4] tension operation, Chapter 3 operation – IAI America SCON-CA User Manual
Page 142
Chapter 3 Operation
132
[4] Tension Operation
Warning: Do not perform tension operation by pressing operation using force sensor.
The pressing operation using force sensor requires an actuator applicable for
dedicated loadcell and pressing operation using force sensor.
The tension operation by using an actuation equipped with loadcell causes the
loadcell to be damaged.
�
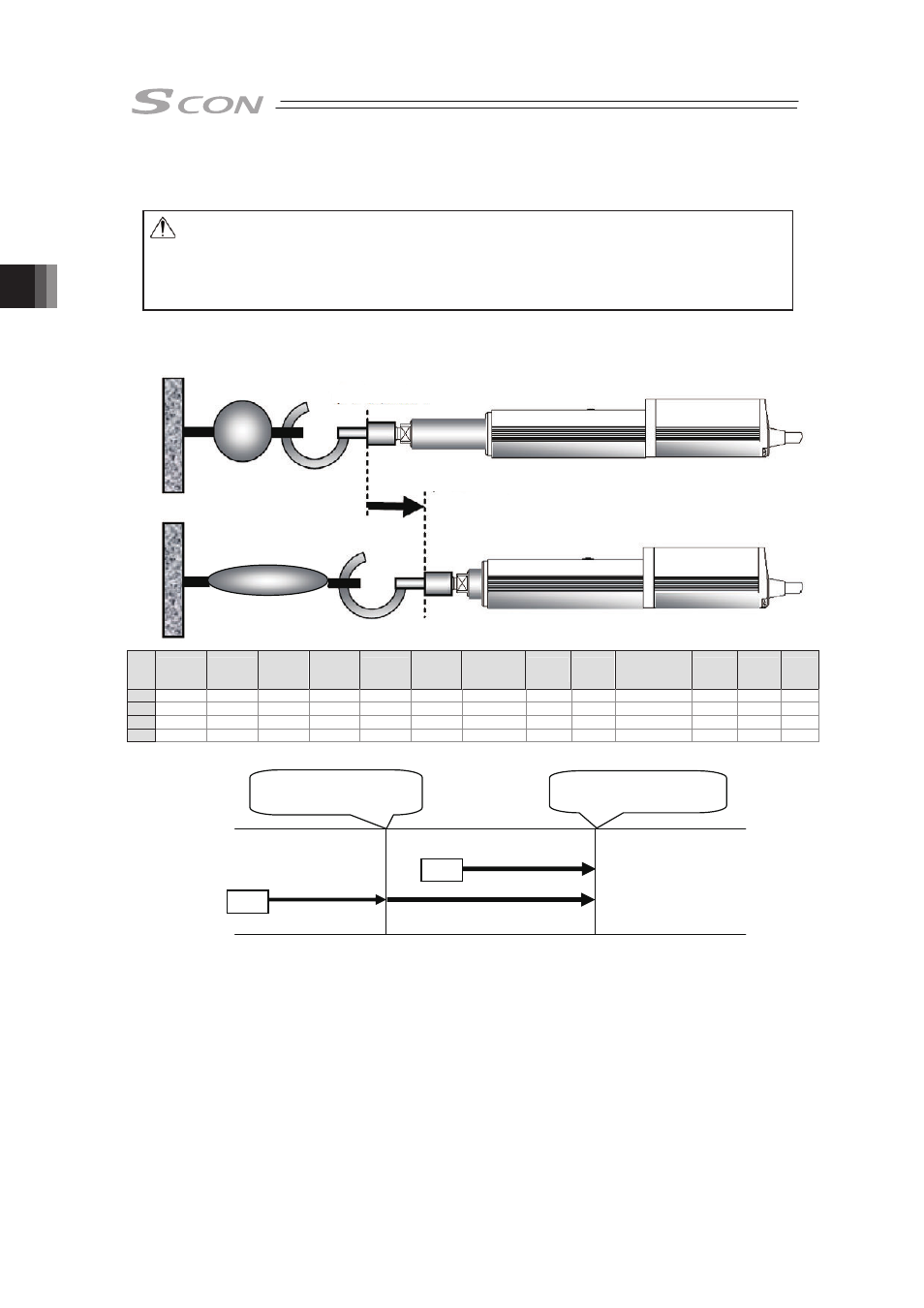
Image diagram
No.
Position
[mm]
Velocity
[mm/s]
Accele-
ration
[G]
Decele-
ration
[G]
Pressing
[%]
Thresh-
old
[%]
Positioning
width
[mm]
Zone+
[mm]
Zone-
[mm]
Acceleration/
Deceleration
mode
Incre-
mental
Gain
set
Stop
mode
0
1
100.00
250.00
0.20
0.20
0
0
0.10
0.00
0.00
0
0
0
0
2
80.00
250.00
0.20
0.20
50
0
–50.00
0.00
0.00
0
0
0
0
3
�
Control method
The method of controlling the tension operation is the same as that described in [3] Pressing
operation. The control method is explained below by using the sample position table shown
above.
1) Position No.2 indicates the settings of tension operation. The settings of “Position” and
“Positioning width” show the tension start position and the tension quantity, respectively.
Attach – (negative sign) to the tension quantity. Specify the upper limit of the torque
required for tension in percent (limited current value) in “Pressing”. The speed,
acceleration, and deceleration are the conditions of positioning to the coordinate value
(80mm) set in “Position”.
2) Position No.1 indicates the tension start preparation position. Specify a value larger than
the coordinate value at which the tension provided by position No.2 ends (80 – 50 = 30mm)
in “Position”.
ST*
ST*
ST*: Start position
Position No.1
Position No.2
Tension Operation
Approach Operation
Tension Operation
Tension start position
80mm
Tension end position
80 – 50 = 30mm
