1 32-bit data bus operation, 1 32-bit data bus operation -27, Bit data bus operation – Intel STRONGARM SA-1100 User Manual
Page 141
SA-1100 Developer’s Manual
10-27
Memory and PCMCIA Control Module
10.6.1
32-Bit Data Bus Operation
The SA-1100 PCMCIA interface supports the use of a 32-bit data bus. Because the PCMCIA 2.0 is
8- or 16-bit only, the 32-bit operation is outside the scope of the PCMCIA specification. This 32-bit
mode is intended for use as a nonstandard expansion bus for communication with
customer-designed logic. The operation is fairly simple; if a word read or write is performed to
PCMCIA memory space, then the entire 32-bit bus is read or written. Normal PCMCIA operations
should be performed using byte or half-word accesses only. Thirty-two bit accesses should be word
aligned and only to "16-bit" space, as opposed to 8-bit space. Memory and attribute space is 16 bits
by definition. However, I/O space may be 8- or 16-bit depending upon the state of the nIOIS16
input pin. Thirty-two bit accesses to I/O space require that the target assert nIOIS16.
For 32-bit accesses, the only size information present on the bus is the assertion of the nPCE1 and
nPCE2 pins. This is the same information that is present during half-word accesses. As such, there
is no way by looking at the SA-1100 pins to determine whether the access is a half-word or word.
This information can be derived only though a user-defined address decode outside the SA-1100.
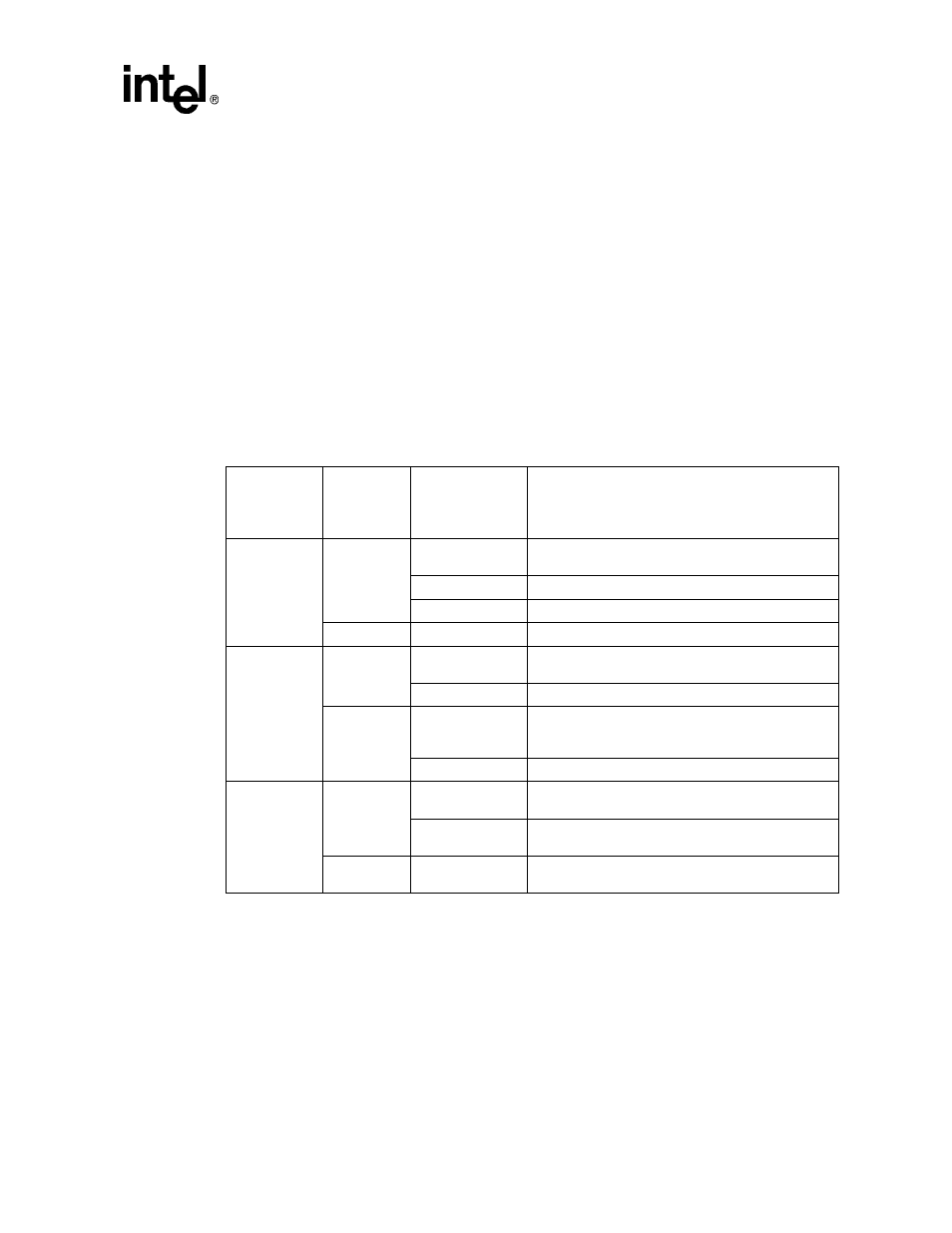
The following table shows the operation of the PCMCIA interface and its relation to data width.
Access Type
Data Bus
Width
1 = 16 Bit
0 = 8 Bit
Address (1:0
)
Resulting Operation
Word
1
00
Word read or write, nPCE1 and nPCE2 asserted (low).
nIOIS16 must be asserted for I/O space.
1x
Undefined operation.
x1
Undefined operation.
0
xx
Undefined operation.
Half-word
1
x0 (even)
Single half-word access, nPCE1 and nPCE2 asserted
(low). nIOIS16 must be asserted for I/O space.
x1 (odd)
Undefined operation.
0
x0 (even)
Two-byte accesses, both on the lower byte lane. Even
access first (nPCE1 asserted and nPCE2 negated for
both).
x1 (odd)
Undefined operation.
Byte
1
x0 (even)
Load or store byte on the lower byte lane (nPCE1
asserted, nPCE2 negated).
x1 (odd)
Load or store byte on the upper byte lane (nPCE1
negated, nPCE2 asserted).
0
xx (even or odd)
Load or store byte on the low byte lane (nPCE2
negated and nPCE1 asserted).
