Next-gen - generic framing procedure (gfp) – EXFO IQS-8100 Series Transport Blazer for IQS-600 User Manual
Page 661
Glossary
SONET/SDH Application
647
Next-Gen - Generic Framing Procedure (GFP)
Next-Gen - Generic Framing Procedure (GFP)
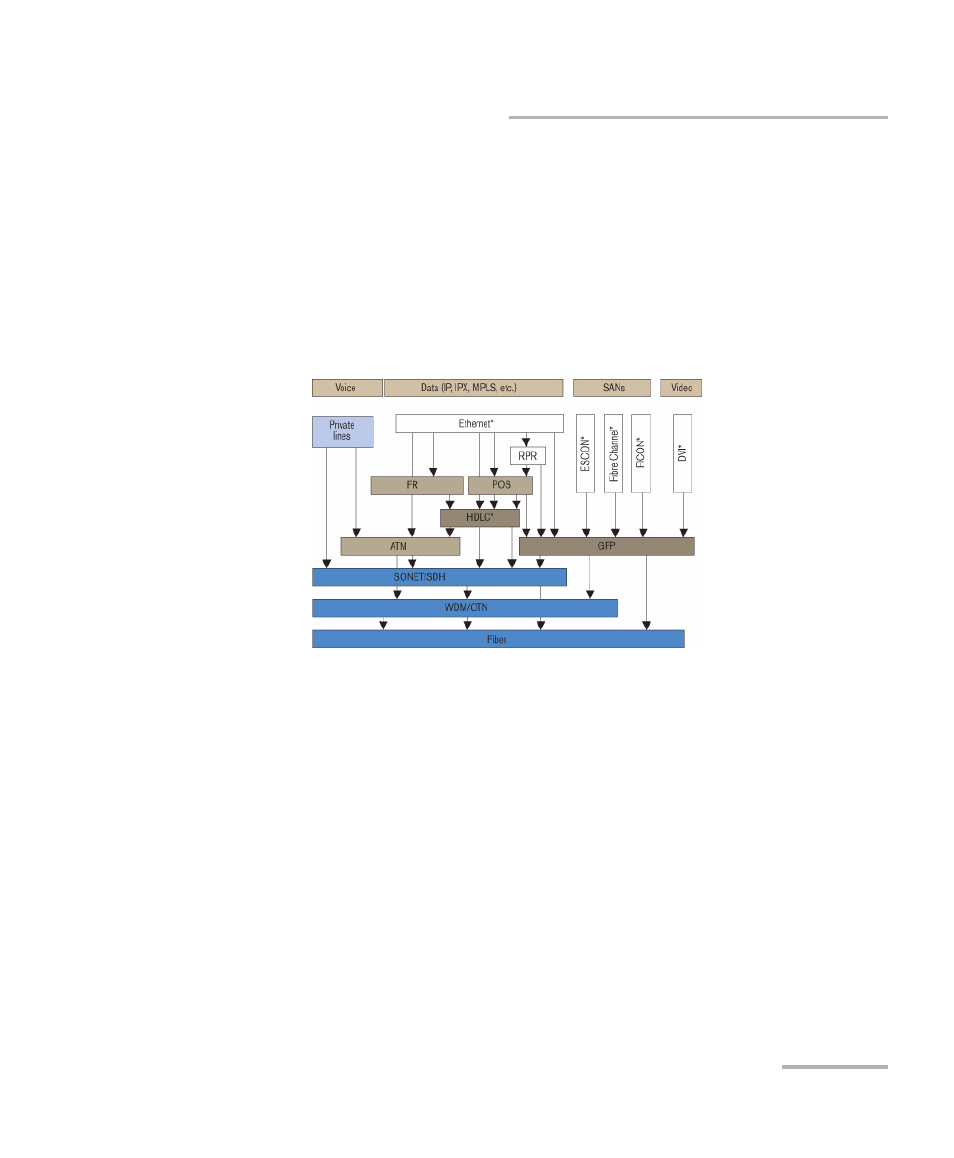
Generic framing procedure (GFP), defined in ITU recommendation
G.7041/Y.1303, is a framing mechanism to transport packet-based client
signals, such as Ethernet, Fibre Channel, ESCON, FICON, over
fixed-data-rate optical channels. As such, GFP provides a single, flexible
mechanism to map these client signals into SONET/SDH and OTN
networks, as shown in figure below.
Client Signal Mapping over GFP
Prior to the introduction of GFP, several methods had been used to
transport packet services over SONET/SDH networks. The first method was
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) Adaptation Layer 5 (AAL 5) over
SONET/SDH. ATM is a very efficient switching and multiplexing technology,
whose transfer rates scale with SONET/SDH rates. However, ATM does not
make the most efficient use of bandwidth because the payload data is
separated into groups of 48 bytes, called cells, with an additional 5-byte
header of software overhead. It became immediately apparent that almost
10% of the bandwidth would be lost. In addition, certain types of data
required even more ATM overhead.
