Preface – Rockwell Automation 9323-PA1E USER MANUAL APS 6.0 User Manual
Page 244
Preface
Advanced Programming Software User Manual
12–10
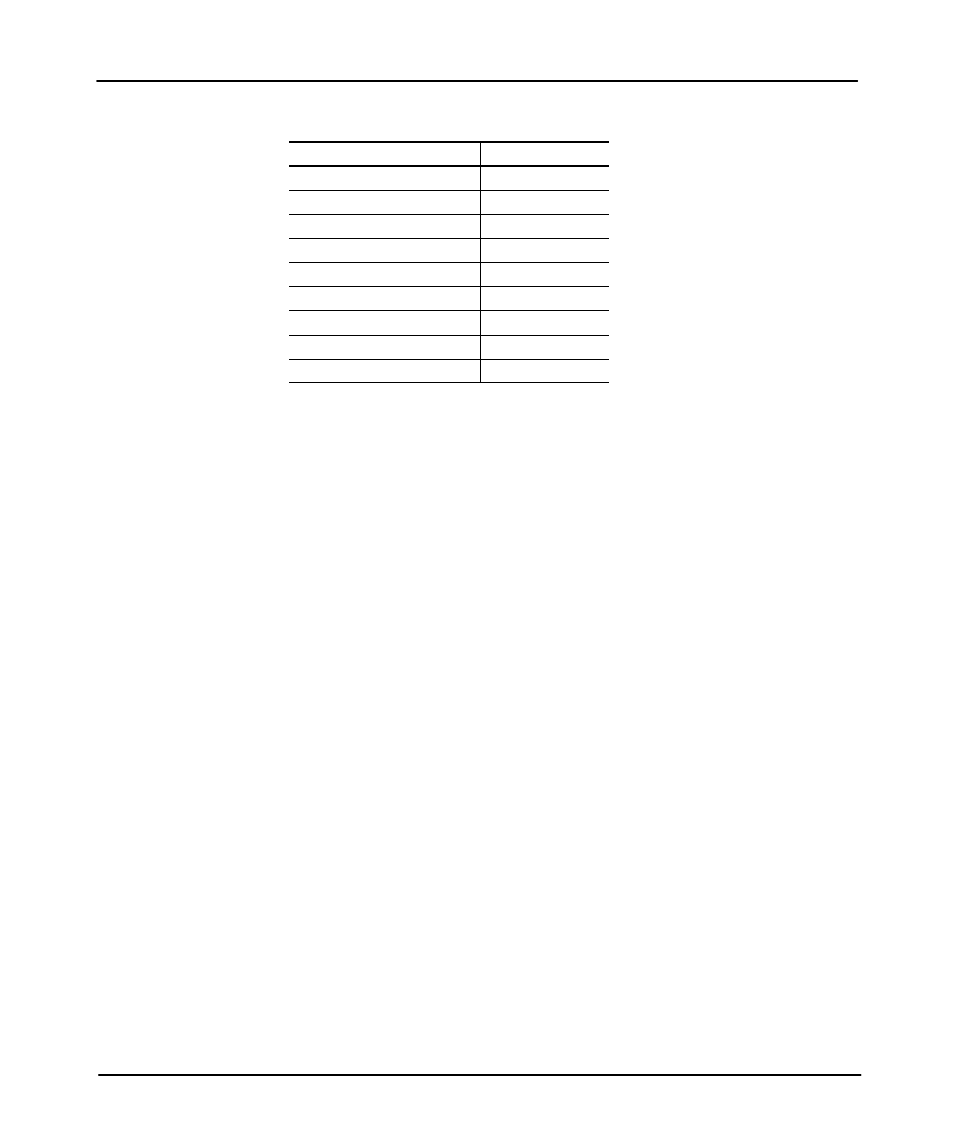
The counters listed under network diagnostics have the following ranges:
Network Diagnostics
Valid Ranges
Total Nodes
0Ć31
Max. Node Address
0Ć31
Messages Transmitted
0Ć65535
Messages Received
0Ć65535
Retries
0Ć255
Retry Limit Exceeded
0Ć255
Bad Messages Received
0Ć255
Nak No Memory Sent
0Ć255
Nak No Memory Rcvd
0Ć255
Node diagnostics are for the cursored node shown in the Who Active display.
Note
The firmware revision and firmware series fields refer to the processor’s series and
revision fields in the status file for the SLC 5/03 and SLC 5/04 processors. The
operating system (OS) series and revision fields are found only in the status file
(S:58 and S:59 respectively).
Establishing Processor Node Addresses on a Multi-Node Network
The default node address for a processor file is 1. This means that unless addresses
have been changed previously, all processor nodes on the network initially have
address 1. This makes it impossible to communicate with an individual processor.
You must bring up the network one node at a time.
Refer to the typical DH-485 network on page 12–11. An APS terminal at node 0
(the default node) is connected to link coupler A. There are 3 processors on the
network plus a gateway module to bridge to a DH
+
network. The gateway module
has been assigned to node 4 by means of DIP switch settings on the device.
Assuming that the default node address value of 1 has not been changed for any of
the processors, set processor addresses as follows:
1.
Apply power only to the processor connected to link coupler D. Restore
(download) the appropriate processor file to the processor.
2.
Assign node address 3 to the processor using the Who Active function or set the
node address in the system status file before saving the program you wish to
download. Address 3 takes effect when you cycle power to the processor.
