Peak on highly curved baseline, Peak overlapping – Metrohm 797 VA Computrace User Manual
Page 285
9.6 Voltammetric problems
797 VA Computrace – Software
273
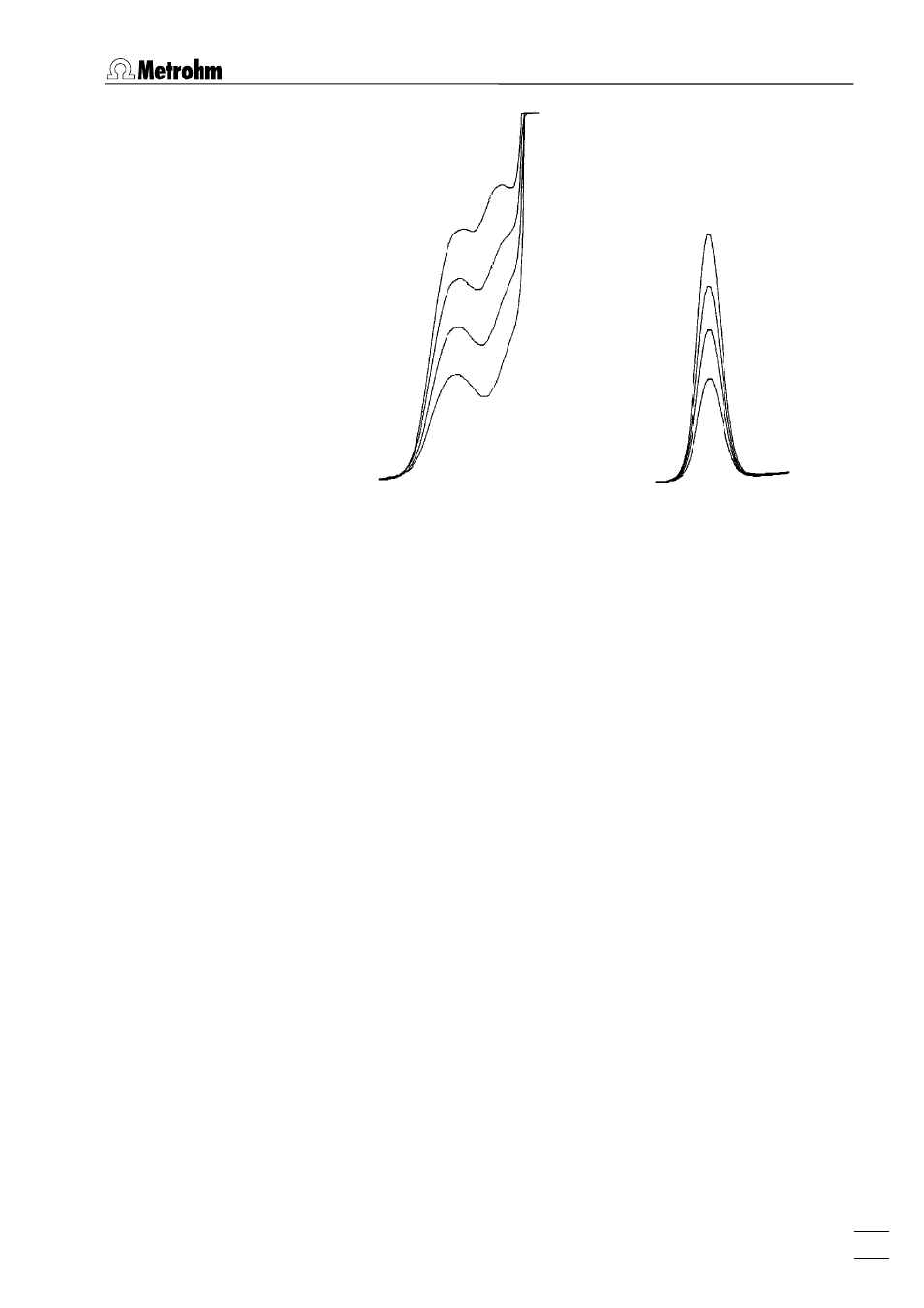
Analysis solution:
25 μg/L Cu; 10 μL HCl 30%
Standard addition:
with 250 ng Cu
Electrode:
HMDE (enrichment 90 s at –600 mV)
Peak on highly curved baseline
If peaks lie on a highly curved baseline, the first attempts at rectifi-
cation should involve chemical or measurement technique coun-
termeasures to eliminate the adverse effect on the peak evaluation
due to the highly curved baseline. Such measures include longer
purging times
(see Oxygen interference, section 9.6),
changing the
pH value, changing the supporting electrolyte concentration, modi-
fying or changing the supporting electrolyte, use of complexing
agents
(see Complex formation, section 9.6),
longer
deposition
times and changing the measurement technique.
If the curvature of the baseline can not or only partially be elimina-
ted by the above measures, the 797 VA Computrace offers the pos-
sibility to approximate a curved baseline by selecting
Polynomial
or
Exponential
for the baseline
Type
(see Baseline, section 5.2).
A further possibility to evaluate peaks on curved baselines involves
the background subtraction after measuring a blank solution, in
particular when the curved baseline can be clearly attributed to the
supporting electrolytes
(see Determination, section 5.2).
Peak overlapping
If the peak overlapping has reached a critical level at which the cal-
culated peak height or peak area is falsified by the neighboring
peak, it is advisable to take the overlapping into account by a
change in the baseline calculation. For this, select the
Front end
or
Rear end
option for the baseline
Scope
(see Baseline, section 5.2).
CuCl
4
2–
CuCl
2
–
CuEDTA
