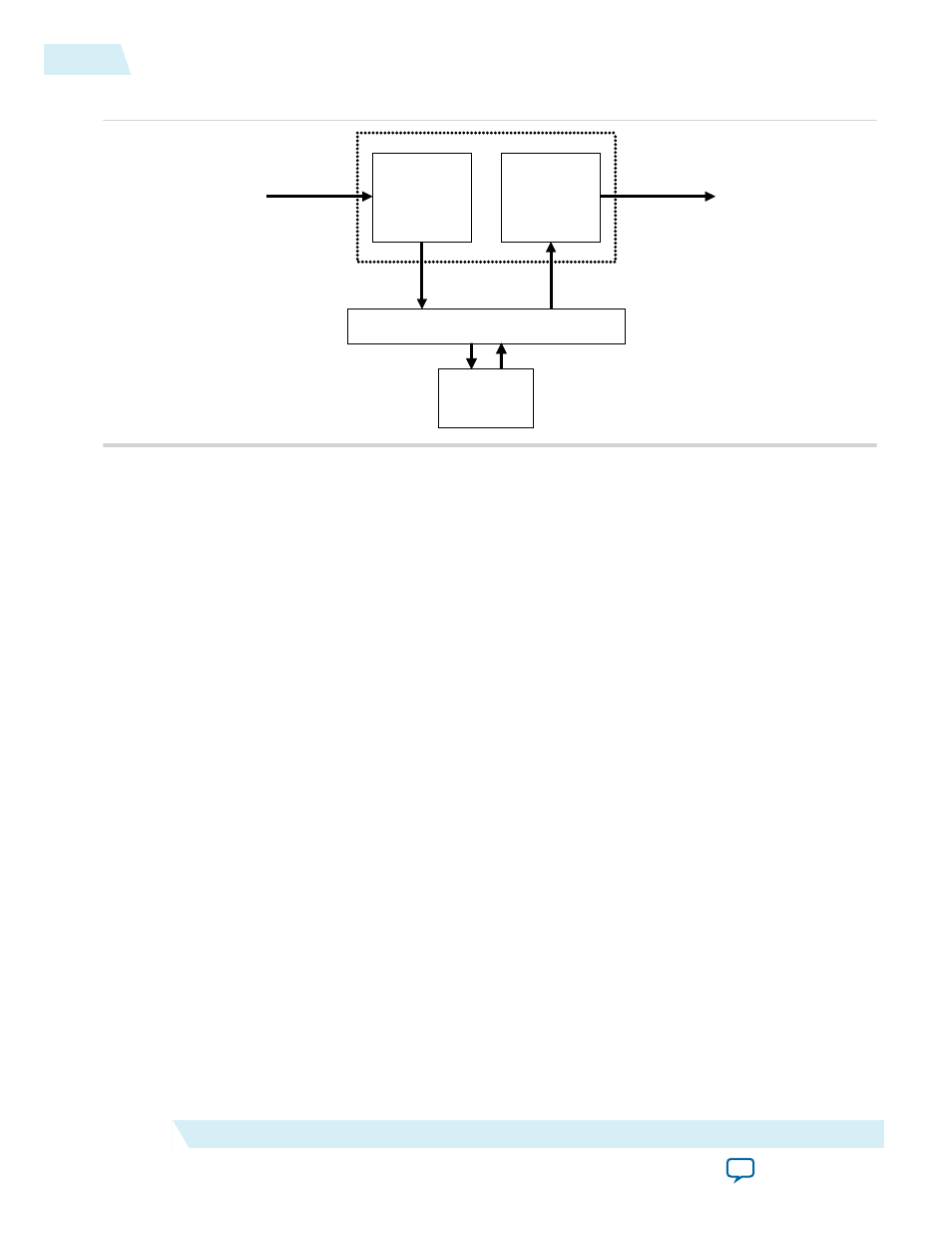
Figure 14-1: Frame Buffer Block Diagram
Memory
Writer
Memory
Reader
Avalon-ST Input
(din)
Avalon-ST Output
(dout)
DDR2
Arbitration Logic
Avalon-MM Master
(read_master)
Avalon-MM Master
(write_master)
Double Buffering
For double-buffering, the IP cores use two frame buffers in external RAM.
• The writer uses one buffer to store input pixels.
• The reader locks the second buffer that reads the output pixels from the memory.
• When both writer and reader complete processing a frame, the buffers are exchanged.
• The input frame can then be read back from the memory and sent to the output, while the buffer that
has just been used to create the output can be overwritten with fresh input.
• This feature used when:
• The frame rate is the same both at the input and at the output sides but the pixel rate is highly
irregular at one or both sides.
• A frame has to be received or sent in a short period of time compared with the overall frame rate.
For example, after the Clipper IP core or before one of the foreground layers of the Alpha Blending
Mixer IP core.
Triple Buffering
For triple-buffering, the IP cores use three frame buffers in external RAM.
14-2
Double Buffering
UG-VIPSUITE
2015.05.04
Altera Corporation
Frame Buffer IP Cores
